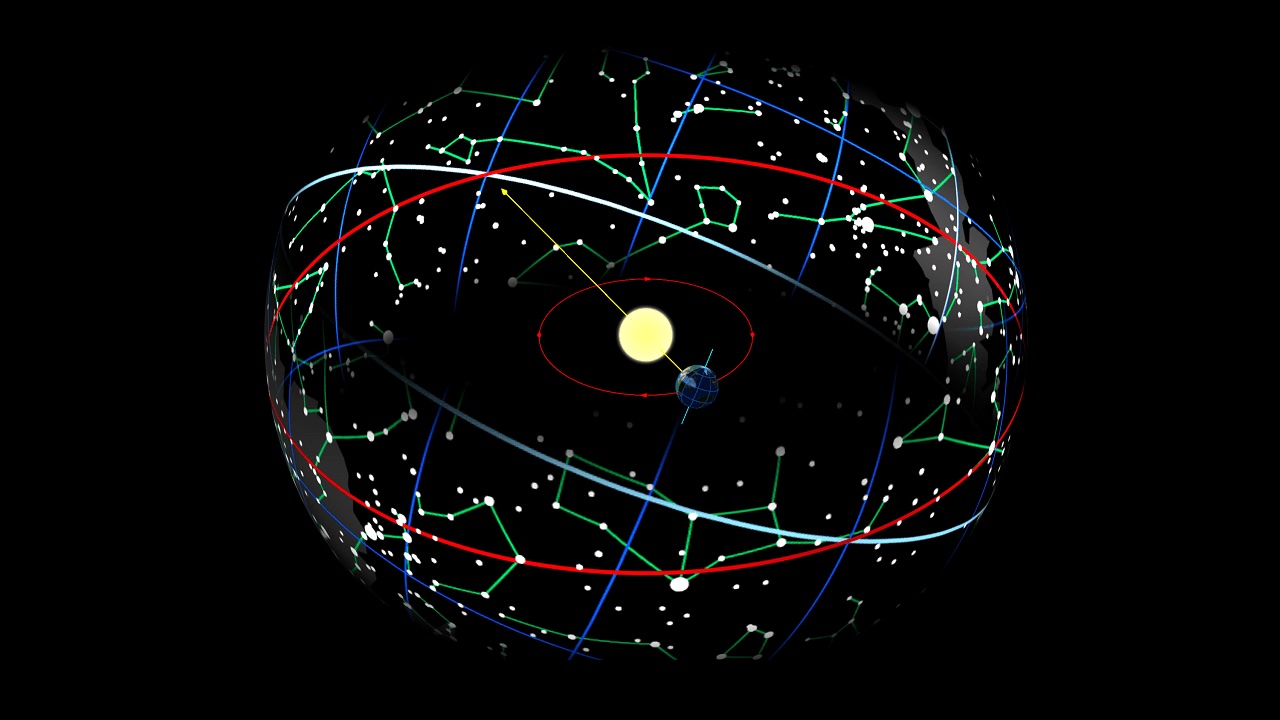
Precession is a fascinating phenomenon that affects everything from spinning tops to the Earth's rotation. But what exactly is it? Precession refers to the slow, conical motion of the axis of a spinning object, caused by external forces acting on it. Imagine a spinning top wobbling as it slows down—that wobble is a form of precession. This concept isn't just limited to toys; it plays a crucial role in astronomy, affecting how we observe stars and planets. For instance, the Earth's axis itself undergoes precession, which influences our climate and the way we measure time. Curious to learn more? Here are 35 intriguing facts about precession that will expand your understanding of this captivating subject.
What is Precession?
Precession is a fascinating phenomenon observed in rotating objects. It occurs when the axis of rotation of an object slowly traces out a cone over time. This movement is caused by external forces acting on the object, such as gravity. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about precession.
The Basics of Precession
Understanding the fundamental aspects of precession helps grasp its broader implications.
- Precession is the gradual change in the orientation of an object's rotational axis.
- Earth's precession is primarily caused by gravitational forces exerted by the Sun and the Moon.
- Gyroscopes exhibit precession, which is why they are used in navigation systems.
- Precession rate depends on the object's angular momentum and the external torque applied.
- Larmor precession occurs in magnetic fields, affecting the spin of atomic nuclei.
Historical Insights
Precession has been studied for centuries, with significant contributions from various cultures and scientists.
- Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer, discovered Earth's precession around 130 BCE.
- Isaac Newton explained precession using his laws of motion and universal gravitation.
- Albert Einstein refined the understanding of precession with his theory of general relativity.
- Ancient Egyptians noticed precession and used it to align their pyramids with celestial bodies.
- Mayan astronomers accounted for precession in their complex calendar systems.
Precession in Astronomy
Precession plays a crucial role in astronomy, affecting how we observe celestial objects.
- Axial precession causes the position of the North Star to change over millennia.
- Equinox precession shifts the dates of the equinoxes over a 26,000-year cycle.
- Planetary precession affects the orbits of planets, causing them to slowly shift over time.
- Lunar precession influences the Moon's orbit, leading to variations in its phases.
- Stellar precession alters the apparent positions of stars in the sky.
Precession in Physics
Precession is not limited to astronomy; it also has significant implications in physics.
- Spin precession occurs in particles with intrinsic angular momentum, like electrons.
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relies on precession to study atomic nuclei.
- Foucault pendulum demonstrates Earth's rotation through precession.
- Precessional damping is a phenomenon where energy is lost due to precession.
- Quantum mechanics incorporates precession in the behavior of subatomic particles.
Precession in Everyday Life
Precession might seem abstract, but it has practical applications in our daily lives.
- Bicycle wheels exhibit precession, helping riders maintain balance.
- Spinning tops show precession, which keeps them upright.
- Wobbling footballs demonstrate precession when thrown with a spin.
- Precessing gyroscopes are used in smartphones for orientation detection.
- Precession in satellites helps maintain their proper orientation in space.
Interesting Phenomena Related to Precession
Precession leads to some captivating and sometimes unexpected phenomena.
- Chandler wobble is a small deviation in Earth's rotation axis caused by precession.
- Milankovitch cycles are influenced by precession, affecting Earth's climate over long periods.
- Precession of the perihelion of Mercury's orbit was explained by Einstein's general relativity.
- Relativistic precession occurs in strong gravitational fields, like those near black holes.
- Precession in pulsars affects the timing of their radio pulses.
Fun Facts about Precession
Let's end with some fun and quirky facts about precession.
- Precession in hula hoops helps keep them spinning around the waist.
- Precessing frisbees fly more stably due to their spinning motion.
- Precession in yo-yos allows for complex tricks and stunts.
- Precessing boomerangs return to the thrower because of their spinning motion.
- Precession in figure skating helps skaters maintain balance during spins.
The Fascinating Dance of Precession
Precession, the slow wobble of Earth's axis, impacts our planet in surprising ways. It affects climate patterns, star positions, and even the timing of seasons. This phenomenon, caused by gravitational forces from the sun and moon, takes about 26,000 years to complete a full cycle. Ancient civilizations, like the Egyptians and Greeks, observed precession and used it to align their monuments with the stars. Modern science continues to study precession to understand its effects on Earth's climate and history.
Understanding precession helps us appreciate the intricate movements of our planet and its place in the cosmos. It reminds us that Earth is part of a dynamic, ever-changing universe. So next time you gaze at the night sky, remember the slow, majestic dance of precession shaping the world around us.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
