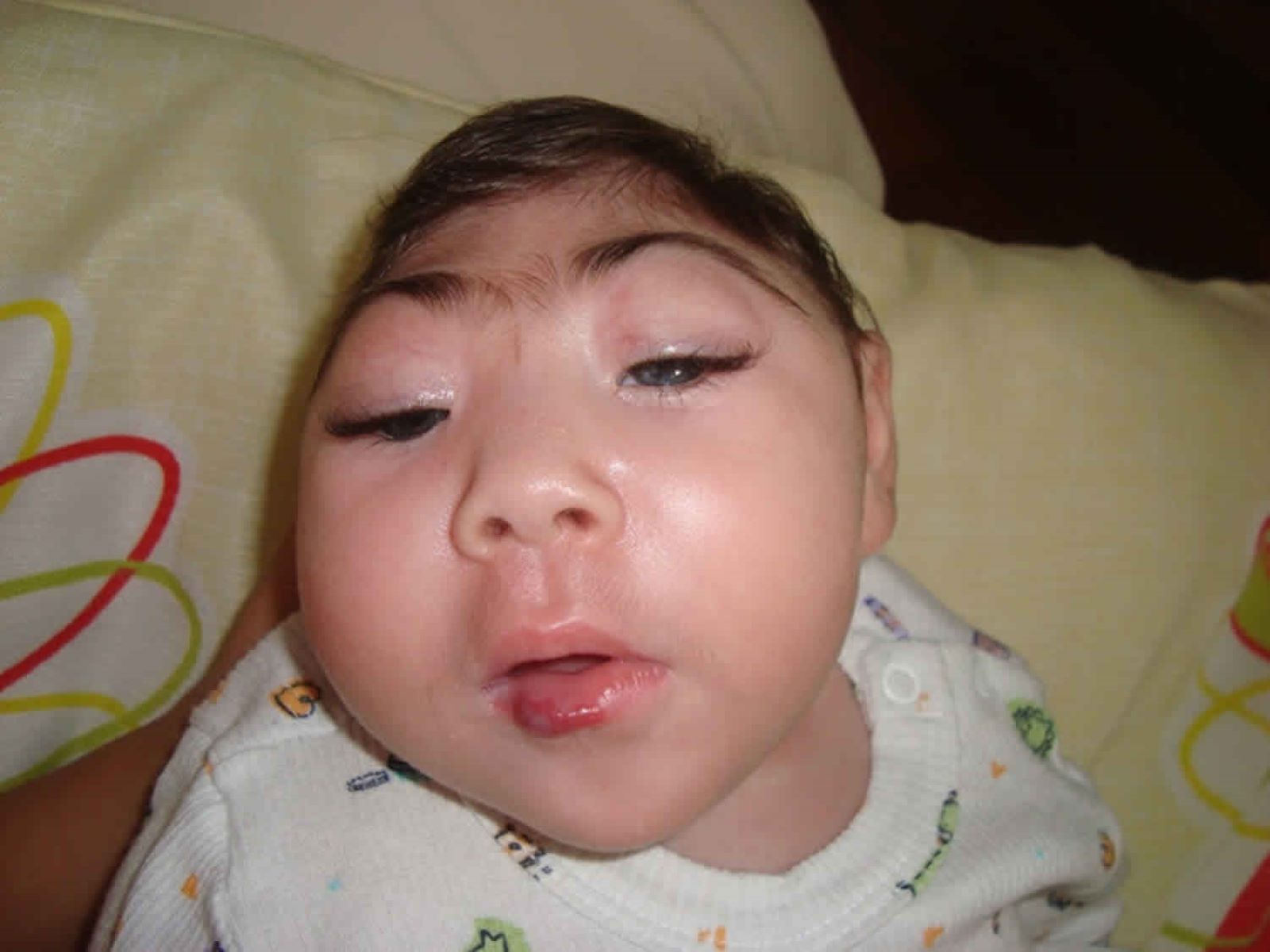
Anencephaly is a rare but serious birth defect where a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull. This condition happens during the early stages of pregnancy when the neural tube, which forms the brain and spinal cord, doesn't close properly. Babies with anencephaly are often stillborn or die shortly after birth. Understanding anencephaly can help families prepare and make informed decisions. This article will cover 50 essential facts about anencephaly, from causes and symptoms to diagnosis and support options. Whether you're a parent, caregiver, or simply curious, these facts will provide a comprehensive overview of this challenging condition.
Understanding Anencephaly
Anencephaly is a serious birth defect where a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull. This condition happens during the early stages of pregnancy and affects the development of the neural tube. Here are some important facts about anencephaly.
- Anencephaly occurs when the upper part of the neural tube fails to close.
- This condition is usually detected during pregnancy through ultrasound.
- Babies with anencephaly are often born without the forebrain.
- The remaining parts of the brain are not covered by bone or skin.
- Anencephaly is a type of neural tube defect (NTD).
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in prevention and early detection. Here are some key points about what might contribute to anencephaly.
- The exact cause of anencephaly is unknown.
- Genetic factors may play a role in the development of anencephaly.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals, can increase the risk.
- A lack of folic acid during pregnancy is a significant risk factor.
- Women with diabetes have a higher risk of having a baby with anencephaly.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition and preparing for the birth. Here are some ways anencephaly can be detected.
- Anencephaly can be diagnosed through prenatal screening tests.
- Ultrasound is the most common method for detecting anencephaly.
- Blood tests can also indicate the presence of neural tube defects.
- Amniocentesis is another diagnostic tool used to detect anencephaly.
- High levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the mother's blood may suggest anencephaly.
Symptoms and Physical Characteristics
Babies with anencephaly have distinct physical characteristics and symptoms. Here are some of the most common ones.
- Babies with anencephaly are usually born blind.
- They often have missing parts of the skull.
- The brain tissue is exposed due to the lack of skull bones.
- Babies with anencephaly may have a cleft palate.
- They often have abnormal facial features.
Life Expectancy and Quality of Life
Anencephaly significantly affects life expectancy and quality of life. Here are some important facts about what to expect.
- Most babies with anencephaly are stillborn.
- Those who are born alive usually survive only a few hours to days.
- There is no cure or standard treatment for anencephaly.
- Palliative care is often provided to keep the baby comfortable.
- Families may choose to donate the baby's organs for research.
Prevention and Prenatal Care
Preventing anencephaly involves taking certain precautions before and during pregnancy. Here are some tips for reducing the risk.
- Taking folic acid supplements before and during pregnancy can reduce the risk.
- Women should start taking folic acid at least one month before conception.
- A daily intake of 400 micrograms of folic acid is recommended.
- Avoiding harmful substances, like alcohol and drugs, can lower the risk.
- Regular prenatal check-ups are essential for early detection.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The diagnosis of anencephaly can have a profound emotional and psychological impact on families. Here are some aspects to consider.
- Parents may experience grief and loss upon diagnosis.
- Support groups can provide emotional support and resources.
- Counseling can help families cope with the diagnosis.
- Some parents find comfort in creating memories with their baby.
- Siblings may also need support to understand and cope with the situation.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research aims to better understand and manage anencephaly. Here are some recent advances and areas of study.
- Researchers are studying the genetic factors involved in anencephaly.
- Advances in prenatal screening are improving early detection.
- Studies are exploring the role of environmental factors in neural tube defects.
- Research on folic acid supplementation continues to provide insights.
- Scientists are investigating potential treatments and interventions.
Support and Resources
Various organizations and resources are available to support families affected by anencephaly. Here are some helpful options.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers information on anencephaly.
- The March of Dimes provides resources for families dealing with birth defects.
- Support groups like Anencephaly.info offer community and information.
- Genetic counseling can help families understand the risk of recurrence.
- Online forums and social media groups provide a platform for sharing experiences.
Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about anencephaly can help in prevention and support. Here are some ways to spread the word.
- Participating in awareness campaigns can educate the public.
- Sharing personal stories can help others understand the impact of anencephaly.
- Supporting research organizations can contribute to finding solutions.
- Educating pregnant women about the importance of folic acid is crucial.
- Advocacy can lead to better healthcare policies and support for affected families.
Understanding Anencephaly
Anencephaly is a serious birth defect where a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull. This condition happens early in pregnancy when the neural tube, which forms the brain and spine, doesn't close properly. Babies with anencephaly are usually blind, deaf, unconscious, and unable to feel pain. Sadly, most don't survive long after birth.
Awareness and education about anencephaly are crucial. Knowing the facts can help expectant parents make informed decisions and seek appropriate medical care. Folic acid intake before and during early pregnancy can reduce the risk of neural tube defects, including anencephaly.
Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support for families affected by this condition. While there's no cure, ongoing research aims to understand and prevent anencephaly better. By spreading knowledge, we can offer hope and support to those facing this challenging diagnosis.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


