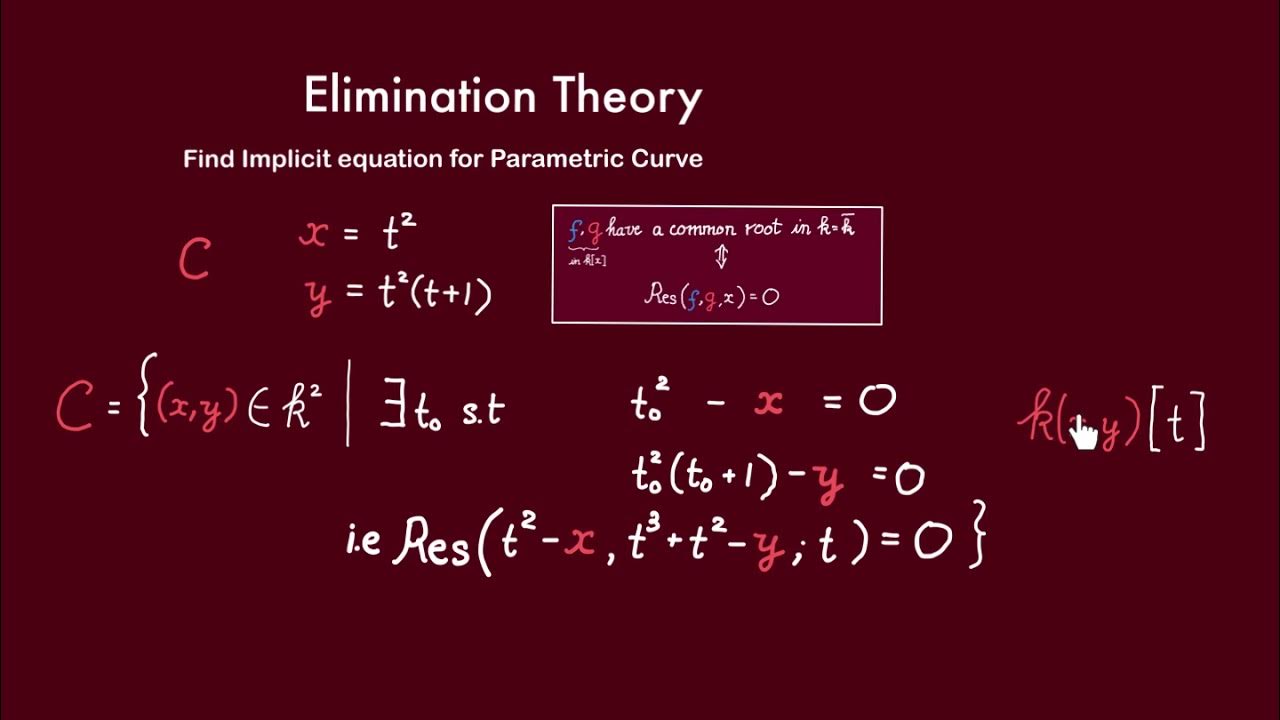
What is Elimination Theory? Elimination Theory is a branch of algebra that focuses on eliminating variables between polynomial equations. This mathematical concept helps solve systems of equations by reducing them to simpler forms. Why is it important? It plays a crucial role in fields like computer science, robotics, and cryptography. By understanding Elimination Theory, we can tackle complex problems more efficiently. How does it work? The process involves using techniques like resultants and Gröbner bases to systematically remove variables. Who uses it? Mathematicians, engineers, and scientists rely on Elimination Theory to simplify and solve intricate equations. Ready to dive into the fascinating world of Elimination Theory? Let's explore 39 intriguing facts that will deepen your understanding and appreciation of this essential mathematical tool.
What is Elimination Theory?
Elimination Theory is a branch of algebra that deals with eliminating variables from systems of polynomial equations. It's a powerful tool in mathematics, especially useful in solving complex problems.
-
Origin: Elimination Theory has roots in ancient mathematics, dating back to the works of Euclid and Diophantus.
-
Polynomial Equations: It primarily focuses on polynomial equations, which are equations involving variables raised to whole number powers.
-
Applications: Used in fields like computer science, robotics, and cryptography to solve systems of equations.
-
Groebner Bases: A key concept in Elimination Theory is Groebner bases, which help simplify polynomial systems.
-
Resultants: Another important tool is the resultant, a single polynomial derived from a system that helps eliminate variables.
-
Sylvester Matrix: Named after James Joseph Sylvester, this matrix is used to compute resultants.
-
Buchberger's Algorithm: This algorithm, developed by Bruno Buchberger, is essential for computing Groebner bases.
-
Intersection Theory: Elimination Theory is closely related to intersection theory in algebraic geometry.
-
Symbolic Computation: It plays a significant role in symbolic computation, which involves manipulating mathematical symbols rather than numbers.
-
Historical Development: The theory evolved significantly during the 19th century, thanks to mathematicians like Sylvester and Cayley.
Key Concepts in Elimination Theory
Understanding the core concepts is crucial for grasping Elimination Theory. These concepts form the foundation of the theory and its applications.
-
Variables: The unknowns in polynomial equations that Elimination Theory aims to eliminate.
-
Polynomials: Expressions involving variables and coefficients, combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents.
-
Systems of Equations: Sets of multiple polynomial equations that are solved simultaneously.
-
Algebraic Geometry: The study of geometric properties of solutions to polynomial equations, closely linked to Elimination Theory.
-
Ideal Theory: Involves studying sets of polynomials that share common solutions, known as ideals.
-
Zeroes of Polynomials: The values of variables that satisfy a polynomial equation, also known as roots.
-
Field Theory: The study of fields, which are algebraic structures where addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined.
-
Affine Space: A geometric structure that generalizes the properties of Euclidean space, used in algebraic geometry.
-
Projective Space: An extension of affine space that includes points at infinity, useful in solving polynomial equations.
-
Homogeneous Polynomials: Polynomials where all terms have the same total degree, often used in projective space.
Applications of Elimination Theory
Elimination Theory isn't just theoretical; it has practical applications in various fields. These applications demonstrate its versatility and importance.
-
Robotics: Used to solve kinematic equations for robot motion and control.
-
Computer Graphics: Helps in rendering 3D graphics by solving systems of polynomial equations.
-
Cryptography: Assists in designing and breaking cryptographic systems through algebraic methods.
-
Control Theory: Applied in designing control systems for engineering applications.
-
Signal Processing: Used in filtering and analyzing signals by solving polynomial equations.
-
Coding Theory: Helps in error detection and correction in digital communication systems.
-
Optimization: Used in finding optimal solutions to problems involving polynomial equations.
-
Economics: Assists in modeling and solving economic problems using polynomial equations.
-
Physics: Applied in solving equations related to physical phenomena.
-
Chemistry: Used in modeling chemical reactions and solving related equations.
Famous Mathematicians in Elimination Theory
Several mathematicians have made significant contributions to Elimination Theory. Their work has shaped the field and advanced our understanding.
-
Euclid: Ancient Greek mathematician who laid the groundwork for algebra.
-
Diophantus: Known as the "father of algebra," his work influenced Elimination Theory.
-
Isaac Newton: Developed methods for solving polynomial equations.
-
James Joseph Sylvester: Made significant contributions to matrix theory and resultants.
-
Arthur Cayley: Worked on algebraic geometry and polynomial equations.
-
Bruno Buchberger: Developed Buchberger's algorithm for computing Groebner bases.
-
David Hilbert: Made foundational contributions to algebraic geometry and polynomial theory.
-
Emmy Noether: Known for her work in abstract algebra and theoretical physics.
-
Alexander Grothendieck: Revolutionized algebraic geometry, influencing Elimination Theory.
Final Thoughts on Elimination Theory
Elimination theory isn't just for math geeks. It’s a powerful tool used in various fields like computer science, engineering, and even economics. By understanding how to eliminate variables, you can solve complex systems of equations more efficiently. This theory helps in simplifying problems, making them easier to tackle. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, grasping the basics of elimination theory can be incredibly beneficial. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about finding solutions in a logical, straightforward way. So next time you face a tricky problem, remember elimination theory might just be the key to cracking it. Keep exploring, keep learning, and you’ll find that even the most complicated problems can become manageable.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
