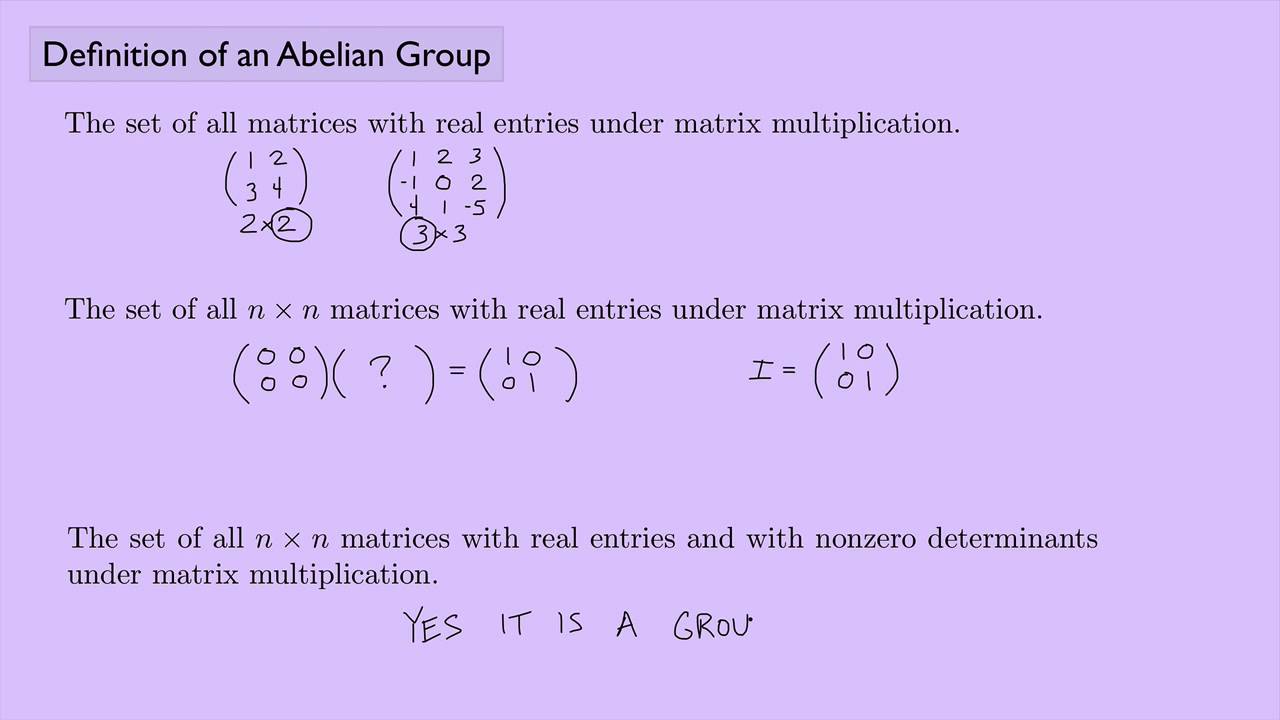
What is an Abelian Group? An Abelian group is a set equipped with an operation that combines any two elements to form a third element, where the operation is both associative and commutative. Named after the Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel, these groups are fundamental in abstract algebra. In simpler terms, if you can add or multiply two elements in any order and get the same result, you're dealing with an Abelian group. Think of it like adding numbers: 3 + 5 is the same as 5 + 3. This property makes Abelian groups easier to study and apply in various fields like cryptography, physics, and coding theory. Ready to dive into some cool facts about Abelian groups? Let's get started!
What is an Abelian Group?
An Abelian group is a fundamental concept in abstract algebra. Named after the mathematician Niels Henrik Abel, these groups have a special property: their operation is commutative. Let's dive into some interesting facts about Abelian groups.
-
Commutative Property: In an Abelian group, the order of operation doesn't matter. For any two elements (a) and (b), (a + b = b + a).
-
Named After Niels Henrik Abel: The term "Abelian" honors Niels Henrik Abel, a Norwegian mathematician who made significant contributions to group theory.
-
Identity Element: Every Abelian group has an identity element, (e), such that for any element (a), (a + e = a).
-
Inverse Elements: Each element in an Abelian group has an inverse. For any element (a), there exists an element (-a) such that (a + (-a) = e).
-
Closure: Abelian groups are closed under their operation. If (a) and (b) are in the group, then (a + b) is also in the group.
Examples of Abelian Groups
Abelian groups appear in various mathematical contexts. Here are some common examples.
-
Integers Under Addition: The set of all integers (mathbb{Z}) with addition is an Abelian group.
-
Rational Numbers: The set of rational numbers (mathbb{Q}) with addition forms an Abelian group.
-
Real Numbers: The set of real numbers (mathbb{R}) with addition is another example.
-
Complex Numbers: The set of complex numbers (mathbb{C}) with addition also forms an Abelian group.
-
Vectors: Vectors in a vector space with vector addition form an Abelian group.
Properties of Abelian Groups
Abelian groups have several interesting properties that set them apart from non-Abelian groups.
-
Subgroups: Any subgroup of an Abelian group is also Abelian.
-
Quotient Groups: The quotient group of an Abelian group by one of its subgroups is also Abelian.
-
Direct Sum: The direct sum of two Abelian groups is also Abelian.
-
Finite Abelian Groups: Every finite Abelian group can be expressed as a direct sum of cyclic groups.
-
Homomorphisms: The set of all homomorphisms between two Abelian groups forms an Abelian group.
Applications of Abelian Groups
Abelian groups are not just theoretical constructs; they have practical applications in various fields.
-
Cryptography: Abelian groups are used in cryptographic algorithms, such as the Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
-
Coding Theory: In coding theory, Abelian groups help in constructing error-detecting and error-correcting codes.
-
Physics: Symmetry groups in physics, especially in quantum mechanics, often form Abelian groups.
-
Fourier Analysis: The study of Fourier series and transforms relies on the properties of Abelian groups.
-
Topology: Fundamental groups in topology can be Abelian, providing insights into the structure of topological spaces.
Abelian Group Theorems
Several theorems highlight the unique characteristics of Abelian groups.
-
Fundamental Theorem of Finite Abelian Groups: This theorem states that every finite Abelian group is isomorphic to a direct sum of cyclic groups of prime power order.
-
Structure Theorem for Finitely Generated Abelian Groups: Any finitely generated Abelian group is isomorphic to a direct sum of a free Abelian group and a finite Abelian group.
-
Classification Theorem: Finite Abelian groups are classified by their invariant factors or elementary divisors.
-
Jordan-Hölder Theorem: This theorem applies to Abelian groups, stating that any two composition series of a group have the same length and the same factors, up to isomorphism.
-
Schur-Zassenhaus Theorem: In the context of Abelian groups, this theorem provides conditions under which a group can be decomposed into a semidirect product.
Historical Context
Understanding the history behind Abelian groups provides a richer perspective.
-
Niels Henrik Abel: Abel's work in the early 19th century laid the groundwork for group theory, leading to the concept of Abelian groups.
-
Évariste Galois: Galois' contributions to group theory also influenced the development of Abelian groups.
-
Early 20th Century: The formal definition and study of Abelian groups became more rigorous in the early 20th century.
-
Modern Algebra: Abelian groups are a cornerstone of modern algebra, influencing various branches of mathematics.
-
Educational Impact: Abelian groups are a fundamental topic in undergraduate and graduate mathematics courses.
Advanced Concepts
For those interested in deeper mathematical waters, here are some advanced concepts related to Abelian groups.
-
Torsion Subgroup: The torsion subgroup of an Abelian group consists of all elements of finite order.
-
Free Abelian Group: A free Abelian group is one that has a basis, similar to a vector space.
-
Divisible Group: An Abelian group is divisible if every element is divisible by any positive integer.
-
Pontryagin Duality: This duality relates locally compact Abelian groups to their dual groups.
-
Ext and Tor Functors: In homological algebra, these functors measure the extent to which a module fails to be projective or injective.
Fun Facts
Let's end with some lighter, fun facts about Abelian groups.
-
Symmetry: Abelian groups often describe symmetrical structures, making them aesthetically pleasing in mathematics.
-
Simple Yet Powerful: Despite their simple definition, Abelian groups have profound implications in various fields.
-
Group Theory Pioneers: Abelian groups were among the first groups studied in detail, paving the way for more complex group theories.
-
Mathematical Beauty: Many mathematicians find the properties of Abelian groups to be elegant and beautiful.
-
Universal Language: Abelian groups provide a universal language for discussing symmetry and structure in mathematics.
Final Thoughts on Abelian Groups
Abelian groups, named after the mathematician Niels Henrik Abel, play a crucial role in modern algebra. These groups are defined by their commutative property, meaning the order of operations doesn't affect the result. This simple yet powerful concept has applications in various fields, from cryptography to physics.
Understanding the basics of Abelian groups can provide a solid foundation for further studies in mathematics. Their properties, such as the existence of an identity element and inverses for each element, make them a fundamental topic in group theory.
Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just a math enthusiast, grasping the essentials of Abelian groups can open doors to more advanced mathematical concepts. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and you'll find that the world of mathematics is full of fascinating discoveries waiting to be made.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
