What are polyhedra? Polyhedra are three-dimensional shapes with flat faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices. Imagine a cube, pyramid, or even a soccer ball—these are all examples of polyhedra. These fascinating shapes have intrigued mathematicians, artists, and architects for centuries. They come in various forms, from the simple tetrahedron with four faces to the complex dodecahedron with twelve. Polyhedra are not just abstract concepts; they appear in nature, art, and even in the design of buildings and everyday objects. Why are polyhedra important? They help us understand spatial relationships, symmetry, and geometry, making them essential in fields like mathematics, engineering, and art. Ready to dive into the world of polyhedra? Let's explore 36 amazing facts about these captivating shapes!
What Are Polyhedra?
Polyhedra are fascinating 3D shapes made up of flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and vertices. These geometric wonders have intrigued mathematicians, artists, and architects for centuries. Let's explore some mind-blowing facts about polyhedra.
-
The term "polyhedron" comes from Greek, meaning "many faces."
-
Polyhedra can be classified into two main types: convex and concave. Convex polyhedra have all their faces pointing outward, while concave ones have some faces pointing inward.
-
The simplest polyhedron is the tetrahedron, which has four triangular faces.
-
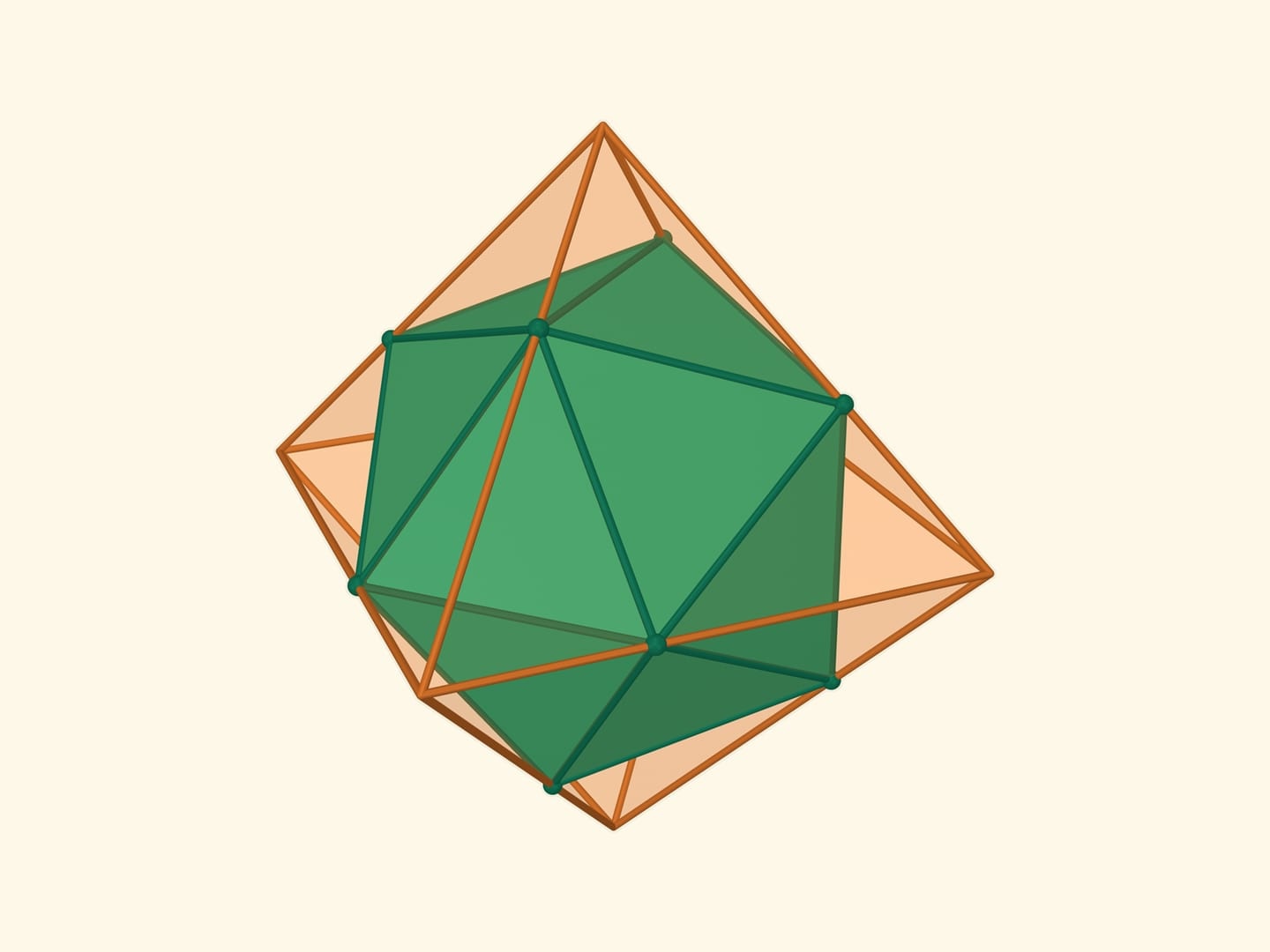
There are five Platonic solids: tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron. Each has faces made of identical regular polygons.
Historical Significance of Polyhedra
Polyhedra have played a crucial role in the history of mathematics and art. Their symmetrical beauty and structural integrity have inspired countless works and theories.
-
The ancient Greeks, including Plato and Euclid, studied polyhedra extensively. Plato associated each of the five Platonic solids with an element: earth, air, fire, water, and the universe.
-
Johannes Kepler, a famous astronomer, used polyhedra to model the solar system in his work "Mysterium Cosmographicum."
-
Leonardo da Vinci illustrated polyhedra for Luca Pacioli's book "De Divina Proportione," showcasing their artistic and mathematical beauty.
-
The Fullerene molecule, discovered in 1985, resembles a truncated icosahedron and is named after architect Buckminster Fuller, known for his geodesic domes.
Mathematical Properties of Polyhedra
Polyhedra are not just visually appealing; they also possess intriguing mathematical properties. These properties have led to significant discoveries and advancements in geometry.
-
Euler's formula, V – E + F = 2, relates the number of vertices (V), edges (E), and faces (F) of a convex polyhedron.
-
Dual polyhedra are pairs of polyhedra where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other. For example, the cube and the octahedron are duals.
-
Archimedean solids are polyhedra with identical vertices and faces made of two or more types of regular polygons. There are 13 Archimedean solids.
-
Catalan solids are the duals of Archimedean solids. They have faces that are identical but not regular polygons.
Polyhedra in Nature and Technology
Polyhedra are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they appear in nature and modern technology. Their unique structures provide strength and efficiency.
-
Many viruses, such as the adenovirus, have icosahedral symmetry, which helps them pack genetic material efficiently.
-
Honeycombs are made of hexagonal prisms, a type of polyhedron, which allows bees to store the maximum amount of honey with minimal wax.
-
Crystals often form polyhedral shapes due to their atomic structure. For example, pyrite crystals commonly form cubes.
-
Geodesic domes, popularized by Buckminster Fuller, use polyhedral structures to create strong, lightweight buildings.
Polyhedra in Art and Architecture
Artists and architects have long been inspired by the beauty and symmetry of polyhedra. These shapes have been used to create stunning works of art and innovative architectural designs.
-
The Louvre Pyramid in Paris, designed by I. M. Pei, is a famous example of polyhedral architecture.
-
M. C. Escher, a renowned artist, often incorporated polyhedra into his intricate, mind-bending drawings.
-
The Atomium in Brussels, Belgium, is a building shaped like a unit cell of an iron crystal, magnified 165 billion times.
-
The Eden Project in the UK features geodesic domes made of hexagonal and pentagonal panels, inspired by polyhedral structures.
Fun and Unusual Facts About Polyhedra
Polyhedra have some quirky and lesser-known aspects that make them even more intriguing. Let's dive into some fun and unusual facts.
-
The Great Stellation of the dodecahedron is a complex polyhedron with 60 intersecting triangular faces.
-
Zonohedra are polyhedra with faces that are parallelograms. They can be formed by stacking zones of parallelograms.
-
The Goldberg polyhedron is a type of polyhedron with hexagonal and pentagonal faces, similar to a soccer ball.
-
The Szilassi polyhedron has seven hexagonal faces, each sharing an edge with every other face, making it a unique and complex shape.
Polyhedra in Games and Puzzles
Polyhedra have found their way into various games and puzzles, challenging and entertaining people of all ages. Their geometric properties make them perfect for these applications.
-
The Rubik's Cube, a popular 3D puzzle, is a type of polyhedron called a cube.
-
Dungeons & Dragons and other tabletop role-playing games use polyhedral dice, including tetrahedrons, cubes, octahedrons, dodecahedrons, and icosahedrons.
-
The Soma cube is a dissection puzzle consisting of seven polyhedral pieces that can be assembled into a 3x3x3 cube.
-
The Pentominoes puzzle involves fitting 12 different polyhedral shapes, each made of five squares, into a rectangular grid.
Polyhedra in Modern Research
Researchers continue to study polyhedra, uncovering new properties and applications. These discoveries have implications for various fields, from materials science to computer graphics.
-
Mathematicians have discovered over 50,000 different types of polyhedra, each with unique properties and structures.
-
Polyhedral combinatorics is a field of study that focuses on the enumeration and classification of polyhedra.
-
In computer graphics, polyhedra are used to create 3D models and animations, providing a foundation for realistic rendering.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of polyhedral structures in designing new materials with unique properties, such as increased strength and flexibility.
Polyhedra in Education
Polyhedra are valuable tools for teaching geometry and spatial reasoning. Their study helps students develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills.
-
Building polyhedral models with paper or other materials is a common classroom activity that helps students visualize and understand 3D shapes.
-
Polyhedral nets, which are 2D representations of polyhedra, are used to teach students about surface area and volume.
-
Interactive software and apps allow students to explore and manipulate polyhedra, enhancing their learning experience.
-
Polyhedra are often featured in math competitions and challenges, encouraging students to think critically and creatively about geometric problems.
The Fascinating World of Polyhedra
Polyhedra are more than just shapes; they’re a blend of mathematics, art, and history. From the ancient Greeks to modern-day architects, these geometric wonders have captured imaginations for centuries. Whether it’s the Platonic solids with their perfect symmetry or the complex Archimedean solids, each polyhedron tells a unique story.
Understanding polyhedra can deepen your appreciation for the structures around us, from buildings to molecules. They’re not just academic concepts but practical tools in engineering, architecture, and even art. So next time you see a soccer ball or a crystal, remember, you’re looking at a piece of mathematical art.
Keep exploring, keep questioning, and who knows? You might just uncover a new facet of these incredible shapes. Polyhedra are a testament to the beauty and complexity of the world we live in.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
