What is Choroideremia? Choroideremia is a rare, inherited eye disorder that causes progressive vision loss, primarily affecting males. This condition stems from mutations in the CHM gene, which disrupts normal cellular functions in the retina, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and choroid. How does it manifest? Early symptoms often include night blindness and peripheral vision loss, eventually leading to central vision deterioration. Why is it significant? Understanding choroideremia is crucial because there are currently no approved treatments, making ongoing research and awareness vital. Who is affected? While males are predominantly impacted due to the X-linked recessive inheritance pattern, female carriers can also exhibit mild symptoms. What are the current research directions? Promising therapies like gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and retinal prostheses are under investigation, offering hope for future treatments.
Key Takeaways:
- Choroideremia is a rare eye disorder primarily affecting males, leading to progressive vision loss. Genetic testing and imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosis and monitoring the disease.
- Coping strategies, regular eye exams, and participation in clinical trials offer hope for managing choroideremia and improving quality of life. Counseling for mental health and genetics is essential for individuals and their families.
What is Choroideremia?
Choroideremia is a rare eye disorder that leads to progressive vision loss. It primarily affects males and is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. Let's dive into the details.
- Choroideremia affects approximately 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 100,000 people.
- It is an X-linked recessive disease, meaning it predominantly affects males.
- The disorder is caused by mutations in the CHM gene.
- The CHM gene encodes the Rab escort protein 1 (REP1).
How Does Choroideremia Develop?
Understanding the pathogenesis of choroideremia helps in grasping how the disease progresses and affects vision.
- Dysfunctional REP1 leads to accumulated unprenylated Rabs.
- This dysfunction causes abnormal photoreceptor outer segment phagocytosis.
- Ineffective melanosome transport within the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) results in cell death.
- Progressive degeneration of the retina and choroid occurs over time.
Clinical Features of Choroideremia
The clinical features of choroideremia can vary, but there are common symptoms that most patients experience.
- Male patients typically experience progressive reduction in visual acuity.
- The initial symptom is often night blindness (nyctalopia).
- Night blindness can appear in teenage years.
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision follows.
- Central vision loss occurs in later adulthood.
Symptoms in Female Carriers
Female carriers of the CHM gene may also exhibit symptoms, though usually milder than in males.
- Female carriers often remain asymptomatic.
- Some may experience mild symptoms like night blindness.
- Pigmentary changes in the fundus oculi can occur.
- Female carriers have a 50% chance of passing the faulty gene to their offspring.
Diagnosing Choroideremia
Diagnosing choroideremia involves a combination of genetic testing and clinical evaluation.
- Diagnosis is primarily based on genetic testing.
- Specific mutations in the CHM gene can be identified through DNA sequencing.
- Clinical features such as night blindness and visual field constriction support the diagnosis.
- Imaging techniques like optical coherence tomography (OCT) help monitor disease progression.
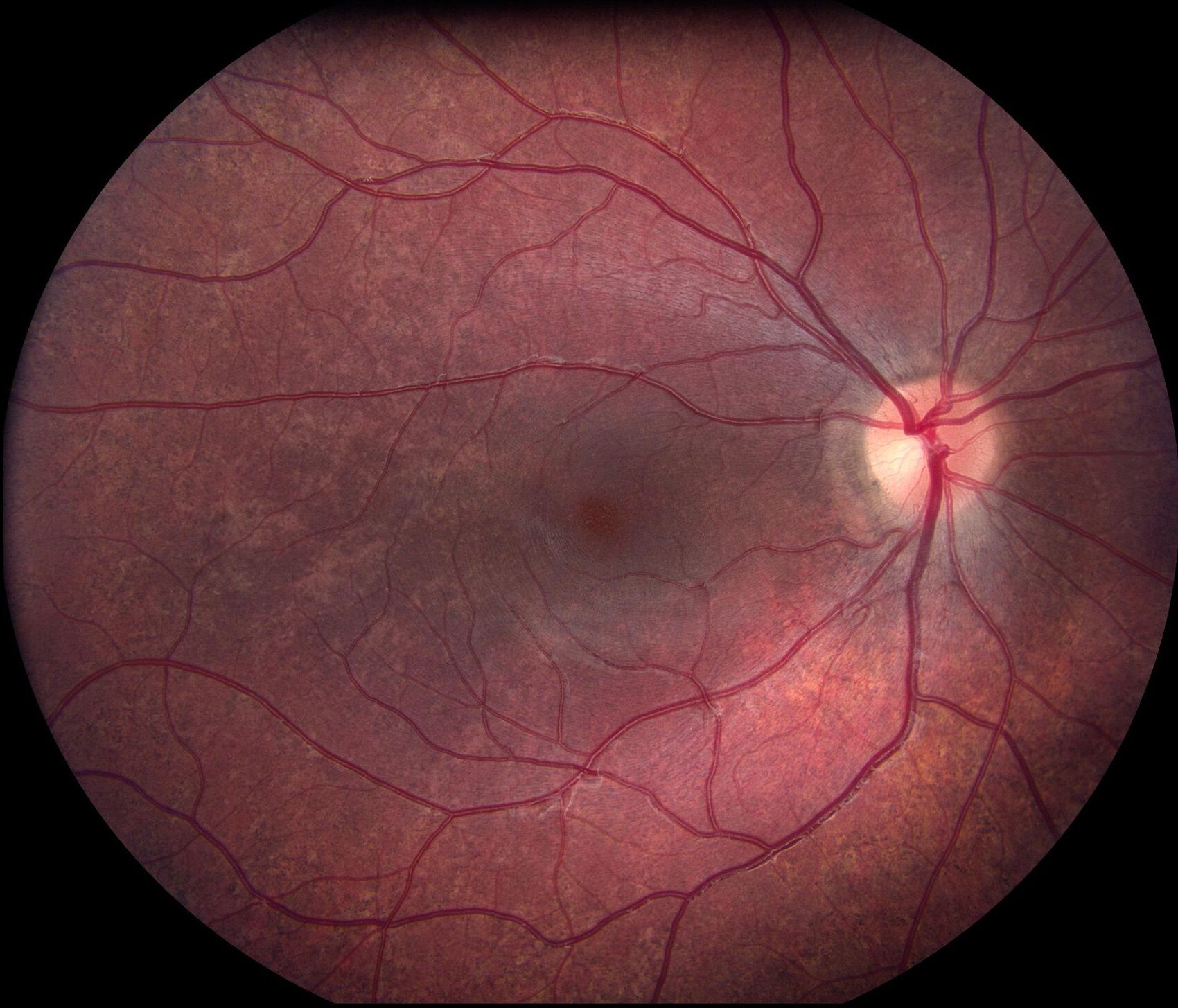
Imaging Techniques for Choroideremia
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring choroideremia.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) measures central macular thickness (CMT).
- OCT also measures subfoveal choroidal thickness (SCT).
- Areas of preserved choriocapillaris (CC), ellipsoid zone (EZ), and autofluorescence (PAF) are assessed.
- OCT angiography visualizes vascular abnormalities in the eye.
Functional Investigations
Functional investigations help assess the impact of choroideremia on vision.
- Visual acuity (VA) tests measure clarity of vision.
- Contrast sensitivity (CS) tests evaluate the ability to distinguish between different shades.
- Color testing assesses color discrimination.
- Microperimetry measures retinal sensitivity.
- Dark adaptometry tests evaluate the ability to adapt to low light.
- Handheld electroretinogram (ERG) measures electrical activity in the retina.
Quality-of-Life Assessment
Assessing the quality of life for individuals with choroideremia is essential for comprehensive care.
- The NEI-VFQ-25 questionnaire evaluates vision-related quality of life.
- This tool assesses general health, vision profile, and ocular pain.
- It also measures dependency and emotional well-being.
Current Treatment Options
While there are no approved treatments for choroideremia, several promising approaches are under investigation.
- Gene therapy aims to correct the genetic mutation by introducing a healthy copy of the CHM gene.
- Stem cell therapy could potentially replace damaged retinal cells.
- Small molecules like ataluren and PTC-414 are being investigated for nonsense suppression therapy.
- Retinal prostheses are being developed to bypass damaged photoreceptors and stimulate the retina.
Challenges in Management
Managing choroideremia involves addressing the lack of approved treatments and focusing on coping strategies.
- Current management focuses on coping strategies like using magnifiers.
- Counseling for mental health and genetics is essential.
- Participating in clinical trials for emerging treatments offers hope.
Coping Strategies
Coping strategies help individuals with choroideremia adapt to their progressive vision loss.
- Using low vision aids like magnifiers can improve daily functioning.
- Assistive technology helps maintain independence.
- Seeking counseling for mental health and genetic counseling is crucial.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are vital for monitoring disease progression and managing symptoms effectively.
- Early detection through regular eye exams can improve quality of life.
Understanding Choroideremia
Choroideremia is a rare, progressive eye disorder that primarily affects males due to its X-linked recessive inheritance. It results from mutations in the CHM gene, leading to the degeneration of the retina, retinal pigment epithelium, and choroid. Symptoms often start with night blindness in teenage years, followed by a gradual loss of peripheral vision and eventual central vision loss. Diagnosis relies on genetic testing, supported by imaging techniques like OCT and FAF.
Currently, no approved treatments exist, but promising therapies like gene therapy, stem cell therapy, and retinal prostheses are under investigation. Regular eye exams, genetic counseling, and emotional support are crucial for managing the condition. Ongoing research aims to develop effective treatments and improve the quality of life for those affected. Understanding choroideremia's genetic basis and clinical features is key to better management and future advancements in treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


