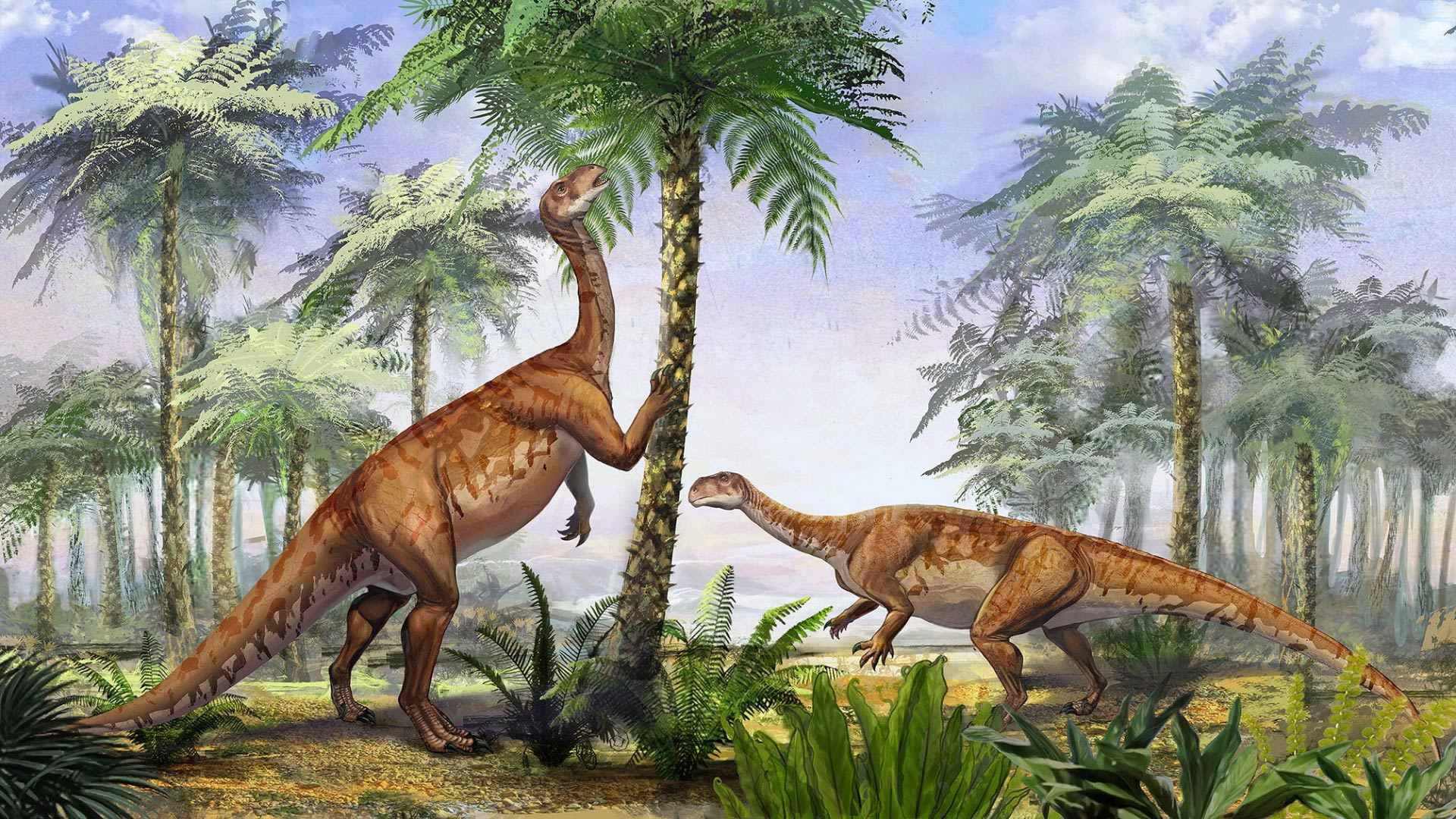
Are you curious about the amazing world of herbivore dinosaurs? Look no further! In this article, we will explore 10 fascinating facts about these incredible creatures that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Herbivore dinosaurs, as the name suggests, were plant-eating giants and played a crucial role in shaping the ecosystems of their time. From the gentle giants like the Brachiosaurus to the agile and horned Triceratops, herbivore dinosaurs were diverse in size, shape, and behavior. Join us as we delve into the world of these magnificent creatures, uncovering intriguing details about their diets, defences, and social behaviors. So, get ready to unravel the mysteries of herbivore dinosaurs as we embark on an exciting journey back in time!
Key Takeaways:
- Herbivore dinosaurs had unique teeth, digestive systems, and defensive adaptations to survive and thrive in their prehistoric ecosystem. They played a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem by consuming plants and spreading seeds through their droppings.
- Herbivore dinosaurs came in various sizes, from small to enormous creatures, and had diverse feeding strategies. They formed large herds for protection and evolved different adaptations for defense, such as horns, frills, and spines, to deter predators or engage in combat.
Herbivorous dinosaurs had specialized teeth for chewing plants.
These dinosaurs had teeth that were adapted for grinding and shredding vegetation, allowing them to efficiently extract nutrients from plants.
Herbivore dinosaurs formed large herds for protection.
In order to defend themselves against predators, herbivorous dinosaurs often traveled in large groups, providing safety in numbers.
Some herbivore dinosaurs had long necks to reach vegetation.
Dinosaurs such as Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus possessed incredibly long necks, enabling them to access foliage that was out of reach for other dinosaurs.
Herbivore dinosaurs had specialized digestive systems.
These dinosaurs had complex digestive systems, including elongated intestines and microbial fermentation chambers, which helped break down tough plant material.
Herbivorous dinosaurs played crucial roles in the ecosystem.
By consuming plants and spreading seeds through their droppings, herbivorous dinosaurs played a vital role in maintaining the balance of the prehistoric ecosystem.
Some herbivore dinosaurs had defensive body armor.
Dinosaurs like Ankylosaurus and Stegosaurus developed sharp bony plates and spikes along their bodies, providing protection against predators.
Herbivore dinosaurs had diverse feeding strategies.
While some herbivorous dinosaurs were grazers, feeding on low-lying vegetation, others were browsers, consuming leaves and branches from trees.
Some herbivorous dinosaurs had beak-like mouths.
Certain herbivorous dinosaurs, like the hadrosaurs, had beak-like mouths, similar to modern-day ducks, which they used to strip vegetation from branches.
Herbivore dinosaurs evolved different adaptations for defense.
Herbivorous dinosaurs developed various defense mechanisms, such as horns, frills, and spines, to deter predators or engage in intraspecific combat.
Herbivore dinosaurs existed in various sizes.
From small dinosaurs like Hypsilophodon to enormous creatures like Argentinosaurus, herbivores ranged in size, occupying different ecological niches.
Conclusion
In conclusion, herbivore dinosaurs played a crucial role in the prehistoric world. They were adapted to a plant-based diet, which allowed them to thrive in different environments. These magnificent creatures ranged in size and shape, from small and agile to large and formidable. They had unique adaptations such as specialized teeth and digestive systems that helped them consume and process plant material efficiently.
Herbivore dinosaurs were not only important for maintaining the balance of ecosystems but also served as a food source for carnivorous dinosaurs. Their existence and abundance contributed to the diverse and thriving life forms during the Mesozoic Era. Studying them provides valuable insights into the evolution and behavior of ancient creatures and helps us understand the dynamics of past ecosystems.
Overall, herbivore dinosaurs were remarkable animals that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. Their legacy continues to fascinate and captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike, reminding us of the incredible diversity and wonder of the animal kingdom.
FAQs
1. What is a herbivore dinosaur?
A herbivore dinosaur is a dinosaur species that primarily feeds on plants and vegetation. They have specialized teeth and digestive systems adapted for processing plant material.
2. How did herbivore dinosaurs defend themselves?
Herbivore dinosaurs employed several defense mechanisms, including living in herds to deter predators, using their size and strength to fend off attackers, and some even had bony plates or spikes for protection.
3. What are some examples of herbivore dinosaurs?
Popular examples of herbivore dinosaurs include Triceratops, Brachiosaurus, Stegosaurus, and hadrosaurs like Parasaurolophus.
4. How did herbivore dinosaurs digest plant material?
Herbivore dinosaurs had specialized digestive systems, some with long intestines to aid in digestion. They also had bacteria in their guts that helped break down tough plant fibers.
5. Did herbivore dinosaurs have any predators?
Yes, herbivore dinosaurs had natural predators, including carnivorous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptors. They had to employ various defense strategies to survive.
6. How large could herbivore dinosaurs grow?
Herbivore dinosaurs could vary in size, from small and agile species to massive giants like Argentinosaurus, which could reach lengths of up to 100 feet and weigh over 100 tons.
7. How long did herbivore dinosaurs exist?
Herbivore dinosaurs first appeared during the Triassic Period, around 230 million years ago, and thrived until the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 65 million years ago.
8. What is the significance of studying herbivore dinosaurs?
Studying herbivore dinosaurs helps us understand the ancient ecosystems and how different species interacted with one another. It also provides insights into the evolution and adaptations of plant-eating animals.
9. Are there any herbivorous dinosaurs alive today?
No, all dinosaur species, including herbivores, went extinct around 65 million years ago. However, some modern-day animals, like elephants and giraffes, serve as living examples of large herbivores.
10. What caused the extinction of herbivore dinosaurs?
The exact cause of dinosaur extinction is still debated among scientists, but the most widely accepted theory is that a catastrophic event, possibly a massive asteroid impact, caused widespread changes in climate and environment, leading to the extinction of not only herbivore dinosaurs but also many other species.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
