Aberration is a term that can mean different things depending on the context. In astronomy, it refers to the apparent shift in the position of a celestial object due to the motion of the observer. In optics, it describes the distortion of an image produced by a lens or mirror. Aberration can also mean a deviation from what is normal or expected in everyday language. This blog post will explore 35 intriguing facts about aberration across various fields. Whether you're a science enthusiast or just curious, these facts will help you understand this fascinating concept better. Buckle up for a journey through the world of aberration!
What is Aberration?
Aberration is a term used in various fields, including astronomy, optics, and biology. It generally refers to a deviation or distortion from the expected norm. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about aberration across different domains.
Aberration in Astronomy
Astronomical aberration involves the apparent displacement of celestial objects due to the motion of the observer.
- Discovered by James Bradley: In 1725, British astronomer James Bradley discovered the phenomenon of stellar aberration while attempting to measure stellar parallax.
- Annual Aberration: This type of aberration occurs due to Earth's orbit around the Sun, causing stars to appear slightly displaced from their true positions.
- Aberration Angle: The maximum angle of aberration is about 20.5 arcseconds, which is the result of Earth's orbital speed.
- Light Speed Factor: Aberration is directly related to the speed of light and the velocity of the observer.
- Planetary Aberration: This occurs when observing planets within our solar system, causing their apparent positions to shift slightly.
Aberration in Optics
Optical aberrations are imperfections in the imaging process of lenses and mirrors.
- Spherical Aberration: This happens when light rays passing through a lens or mirror do not converge at a single point, causing a blurred image.
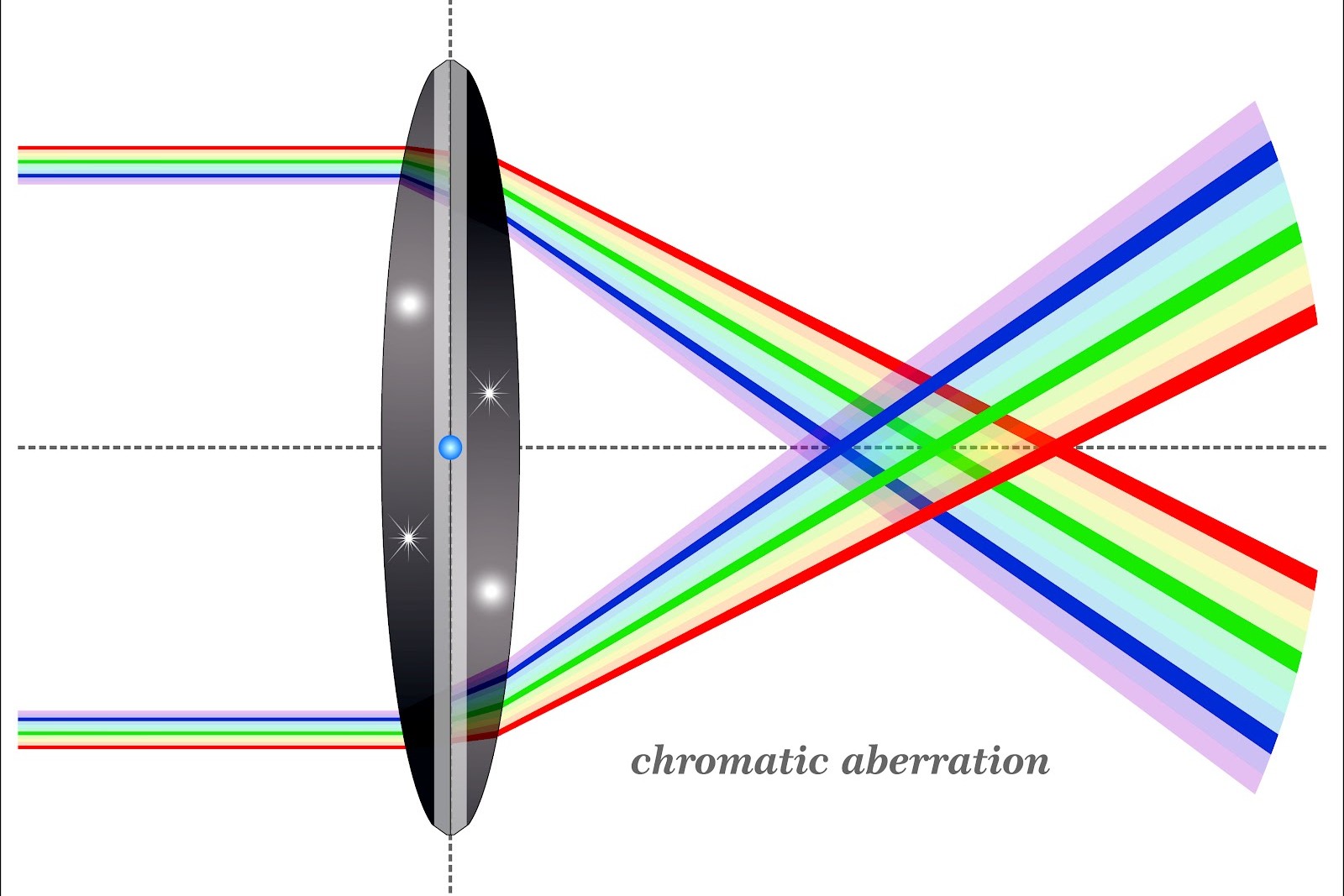
- Chromatic Aberration: Different wavelengths of light refract at different angles, leading to color fringing around objects.
- Coma: An aberration that results in off-axis points of light appearing comet-shaped.
- Astigmatism: This occurs when a lens or mirror fails to focus light into a single point, causing images to be stretched or blurred.
- Field Curvature: A flat object appears curved in the image due to the curvature of the lens or mirror.
- Distortion: This aberration causes straight lines to appear curved in the image, either pincushion or barrel-shaped.
Aberration in Biology
In biology, aberration often refers to deviations in chromosomes or genetic material.
- Chromosomal Aberration: Structural changes in chromosomes, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations.
- Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal aberration known as trisomy 21, where an individual has an extra copy of chromosome 21.
- Cri-du-chat Syndrome: A genetic disorder resulting from a deletion on chromosome 5.
- Klinefelter Syndrome: Males with an extra X chromosome (XXY) exhibit this chromosomal aberration.
- Turner Syndrome: Females with only one X chromosome (45, X) have this condition.
- Cancer: Many cancers are linked to chromosomal aberrations, such as translocations and deletions.
Aberration in Photography
Photographers often deal with various types of aberrations that affect image quality.
- Lens Flare: Caused by light scattering within the lens, leading to bright spots or haze in the image.
- Bokeh Aberration: Imperfections in the out-of-focus areas of an image, affecting the quality of the bokeh.
- Vignetting: Darkening of the image corners due to lens design or improper lens hood use.
- Field Curvature: Similar to optics, this causes flat subjects to appear curved in photographs.
- Distortion: Barrel or pincushion distortion affects the straightness of lines in the image.
Aberration in Physics
Physics also deals with aberrations, particularly in wave and particle behavior.
- Wavefront Aberration: Deviations in the wavefront of light or sound waves from a perfect shape.
- Electron Aberration: In electron microscopy, aberrations can affect the resolution and clarity of images.
- Quantum Aberration: Deviations in the expected behavior of particles at the quantum level.
Aberration in Literature and Art
Aberration can also be a theme or technique in creative fields.
- Literary Aberration: Authors may use aberration to describe characters or situations that deviate from societal norms.
- Artistic Aberration: Artists might intentionally distort reality to convey a message or evoke emotions.
- Surrealism: This art movement often features aberrant elements to challenge perceptions of reality.
- Dadaism: Known for its embrace of chaos and irrationality, often featuring aberrant themes.
Aberration in Everyday Life
Aberration isn't just a scientific term; it can be observed in daily experiences.
- Mirages: Optical aberrations caused by atmospheric conditions, making objects appear displaced or distorted.
- Eyeglasses: Corrective lenses are designed to minimize optical aberrations for clearer vision.
- Camera Lenses: High-quality lenses are engineered to reduce aberrations for better image quality.
- Telescope Design: Advanced telescopes use multiple lenses and mirrors to correct aberrations and improve clarity.
- Virtual Reality: VR headsets must account for optical aberrations to provide a realistic experience.
- Eyeglass Prescriptions: Tailored to correct specific aberrations in an individual's vision, ensuring optimal clarity.
Final Thoughts on Aberration
Aberration isn't just a fancy word; it's a concept that touches many parts of our lives. From optical illusions to astronomical phenomena, these deviations from the norm can be both fascinating and puzzling. Understanding aberrations helps us appreciate the complexity of science and nature. Whether it's the chromatic aberration in your camera lens or the stellar aberration observed by astronomers, these quirks remind us that perfection is rare. They also push us to innovate and find solutions, making technology and science even better. So next time you notice something a bit off, remember, it might just be an aberration, adding a little twist to the ordinary. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let these oddities inspire you to look deeper into the world around you.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
