What is associative memory? Associative memory, also known as content-addressable memory, is a type of memory system that retrieves information based on the content rather than a specific address. Imagine trying to remember a friend's name by recalling their face or a song by humming its tune. This memory system works similarly, allowing for faster and more efficient data retrieval. Associative memory is crucial in both human cognition and computer science, playing a significant role in pattern recognition, learning, and problem-solving. Understanding how it functions can help improve artificial intelligence, enhance learning techniques, and even aid in treating memory-related disorders. Ready to dive into 39 intriguing facts about associative memory? Let's get started!
What is Associative Memory?
Associative memory, also known as content-addressable memory (CAM), is a type of memory that allows data retrieval based on the content rather than the address. This unique feature makes it highly efficient for specific applications.
- Associative memory can quickly locate and retrieve data based on a partial match, making it faster than traditional memory systems.
- It is widely used in networking devices like routers and switches for fast lookups.
- Associative memory is essential in artificial intelligence for pattern recognition and machine learning.
- It can be implemented using both hardware and software, depending on the application requirements.
- The concept of associative memory dates back to the 1950s, with early research conducted by computer scientists like John von Neumann.
How Does Associative Memory Work?
Understanding the mechanics of associative memory helps appreciate its efficiency and applications. It operates differently from conventional memory systems.
- Associative memory stores data in a way that allows for parallel searching, significantly speeding up data retrieval.
- It uses a comparison mechanism to match input data with stored data, returning the associated information.
- The memory cells in associative memory are designed to perform comparison operations, unlike traditional memory cells that only store data.
- Associative memory can handle multiple queries simultaneously, making it highly efficient for large datasets.
- It is often used in applications requiring real-time data processing, such as telecommunications and image processing.
Applications of Associative Memory
Associative memory's unique capabilities make it suitable for various applications across different fields. Here are some notable examples.
- In computer networking, associative memory is used for fast address lookups in routing tables.
- It plays a crucial role in cache memory systems, improving data retrieval speeds.
- Associative memory is used in database management systems for efficient query processing.
- It is employed in image and speech recognition systems for pattern matching.
- Associative memory is used in cybersecurity for detecting and preventing unauthorized access.
Advantages of Associative Memory
Associative memory offers several benefits over traditional memory systems, making it a valuable component in modern computing.
- It provides faster data retrieval due to its parallel searching capabilities.
- Associative memory reduces the need for complex algorithms to locate data, simplifying system design.
- It can handle large volumes of data efficiently, making it suitable for big data applications.
- Associative memory improves system performance by reducing latency in data access.
- It enhances the accuracy of pattern recognition systems, leading to better results in AI applications.
Challenges of Associative Memory
Despite its advantages, associative memory also faces some challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance.
- Associative memory can be more expensive to implement than traditional memory systems due to its complex design.
- It may consume more power, making it less suitable for energy-efficient applications.
- The size of associative memory can be limited by hardware constraints, affecting its scalability.
- Designing efficient associative memory systems requires specialized knowledge and expertise.
- It may not be suitable for all types of data, limiting its applicability in certain scenarios.
Future of Associative Memory
The future of associative memory looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at overcoming its challenges and expanding its applications.
- Advances in semiconductor technology are expected to reduce the cost and power consumption of associative memory.
- Researchers are exploring new materials and designs to improve the scalability of associative memory systems.
- Integration with emerging technologies like quantum computing could further enhance the capabilities of associative memory.
- Associative memory is likely to play a significant role in the development of next-generation AI and machine learning systems.
- Ongoing research aims to make associative memory more adaptable to different types of data, broadening its applicability.
Interesting Facts about Associative Memory
Here are some intriguing facts that highlight the unique aspects and history of associative memory.
- The first associative memory was developed in the 1960s by the Burroughs Corporation for use in their B5000 computer.
- Associative memory is sometimes referred to as "associative storage" or "associative array."
- It is used in DNA computing for solving complex problems through parallel processing.
- Associative memory can be implemented using various technologies, including SRAM, DRAM, and flash memory.
- It has applications in robotics for real-time decision-making and navigation.
Real-World Examples of Associative Memory
Associative memory is used in various real-world applications, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness.
- Google's search engine uses associative memory techniques to provide relevant search results quickly.
- Associative memory is used in financial trading systems for rapid analysis of market data.
- It is employed in medical imaging systems for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Associative memory is used in autonomous vehicles for real-time object recognition and navigation.
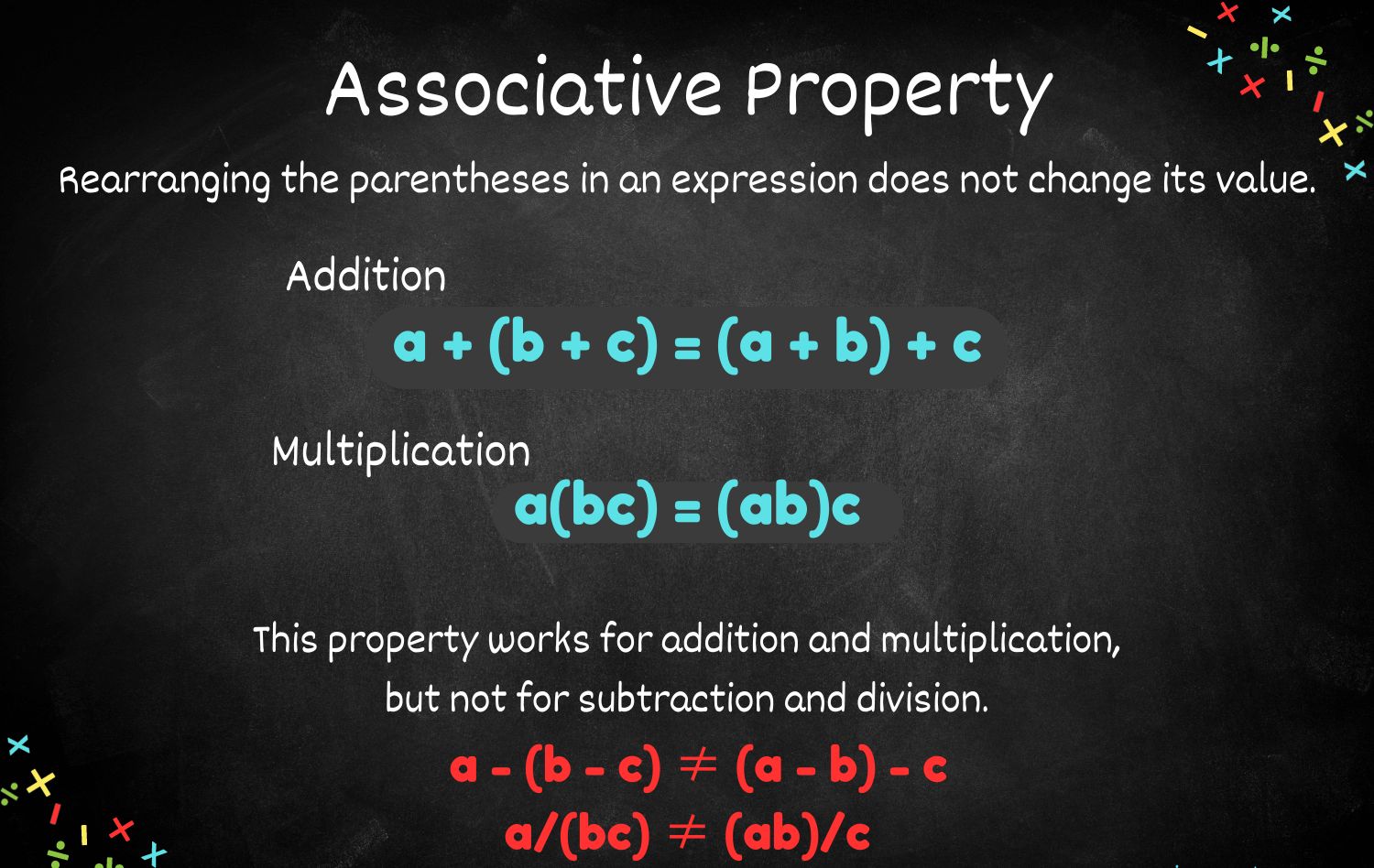
The Final Word on Associative Property
Understanding the associative property can make math a lot easier. It’s a simple yet powerful concept that helps solve problems faster. Whether you’re adding or multiplying, the way numbers are grouped doesn’t change the result. This property is a key building block in math, helping to simplify complex equations and making calculations more efficient.
Knowing these facts about the associative property can boost your math skills. It’s not just for students; even adults use it in everyday life without realizing. From balancing a checkbook to solving puzzles, the associative property is everywhere. Keep these facts in mind, and you’ll find math less intimidating and more manageable.
So, next time you’re faced with a tricky math problem, remember the associative property. It’s your secret weapon for making math a breeze.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
