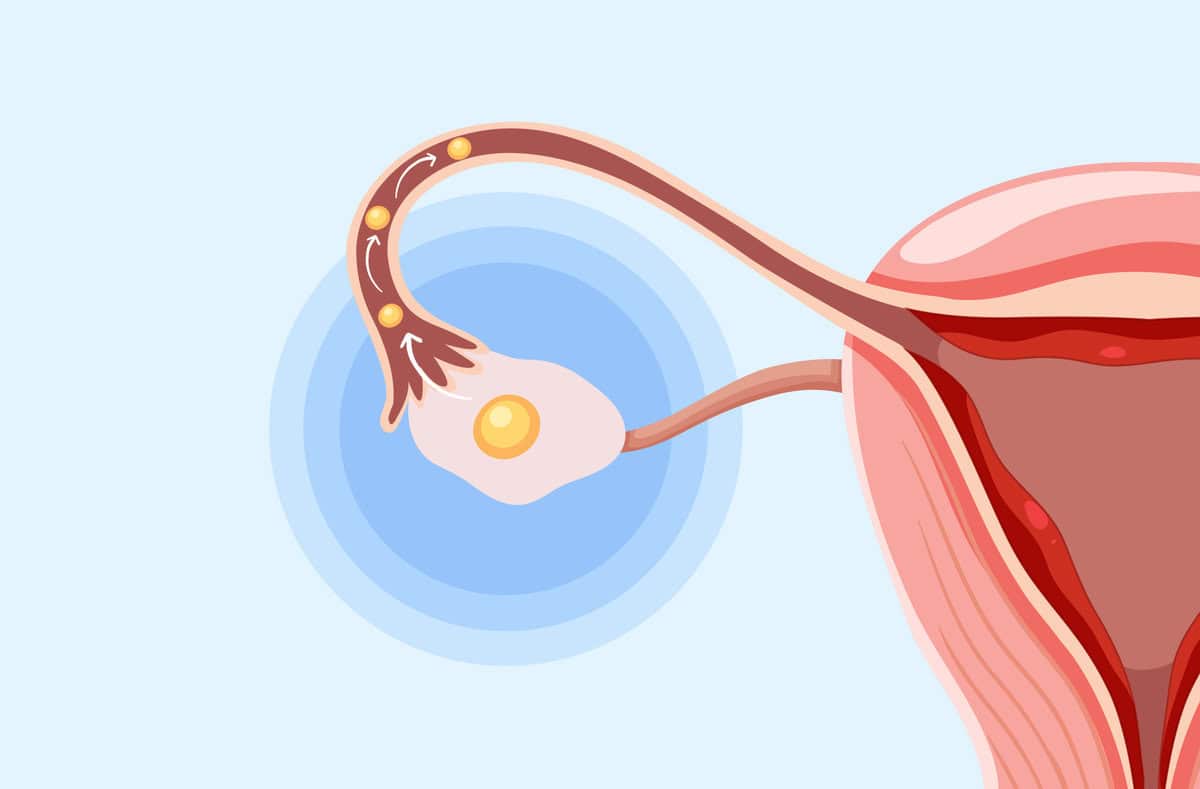
Ever wondered what happens during ovulation? Ovulation is a fascinating process where an egg is released from the ovary, ready for fertilization. This natural cycle plays a crucial role in reproduction and understanding it can help with family planning or recognizing health issues. Did you know that ovulation typically occurs around the 14th day of a 28-day menstrual cycle? However, this can vary greatly among women. Hormones like estrogen and luteinizing hormone (LH) are key players in this process. Signs of ovulation include changes in cervical mucus, slight pain, and even increased libido. Knowing these facts can empower you to take control of your reproductive health. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 38 intriguing facts about ovulation!
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is a key part of the menstrual cycle. It involves the release of an egg from one of the ovaries. Understanding ovulation can help with family planning and recognizing certain health issues.
- Ovulation typically occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle, about 14 days before the start of the next period.
- The process is triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH), which is produced by the pituitary gland.
- Each cycle, one ovary releases a single egg, although sometimes more than one egg can be released, leading to fraternal twins.
- The egg released during ovulation is viable for fertilization for about 12 to 24 hours.
- Sperm can live inside the female reproductive tract for up to five days, increasing the window for potential fertilization.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation
Recognizing the signs of ovulation can be helpful for those trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. Here are some common symptoms.
- A slight rise in basal body temperature occurs after ovulation due to increased progesterone levels.
- Cervical mucus becomes clearer, stretchier, and more slippery, resembling egg whites.
- Some women experience mild pelvic or abdominal pain known as mittelschmerz during ovulation.
- Increased libido is often reported around the time of ovulation.
- Breast tenderness or sensitivity can occur due to hormonal changes.
Factors Affecting Ovulation
Various factors can influence ovulation, making it important to understand what might affect this process.
- Stress can disrupt the hormonal balance necessary for ovulation.
- Significant weight loss or gain can impact ovulation by altering hormone levels.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that can cause irregular or absent ovulation.
- Thyroid disorders can affect ovulation by disrupting the balance of reproductive hormones.
- Excessive exercise can lead to irregular ovulation or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
Tracking Ovulation
Tracking ovulation can help in planning pregnancies or understanding menstrual health. Here are some methods used to track ovulation.
- Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) detect the surge in LH that precedes ovulation.
- Charting basal body temperature daily can help identify the slight rise that occurs after ovulation.
- Monitoring changes in cervical mucus can provide clues about ovulation.
- Some women use fertility monitors, which combine multiple methods to predict ovulation.
- Ultrasound scans can be used by healthcare providers to monitor follicle development and ovulation.
Ovulation and Fertility
Ovulation plays a crucial role in fertility. Understanding its relationship with fertility can be beneficial.
- The most fertile days are the day of ovulation and the five days preceding it.
- Anovulation, the absence of ovulation, is a common cause of infertility.
- Age affects ovulation; fertility begins to decline in the late 20s and more significantly after age 35.
- Certain medications, like Clomiphene citrate, can induce ovulation in women with ovulatory disorders.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), often involve stimulating ovulation to retrieve multiple eggs.
Myths and Misconceptions about Ovulation
There are many myths surrounding ovulation. Here are some common misconceptions debunked.
- Myth: Ovulation always occurs on day 14 of the cycle. Fact: The timing can vary greatly among women.
- Myth: You can’t get pregnant if you have sex during your period. Fact: Sperm can survive long enough to fertilize an egg released shortly after menstruation.
- Myth: Ovulation is always accompanied by noticeable symptoms. Fact: Some women may not experience any symptoms.
- Myth: You can’t ovulate while breastfeeding. Fact: While breastfeeding can suppress ovulation, it is not a reliable form of contraception.
- Myth: Irregular periods mean you can’t ovulate. Fact: Many women with irregular cycles still ovulate, though it may be less predictable.
Health Implications of Ovulation
Ovulation is not just about fertility; it has broader health implications.
- Regular ovulation is a sign of overall reproductive health.
- Irregular ovulation can indicate underlying health issues like PCOS or thyroid disorders.
- Ovulation affects hormone levels, which can influence mood and energy levels.
- Tracking ovulation can help diagnose menstrual disorders and guide treatment.
- Understanding ovulation can aid in managing conditions like endometriosis and fibroids.
Fun Facts about Ovulation
Here are some interesting tidbits about ovulation that you might not know.
- Some animals, like rabbits and cats, are induced ovulators, meaning they ovulate in response to mating.
- Human eggs are the largest cells in the body, visible to the naked eye.
- The word "ovulation" comes from the Latin word "ovulum," meaning small egg.
Ovulation Facts You Should Know
Understanding ovulation can be a game-changer for anyone trying to conceive or just wanting to know more about their body. Knowing when you ovulate helps you track your fertility window, making it easier to plan or prevent pregnancy. Ovulation isn't just about making babies; it affects your mood, energy levels, and even your skin.
Remember, ovulation can vary from woman to woman and even month to month. Stress, diet, and exercise can all impact your cycle. If you're having trouble tracking your ovulation, there are plenty of tools and apps to help you out.
Don't hesitate to talk to a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your ovulation or menstrual cycle. They can offer personalized advice and solutions. Knowledge is power, and understanding your ovulation is a step toward better health and well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
