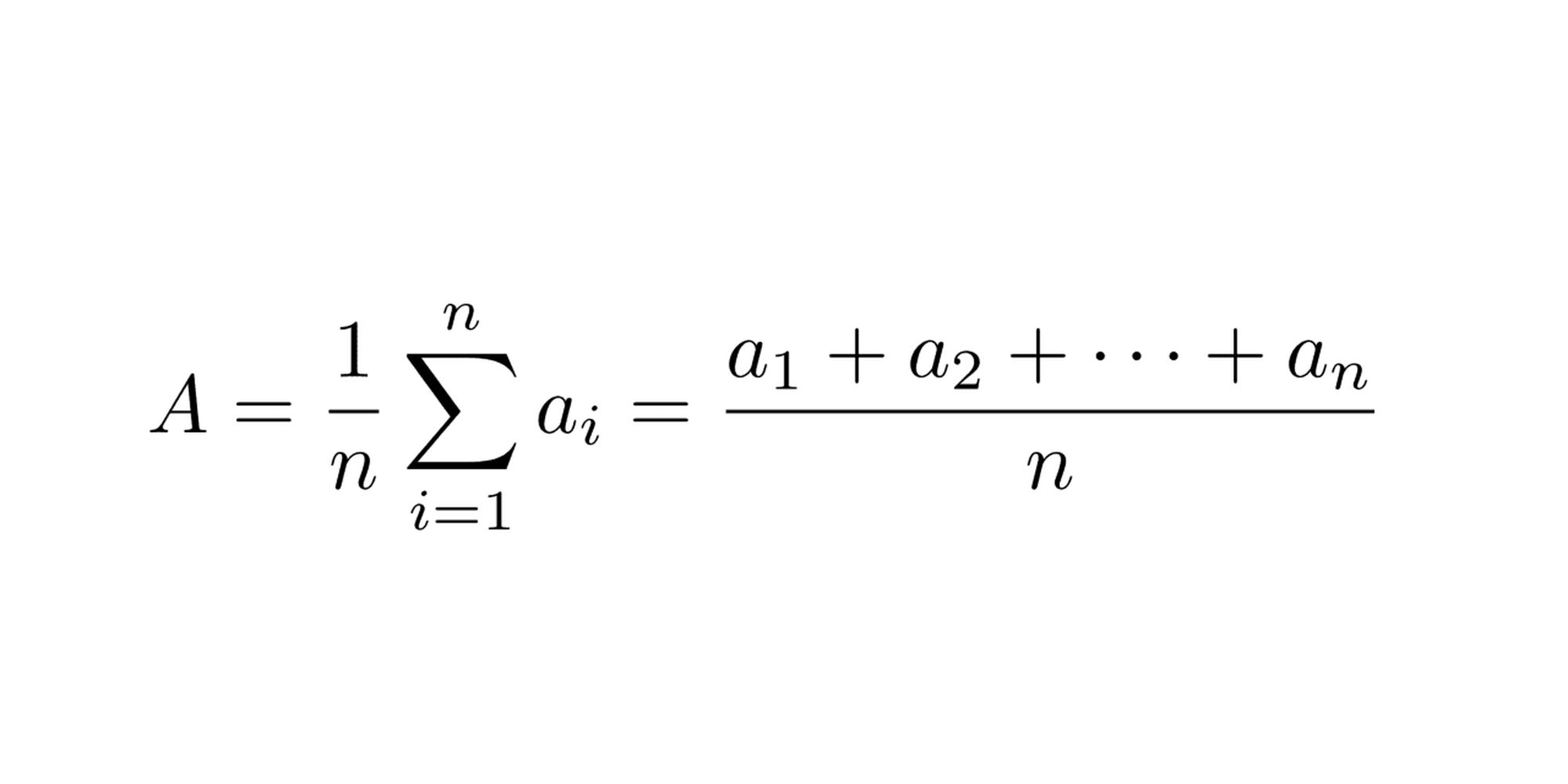
What is mean analysis? Mean analysis is a statistical method used to find the average value of a dataset. This technique helps in understanding the central tendency of data, making it easier to compare different datasets. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious about numbers, knowing how to calculate and interpret the mean can be incredibly useful. From sports statistics to financial reports, mean analysis plays a crucial role in various fields. In this blog post, we'll dive into 35 fascinating facts about mean analysis that will help you grasp its importance and application in everyday life.
What is Mean Analysis?
Mean analysis is a statistical method used to summarize a set of data points by finding their average. This technique helps in understanding the central tendency of the data, making it easier to compare different datasets.
- The mean is calculated by adding all the numbers in a dataset and then dividing by the number of data points.
- Mean analysis is often referred to as average or arithmetic mean.
- It is one of the most commonly used measures in descriptive statistics.
- Mean analysis helps in identifying trends and patterns within data.
- It is widely used in various fields, including economics, psychology, and sociology.
Types of Mean
There are different types of means used in statistics, each serving a unique purpose. Understanding these types can help in choosing the right one for your analysis.
- The arithmetic mean is the most common type, calculated by summing all values and dividing by the count.
- The geometric mean is used for datasets with values that multiply together, like growth rates.
- The harmonic mean is useful for rates and ratios, such as speed or density.
- The quadratic mean, or root mean square, is used in physics and engineering for varying quantities.
- The weighted mean accounts for the importance of each value in the dataset.
Applications of Mean Analysis
Mean analysis is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various domains. Here are some real-world uses.
- In finance, mean analysis helps in calculating average returns on investments.
- Healthcare professionals use it to determine average patient recovery times.
- Education systems employ mean analysis to find average test scores.
- In sports, it helps in calculating average performance metrics like batting averages.
- Marketing teams use it to analyze average customer spending.
Advantages of Mean Analysis
Mean analysis offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for data summarization. Here are some of its advantages.
- It provides a simple and quick summary of data.
- Mean analysis is easy to understand and interpret.
- It is useful for comparing different datasets.
- The mean is sensitive to every data point, making it a comprehensive measure.
- It helps in identifying outliers and anomalies in data.
Limitations of Mean Analysis
Despite its advantages, mean analysis has some limitations. Being aware of these can help in making better analytical decisions.
- The mean is sensitive to extreme values or outliers.
- It may not represent the data accurately if the dataset is skewed.
- Mean analysis does not provide information about the spread or variability of data.
- It can be misleading for categorical data.
- The mean is not suitable for ordinal data, where the order matters but not the exact values.
Mean vs. Median and Mode
Mean, median, and mode are all measures of central tendency, but they serve different purposes. Understanding their differences can enhance your data analysis skills.
- The median is the middle value in a dataset, useful for skewed distributions.
- The mode is the most frequently occurring value, helpful for categorical data.
- Unlike the mean, the median is not affected by outliers.
- The mode can be used for both numerical and categorical data.
- Mean analysis is best for symmetrical distributions, while median and mode are better for skewed distributions.
Historical Background of Mean Analysis
Understanding the history of mean analysis can provide context for its development and usage. Here are some historical facts.
- The concept of the mean dates back to ancient Greece, used by mathematicians like Pythagoras.
- The term "arithmetic mean" was first used in the 17th century.
- Karl Pearson, a British mathematician, popularized the use of mean in statistics.
- Mean analysis became widely used in the 20th century with the advent of computers.
- Today, mean analysis is a fundamental concept taught in introductory statistics courses worldwide.
Final Thoughts on Mean Analysis
Mean analysis, often called the average, is a powerful tool in statistics. It helps us understand data sets by providing a single value that represents the center of the data. This method is used in various fields like economics, sports, and education to make informed decisions. Knowing how to calculate and interpret the mean can offer valuable insights into trends and patterns.
While the mean is useful, it’s not always the best measure for every situation. Outliers can skew the results, making it less reliable for data with extreme values. In such cases, other measures like the median or mode might be more appropriate.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of mean analysis can help you better analyze data and make smarter decisions. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, mastering this concept can be incredibly beneficial.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
