Location Theory is a fascinating field that explores how economic activities are distributed across geographical spaces. Ever wondered why certain businesses cluster together or why cities develop in specific areas? Location Theory holds the answers. It examines factors like transportation costs, land prices, and market accessibility to explain these patterns. From the placement of factories to the rise of urban centers, this theory provides a framework for understanding economic geography. Whether you're curious about why tech companies flock to Silicon Valley or how retail stores choose their locations, Location Theory offers intriguing insights. Ready to dive into 31 captivating facts about this essential subject? Let's get started!
What is Location Theory?
Location Theory explores why businesses and people choose specific locations. It examines factors like transportation, resources, and costs. Here are some fascinating facts about this intriguing subject.
-
Origin: Location Theory began with Johann Heinrich von Thünen in the early 19th century. He studied agricultural land use and its relation to market distance.
-
Central Place Theory: Walter Christaller introduced this concept in 1933. It explains how cities and towns are distributed and why they form certain patterns.
-
Hotelling's Law: Harold Hotelling proposed that businesses tend to cluster together. This is known as the principle of minimum differentiation.
-
Weber's Theory: Alfred Weber focused on industrial location. He believed businesses choose locations to minimize transportation and labor costs.
-
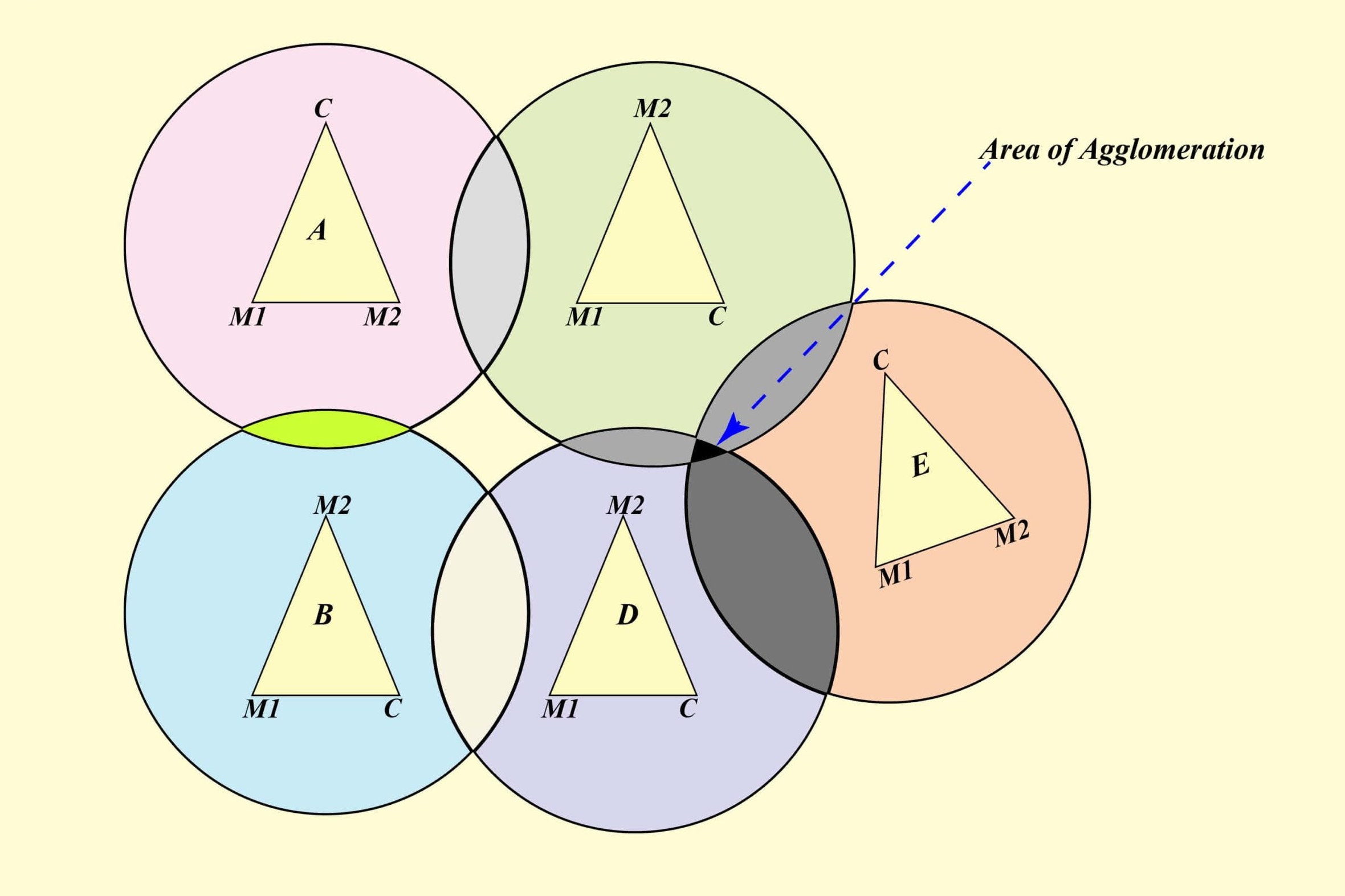
Agglomeration Economies: This concept explains why businesses benefit from being close to each other. It leads to reduced costs and increased innovation.
-
Spatial Interaction: This term refers to the flow of goods, people, and information between locations. It’s a key element in understanding location choices.
-
Bid-Rent Theory: This theory suggests that land value decreases as you move away from the central business district. It helps explain urban land use patterns.
-
Von Thünen Rings: Von Thünen's model includes concentric rings around a city. Each ring represents different types of agricultural activities based on distance from the market.
-
Isodapanes: These are lines on a map showing equal transportation costs. They help businesses decide where to locate based on cost efficiency.
-
Footloose Industries: Some industries, like tech companies, are not tied to specific locations. They can operate anywhere with good infrastructure.
Factors Influencing Location Choices
Several factors influence why businesses and people choose certain locations. These factors can vary widely depending on the industry and individual preferences.
-
Transportation Costs: High transportation costs can deter businesses from locating far from their markets.
-
Labor Availability: Access to skilled labor is crucial for many industries. Areas with a high concentration of skilled workers are often more attractive.
-
Resource Availability: Natural resources like minerals, water, and timber can significantly influence location decisions.
-
Market Proximity: Being close to a large market can reduce transportation costs and increase sales opportunities.
-
Government Policies: Tax incentives, subsidies, and regulations can make certain locations more appealing.
-
Infrastructure: Good roads, ports, and communication networks are essential for many businesses.
-
Climate: Some industries, like agriculture and tourism, are heavily influenced by climate conditions.
-
Land Costs: High land prices can deter businesses from locating in certain areas.
-
Quality of Life: Areas with good schools, healthcare, and recreational facilities attract both businesses and residents.
-
Competition: The presence of competitors can either deter or attract businesses, depending on the industry.
Real-World Applications
Location Theory isn't just academic; it has real-world applications that impact everyday life and business decisions.
-
Retail Location: Retailers use Location Theory to choose store sites that maximize foot traffic and sales.
-
Urban Planning: City planners use these principles to design efficient and livable urban areas.
-
Logistics: Companies like Amazon use Location Theory to optimize their distribution networks.
-
Real Estate: Real estate developers use these concepts to determine the best locations for new projects.
-
Public Services: Governments use Location Theory to decide where to build schools, hospitals, and other public services.
-
Environmental Impact: Understanding location choices can help minimize environmental damage by reducing transportation needs.
-
Tourism: Tourist destinations are often chosen based on their accessibility and attractiveness, both of which are influenced by Location Theory.
-
Manufacturing: Factories are often located near raw materials or markets to minimize costs.
-
Technology Hubs: Areas like Silicon Valley are examples of how agglomeration economies can create tech hubs.
-
Agriculture: Farmers use Location Theory to decide what crops to plant based on soil quality and market distance.
-
Globalization: As the world becomes more interconnected, Location Theory helps explain the shifting patterns of global trade and investment.
The Final Word on Location Theory
Location theory isn't just for academics. It shapes our daily lives, from where we shop to how cities grow. Understanding location theory helps us see why businesses cluster in certain areas and why some neighborhoods thrive while others don't. It's all about finding the best spot to maximize success, whether for a new coffee shop or a tech startup.
By grasping these concepts, we can make smarter decisions about where to live, work, and invest. So next time you wonder why a store opened on one corner and not another, remember, there's a whole theory behind it. Location theory gives us the tools to understand and predict these patterns, making it a powerful part of economics and urban planning. Keep these facts in mind, and you'll start seeing the world in a whole new way.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
