What is fibration? Fibration is a concept in mathematics, specifically in topology, that deals with the structure of spaces. Imagine you have a big, complicated space, and you want to understand it by breaking it down into simpler pieces. Fibration helps by showing how a space can be seen as a collection of smaller, easier-to-understand spaces, all glued together in a specific way. Think of it like a bundle of fibers, where each fiber is a simpler space, and the whole bundle forms the complex space. This idea is crucial in many areas of math and physics, helping to solve problems and understand the universe's structure.
What is Fibration?
Fibration is a concept in mathematics, particularly in topology and algebraic geometry. It involves mapping one space onto another in a way that locally looks like a product space. Here are some intriguing facts about fibration.
-
Fibration is a generalization of the notion of a fiber bundle, which is a space that looks locally like a product of two spaces.
-
The term "fibration" was introduced by the French mathematician Jean-Pierre Serre in the 1950s.
-
A fibration consists of three main components: the total space, the base space, and the fiber.
-
The total space is the space that is being mapped onto the base space.
-
The base space is the space onto which the total space is mapped.
-
The fiber is the space that is "attached" to each point of the base space.
Types of Fibration
Fibrations come in various types, each with unique properties and applications. Let's explore some of these types.
-
Serre Fibration: Named after Jean-Pierre Serre, this type of fibration is used in homotopy theory.
-
Hurewicz Fibration: Named after Witold Hurewicz, this type of fibration is used in algebraic topology.
-
Vector Bundle: A special type of fibration where the fiber is a vector space.
-
Principal Bundle: A type of fibration where the fiber is a group that acts freely on the total space.
-
Fiber Bundle: A general type of fibration where the fiber can be any topological space.
Applications of Fibration
Fibration has numerous applications in various fields of mathematics and science. Here are some notable examples.
-
Homotopy Theory: Fibrations are used to study the properties of spaces up to continuous deformation.
-
Algebraic Geometry: Fibrations are used to study the structure of algebraic varieties.
-
Differential Geometry: Fibrations are used to study the properties of differentiable manifolds.
-
Physics: Fibrations are used in the study of gauge theories and fiber bundles in theoretical physics.
-
Computer Science: Fibrations are used in the study of type theory and category theory.
Interesting Properties of Fibration
Fibrations have some fascinating properties that make them a rich area of study. Here are a few.
-
Lifting Property: Fibrations have a unique lifting property that allows for the lifting of paths and homotopies.
-
Homotopy Fiber: The homotopy fiber of a fibration is a space that measures the failure of a map to be a fibration.
-
Long Exact Sequence: Fibrations give rise to a long exact sequence in homotopy, which is a powerful tool in algebraic topology.
-
Classifying Space: Every fibration has a classifying space, which is a space that classifies all fibrations with a given fiber.
-
Section: A section of a fibration is a map that assigns to each point of the base space a point in the total space lying over it.
Famous Examples of Fibration
Some fibrations are famous in the mathematical community for their interesting properties and applications. Here are a few.
-
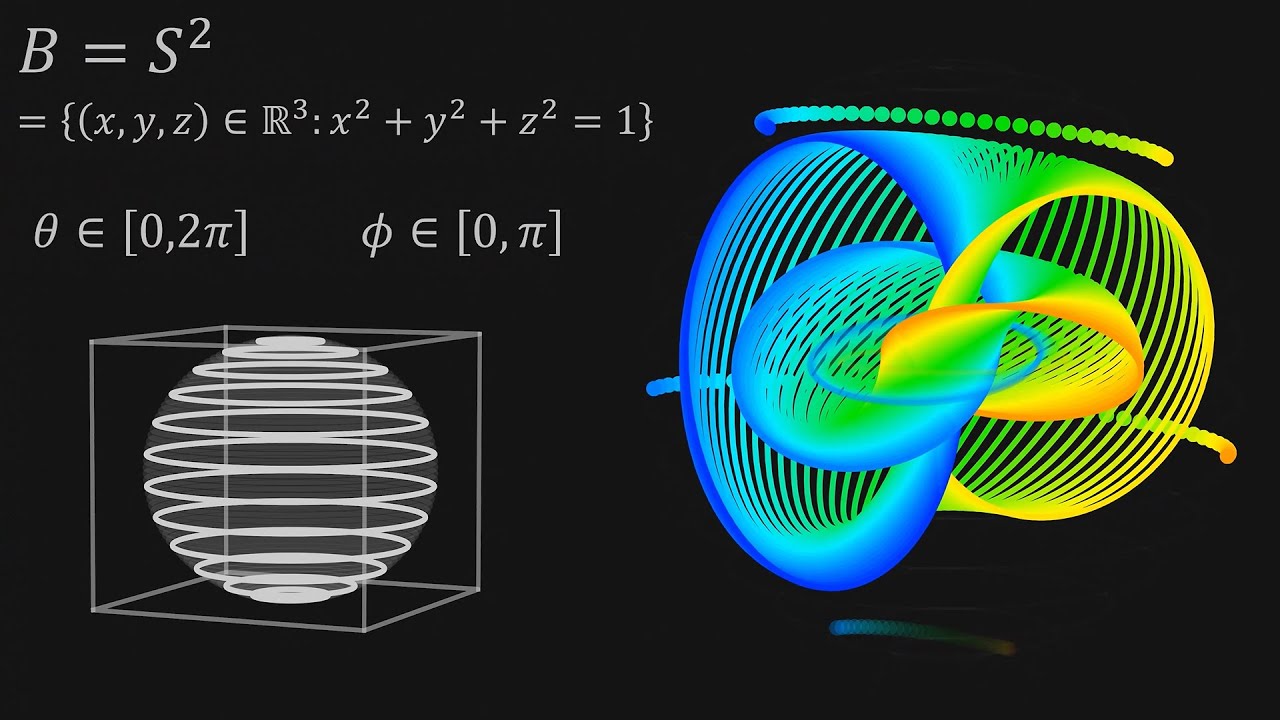
Hopf Fibration: A famous fibration discovered by Heinz Hopf, where the total space is the 3-sphere, the base space is the 2-sphere, and the fiber is the circle.
-
Möbius Strip: A classic example of a non-trivial fibration, where the base space is a circle and the fiber is an interval.
-
Klein Bottle: Another example of a non-trivial fibration, where the base space is a circle and the fiber is also a circle.
-
Projective Space: The projective space can be seen as a fibration where the base space is a sphere and the fiber is a projective line.
-
Torus: The torus can be seen as a fibration where the base space is a circle and the fiber is also a circle.
Challenges in Studying Fibration
Studying fibration is not without its challenges. Here are some of the difficulties mathematicians face.
-
Complexity: The concept of fibration is complex and requires a deep understanding of topology and algebraic geometry.
-
Abstract Nature: Fibrations are highly abstract, making them difficult to visualize and understand intuitively.
The Final Word on Fibration
Fibration might sound complex, but it's a fascinating concept in mathematics and physics. It helps us understand how spaces and structures relate to each other. From its role in topology to its applications in string theory, fibration is more than just a theoretical idea. It has real-world implications, influencing how scientists and mathematicians solve problems and make discoveries. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just curious, knowing about fibration can give you a new perspective on the world around us. So next time you hear about fiber bundles or homotopy, you'll have a better grasp of what they mean and why they matter. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and who knows? You might just uncover the next big thing in the world of math and science.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
