Fossils are the remains or traces of once-living organisms that provide valuable insights into the history of our planet. Among the most fascinating types of fossils are transitional fossils, which offer crucial evidence of evolutionary processes and the gradual changes that occur within species over time. These unique fossils possess traits that are intermediate between earlier and later species, providing a bridge between different periods of Earth’s history.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of transitional fossils and explore 18 astounding facts that highlight their significance in biology and paleontology. From iconic examples like Archaeopteryx to lesser-known but equally important discoveries, these 18 facts will shed light on the intricate web of evolution and how transitional fossils allow us to piece together the puzzle of life’s diversity. So let’s embark on a journey through time and marvel at the wonders of transitional fossils!
Key Takeaways:
- Transitional fossils are like missing puzzle pieces that show how animals changed over time. They prove that species evolved and help us understand the history of life on Earth.
- Fossils like Tiktaalik and Archaeopteryx give us clues about how animals went from water to land, and dinosaurs turned into birds. It’s like a real-life adventure story written in rocks!
Transitional Fossils Fill the Gaps in Evolutionary History.
Transitional fossils are the missing links that provide evidence for the gradual changes and transitions in species over time. They bridge the gaps between different species, confirming the theory of evolution.
Transitional Fossils Show the Evolution of Whales from Land to Sea.
Fossils like Basilosaurus and Ambulocetus offer a glimpse into the fascinating transition of whales from land-dwelling creatures to the magnificent marine mammals we know today.
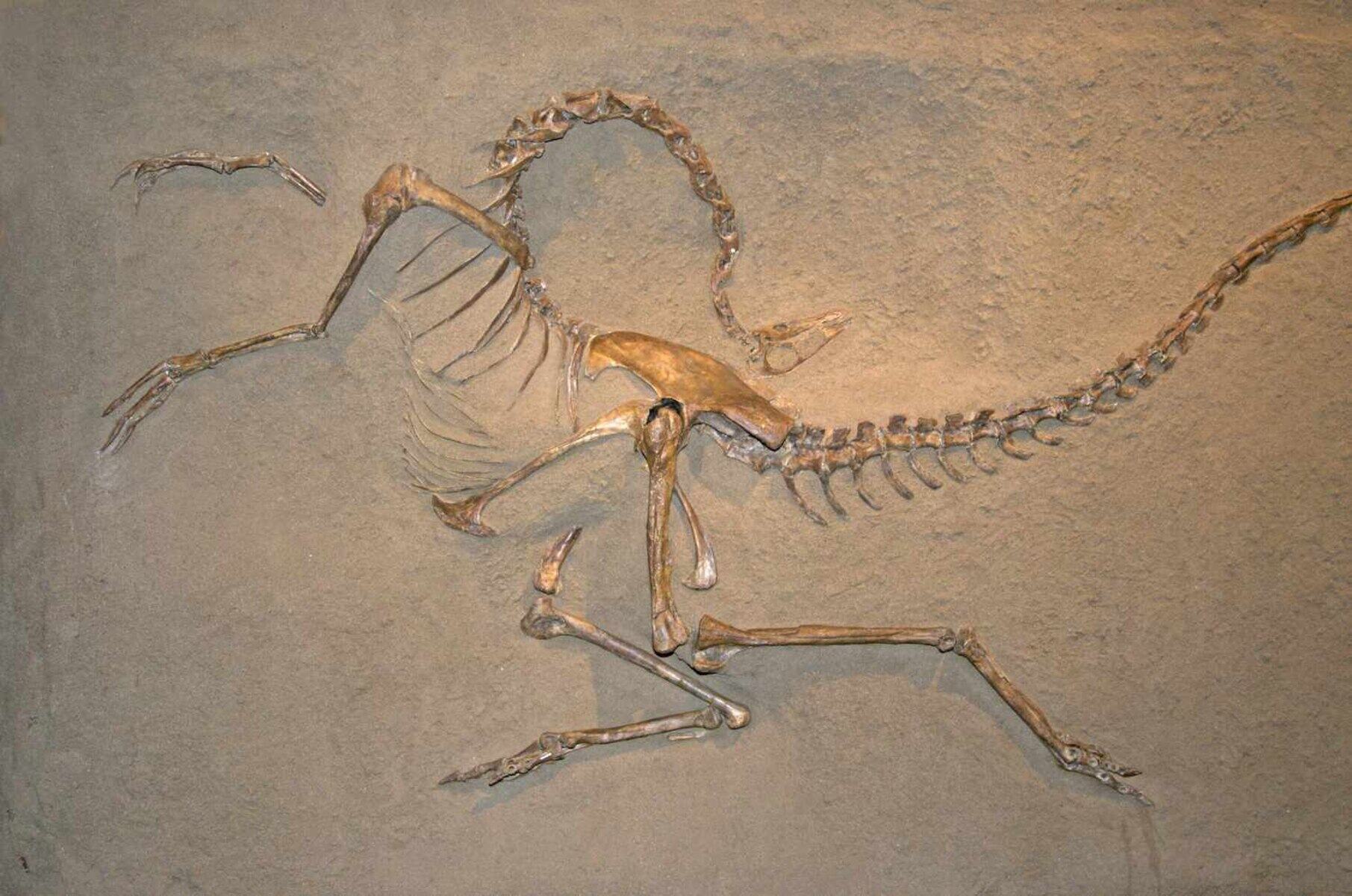
The Archaeopteryx: A Perfect Example of a Transitional Fossil.
The Archaeopteryx, with its combination of reptilian and avian features, is considered one of the most important transitional fossils. It provides undeniable evidence of the evolution of birds from reptilian ancestors.
Tiktaalik: The Fish That Started Walking.
Tiktaalik is a remarkable transitional fossil that showcases the evolution of fish to amphibians. Its fins have distinct limb-like structures, offering insights into the development of walking limbs in vertebrates.
Pakicetus: Ancestral Whales with Legs.
Pakicetus is a fascinating transitional fossil that reveals the presence of ancestral whales with legs. This discovery supports the hypothesis that whales evolved from land-dwelling mammals.
Ambulocetus: From Land to Sea.
Ambulocetus, also known as the “walking whale,” provides evidence of the transition between land-dwelling mammals and aquatic mammals. Its fossilized remains display characteristics of both land animals and early whales.
The Coelacanth: A Living Fossil.
The Coelacanth is a unique transitional fossil that was once thought to be extinct but was rediscovered alive. Its ancient features provide valuable insights into the evolutionary history of fish and the transition to land-dwelling creatures.
Homo habilis: The Handy Man.
Homo habilis, one of our earliest ancestors, is considered a transitional fossil between Australopithecus and Homo erectus. It showcases the development of tool-making skills and the transition to a more sophisticated species.
The Velvet Worm: A Living Fossil with Transitional Features.
The velvet worm is a living fossil with characteristics that link it to both arthropods and worms. Its unique anatomy provides valuable insights into the evolution of terrestrial invertebrates.
The Transition from Fish to Amphibians: Eusthenopteron and Acanthostega.
Fossils like Eusthenopteron and Acanthostega demonstrate the evolution from fish to amphibians. They exhibit features of both fish and early tetrapods, shedding light on the transition from aquatic to terrestrial life.
The Evolution of Horses: From Hyracotherium to Equus.
The fossil record of horse evolution showcases a remarkable transformation over millions of years, from small, multi-toed creatures like Hyracotherium to the modern single-toed horses of the genus Equus.
Fossils of Tiktaalik and Lungfish: The Fish-Tetrapod Transition.
The fossils of Tiktaalik and lungfish provide key evidence for the transition from fish to tetrapods. Their features demonstrate the development of limbs and lungs, marking a significant step towards terrestrial life.
Ichthyosaurs: Marine Reptiles with Fish-Like Characteristics.
Ichthyosaurs were marine reptiles that exhibited fish-like characteristics. These fossils shed light on the incredible adaptations and evolution of reptiles to an aquatic lifestyle.
The Evolution of Birds: From Dinosaurs to Avian Life.
Fossils like Archaeopteryx and Confuciusornis provide strong evidence for the evolution of birds from dinosaurs. They showcase the development of feathers, wings, and other avian characteristics.
Fallotodus: The Transition from Sharks to Rays.
Fallotodus is a transitional fossil that provides insights into the evolution of sharks to rays. Its features display a combination of both shark and ray traits, highlighting the gradual changes in their anatomy over time.
The Emergence of Land Plants: From Marine Algae to Terrestrial Vegetation.
Transitional fossils of early land plants, such as Cooksonia, reveal the transition from marine algae to the first land-based vegetation. These fossils show the development of structures that allowed plants to adapt to terrestrial environments.
The Evolution of Primates: From Prosimians to Humans.
Transitional fossils of early primates, like Darwinius and Proconsul, provide important insights into the evolutionary journey from prosimians to humans. They demonstrate the development of primate characteristics and the emergence of human-like traits.
The Evolution of Elephants: Proving the Co-existence of Different Species.
Fossil records of elephants, including species like Stegodon and Deinotherium, depict a gradual evolution from smaller, tusked ancestors to the majestic elephants we know today. They also demonstrate the co-existence of different elephant species throughout history.
Conclusion
In conclusion, transitional fossils provide us with compelling evidence of the evolutionary history of life on Earth. These remarkable fossils offer a glimpse into the gradual changes and adaptations that have occurred over millions of years. By studying transitional fossils, scientists can piece together the puzzle of how different species have emerged and evolved over time.Through the examination of anatomical features, genetic information, and geological data, researchers can trace the lineage and relationships between different organisms. The discovery of transitional fossils has greatly enhanced our understanding of evolutionary processes and has helped to shape the field of paleontology.From the fascinating archaeopteryx, showcasing the link between dinosaurs and birds, to the iconic Tiktaalik with its fish-like features and limb-like fins, transitional fossils continue to amaze and inspire scientists. They offer a tangible connection between past and present, allowing us to better comprehend the incredible diversity of life on our planet.In summary, transitional fossils are vital in unraveling the story of life’s evolution. They provide us with invaluable insights into the gradual transformations that have shaped the world we live in today.
FAQs
Q: What are transitional fossils?
Transitional fossils are the fossilized remains of organisms that exhibit traits of both ancestral and descendant species. They provide evidence of evolutionary links between different groups of organisms.
Q: Why are transitional fossils important?
Transitional fossils play a crucial role in understanding the evolutionary history of life on Earth. They help scientists identify the intermediate stages of the development of new species and provide evidence for common ancestry among different organisms.
Q: How are transitional fossils formed?
Transitional fossils are formed through a process called fossilization, where the remains of an organism are preserved over time. This can happen through various means such as sedimentation, mineralization, or preservation in ice or amber.
Q: Can transitional fossils prove evolution?
While no single fossil can prove evolution conclusively, the presence of transitional fossils provides strong evidence for the theory of evolution. These fossils demonstrate the gradual changes and adaptations that have occurred over time, supporting the idea that species have descended from common ancestors.
Q: Are transitional fossils rare?
Transitional fossils can be relatively rare due to the specific conditions required for fossilization to occur. However, significant discoveries have been made over the years, and ongoing excavations continue to unveil new transitional fossils, expanding our knowledge of evolutionary history.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
