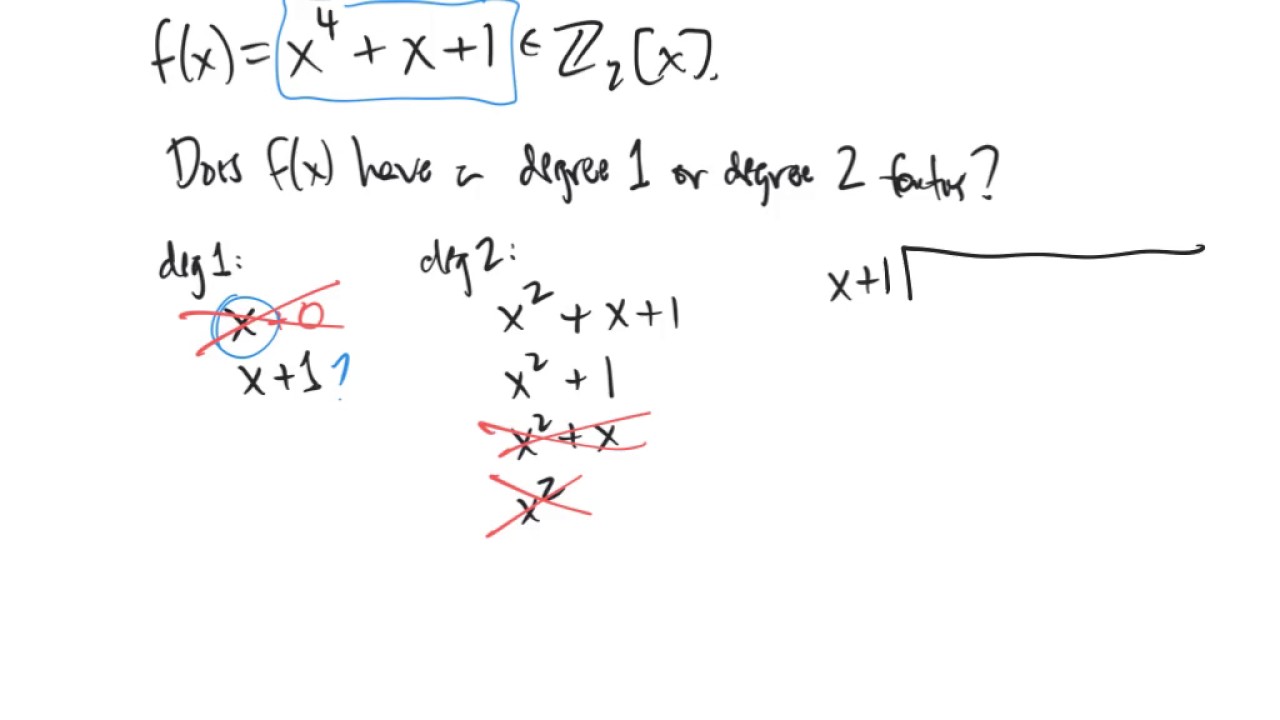
What are irreducible polynomials? Simply put, irreducible polynomials are polynomials that cannot be factored into the product of two non-constant polynomials. Think of them as the prime numbers of the polynomial world. Just like prime numbers, they play a crucial role in various areas of mathematics, including algebra and number theory. Understanding these special polynomials can help in solving complex equations, cryptography, and even coding theory. Ready to dive into the world of irreducible polynomials? Let's explore 30 fascinating facts that will make you appreciate their importance and uniqueness.
What is Irreducible Complexity?
Irreducible complexity is a concept in biology that suggests certain biological systems cannot evolve through successive small modifications. These systems are so complex that removing one part would cause the entire system to fail. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this intriguing idea.
-
Origin of the Term: The term "irreducible complexity" was coined by biochemist Michael Behe in his 1996 book, "Darwin's Black Box."
-
Mouse Trap Analogy: Behe used a simple mouse trap to explain irreducible complexity. A mouse trap has several parts, and removing any one of them renders it useless.
-
Flagellum Example: The bacterial flagellum, a whip-like structure used for movement, is often cited as an example of an irreducibly complex system.
-
Blood Clotting Cascade: The process of blood clotting involves a complex cascade of events. Removing any one component can prevent clotting, making it another example of irreducible complexity.
-
Criticism from Scientists: Many scientists criticize the concept, arguing that what appears irreducibly complex can often be explained through evolutionary processes.
Examples in Nature
Irreducible complexity isn't just a theoretical concept; it has real-world examples. Here are some intriguing instances found in nature.
-
Eye Structure: The human eye, with its intricate parts working together, is often cited as an example of irreducible complexity.
-
Cilium Function: Cilia are tiny hair-like structures that move fluid across cell surfaces. They require multiple proteins to function, making them irreducibly complex.
-
Immune System: The immune system's ability to recognize and fight pathogens involves numerous components working in harmony.
-
Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light into energy involves a series of complex reactions that are interdependent.
-
DNA Replication: The replication of DNA involves multiple enzymes and proteins, each essential for the process to occur.
Controversies and Debates
Irreducible complexity has sparked numerous debates in the scientific community. Here are some key points of contention.
-
Evolutionary Pathways: Critics argue that complex systems can evolve through co-option, where existing parts acquire new functions.
-
Intelligent Design: Proponents of irreducible complexity often use it to support the idea of intelligent design, suggesting that such systems must have been designed by a higher intelligence.
-
Scientific Acceptance: The majority of the scientific community does not accept irreducible complexity as a valid argument against evolution.
-
Peer-Reviewed Research: Many studies have been published attempting to refute or support the concept, leading to ongoing debates.
-
Legal Battles: Irreducible complexity has been a focal point in legal battles over the teaching of intelligent design in schools.
Historical Perspectives
Understanding the history behind irreducible complexity can provide context for its current status in scientific discussions.
-
Pre-Darwinian Ideas: Before Darwin, many naturalists believed in the idea of complex systems being designed.
-
Darwin's Challenge: Charles Darwin himself acknowledged the challenge posed by complex organs to his theory of evolution.
-
Modern Synthesis: The modern synthesis of evolutionary biology incorporates genetics, providing explanations for the evolution of complex systems.
-
Behe's Influence: Michael Behe's work brought irreducible complexity into the public eye, sparking renewed interest and debate.
-
Educational Impact: The concept has influenced how some educational systems approach the teaching of evolution and intelligent design.
Scientific Investigations
Scientific investigations into irreducible complexity have yielded fascinating insights. Here are some notable findings.
-
Molecular Machines: Research into molecular machines like the ribosome has provided insights into their complexity and evolution.
-
Gene Duplication: Studies show that gene duplication can lead to new functions, potentially explaining the evolution of complex systems.
-
Experimental Evolution: Experiments with bacteria and other organisms have demonstrated how complex traits can evolve over time.
-
Comparative Genomics: Comparing genomes of different species has revealed how complex systems can arise through gradual changes.
-
Protein Interactions: Research into protein interactions has shown how new functions can emerge from existing components.
Philosophical Implications
Irreducible complexity also has philosophical implications, particularly in the realms of science and religion.
-
Teleology: The concept raises questions about teleology, the idea that natural phenomena have purpose or design.
-
Naturalism vs. Supernaturalism: Debates over irreducible complexity often touch on broader philosophical issues like naturalism and supernaturalism.
-
Epistemology: The discussion also involves epistemology, the study of knowledge and how we come to understand complex systems.
-
Ethics in Science: The controversy has led to discussions about the ethics of scientific research and education.
-
Public Perception: Irreducible complexity has influenced public perception of science, particularly in the context of evolution and intelligent design.
Final Thoughts on Irreducible Complexity
Irreducible complexity sparks curiosity and debate. Whether you’re a student, a scientist, or just someone who loves learning, understanding this concept can change how you see the world. It challenges us to think about the origins of life, the intricacies of biology, and the limits of scientific explanation.
Some see it as evidence of intelligent design, while others argue it’s a natural outcome of evolution. Either way, it’s a fascinating topic that encourages critical thinking. Keep exploring, questioning, and learning. The more you know, the more you’ll appreciate the wonders of life.
Remember, science is all about asking questions and seeking answers. Irreducible complexity is just one piece of the puzzle. Stay curious and never stop exploring the mysteries of our incredible world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
