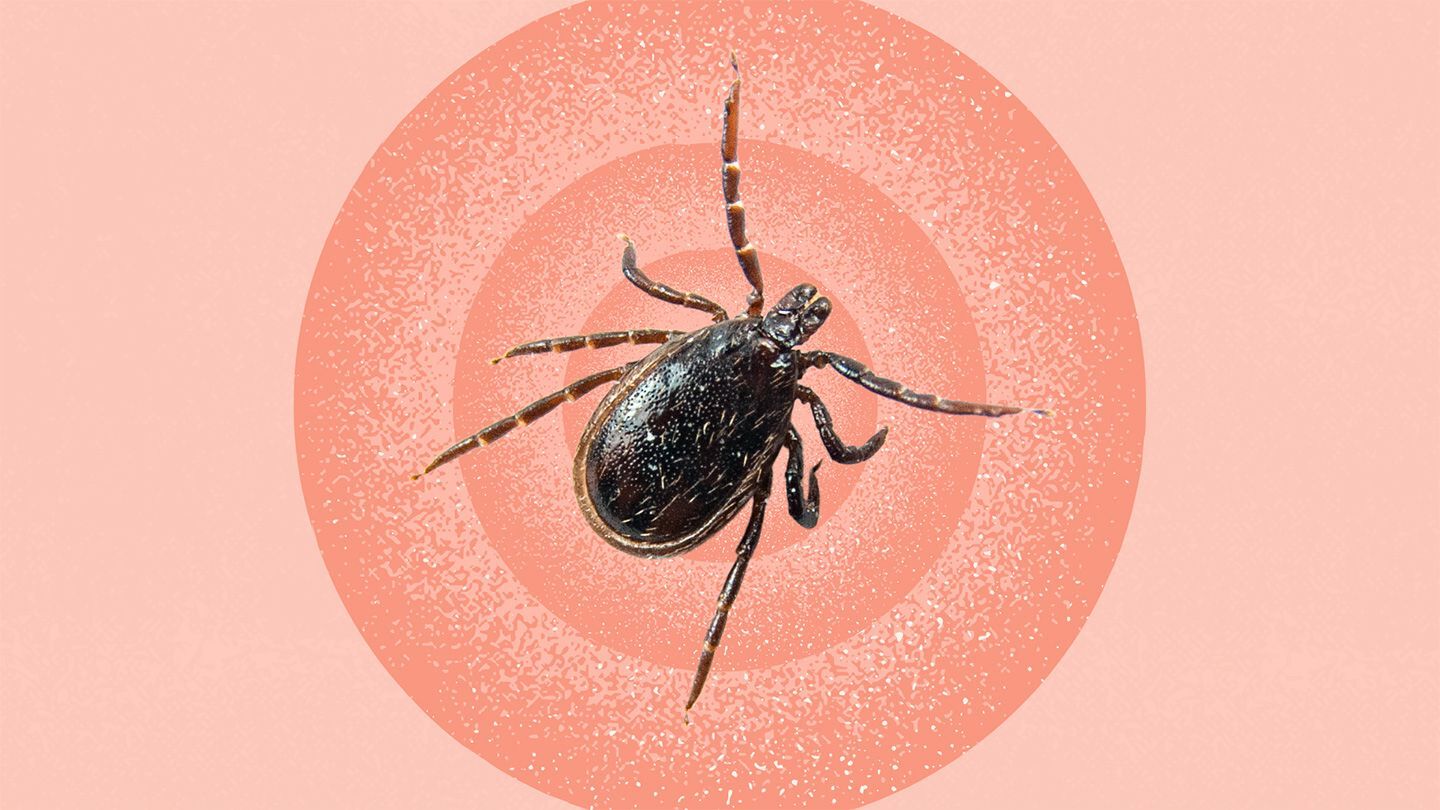
What is babesiosis? Babesiosis is a tick-borne disease caused by microscopic parasites of the genus Babesia. These parasites infect red blood cells, leading to a range of symptoms from mild to severe. Found worldwide, babesiosis is most common in the northeastern and upper Midwestern United States. The primary culprit in the U.S. is Babesia microti, transmitted mainly through the bite of infected blacklegged or deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis). Symptoms often resemble the flu, including fever, chills, and fatigue. While many people may not show symptoms, the disease can be severe, especially for older adults or those with weakened immune systems.
What is Babesiosis?
Babesiosis is a tick-borne disease caused by microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells. This infection can range from mild to severe, and understanding its intricacies is crucial for prevention and treatment.
-
Definition: Babesiosis is caused by Babesia parasites, primarily transmitted through the bite of infected ticks, particularly the blacklegged or deer tick (Ixodes scapularis).
-
Prevalence: This disease is most common in the northeastern and upper Midwestern United States, though it can be found worldwide.
-
Causes: The most common cause in the U.S. is Babesia microti. Other species like Babesia divergens can infect humans, especially in Europe.
How is Babesiosis Transmitted?
Understanding how babesiosis spreads helps in taking preventive measures. The primary mode of transmission is through tick bites, but there are other ways the disease can spread.
-
Transmission: Primarily through infected tick bites, but also possible via blood transfusions and from mother to child during pregnancy or birth.
-
Tick Identification: The blacklegged or deer tick is the main vector in the U.S. These ticks are found in wooded, brushy, or grassy areas.
-
Transmission Cycle: Ticks become infected by feeding on animals with the parasite and can then transmit it to humans.
Symptoms of Babesiosis
Symptoms can vary widely, from none at all to severe illness. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely treatment.
-
Symptoms: Many people show no symptoms, but those who do may experience fever, chills, sweats, headache, body aches, loss of appetite, nausea, and fatigue.
-
Symptom Onset: Symptoms usually appear 1 week to a few months after a tick bite, making diagnosis challenging.
-
Hemolytic Anemia: The parasites destroy red blood cells, leading to hemolytic anemia, which can cause severe complications.
Who is at Risk?
Certain groups are more susceptible to severe babesiosis. Knowing the risk factors can help in taking extra precautions.
-
Risk Factors: Older adults (over 50) and immunocompromised individuals are at higher risk. People without a spleen are also more vulnerable.
-
Pediatric Cases: Most cases occur in adults, but children can also be affected, especially through blood transfusions.
-
Aging and Immunity: Aging alters the immune system's ability to resist B. microti infection, increasing the risk of severe disease.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial for managing babesiosis. Various methods are used to detect the infection and treat it.
-
Diagnosis: Involves examining a blood sample under a microscope, PCR tests for Babesia DNA, and serological tests for antibodies.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Advances in tests have increased sensitivity, making it easier to detect the parasites.
-
Treatment: Typically involves a combination of two drugs for 7 to 10 days. Common treatments include atovaquone and azithromycin, or clindamycin and quinine.
Preventing Babesiosis
Prevention is the best strategy against babesiosis. Taking steps to avoid tick bites can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
-
Prevention: Avoid tick-infested areas, use tick repellents, wear protective clothing, and check for ticks after being outdoors.
-
Tick Habitat: Ticks are most active from late spring through early fall and are commonly found in wooded or brushy areas.
-
Tick Removal: Remove ticks with fine-tipped tweezers, pulling straight up to ensure all parts are removed. Clean the bite area with soap and water or antiseptic.
Geographic Distribution and Historical Context
Babesiosis has a specific geographic distribution and a rich history. Understanding where it is most common and its historical background can provide context.
-
Geographic Distribution: Most common in the northeastern and upper Midwestern U.S., but cases have been reported in Europe and other parts of the world.
-
Historical Context: Documented in humans since antiquity, primarily affecting livestock. The first human case was in 1957 in Yugoslavia.
-
Regional Variations: Different Babesia species are prevalent in different regions, with Babesia microti common in the U.S. and Babesia divergens in Europe.
Public Health and Veterinary Importance
Babesiosis affects both humans and animals, making it a significant public health and veterinary concern.
-
Public Health Threat: Poses a serious threat in highly endemic areas, necessitating continued surveillance and prevention efforts.
-
Veterinary Importance: Also affects domestic livestock, causing economic losses and impacting animal health.
-
Economic Impact: Significant economic impact in terms of veterinary medicine and human healthcare.
Protozoan Nature and Global Distribution
The nature of Babesia parasites and their global distribution highlight the widespread impact of babesiosis.
-
Protozoan Nature: Babesia parasites are protozoan organisms that infect red blood cells, commonly called piroplasms due to their pear-shaped forms.
-
Global Distribution: Babesia parasites are some of the most widespread blood parasites, second only to trypanosomes.
-
Species Infection: Several Babesia species can infect humans, with Babesia microti being the most prevalent in the U.S.
Disease Manifestation and Immunity
The disease can manifest in various ways, and the body's immune response plays a crucial role in managing the infection.
-
Symptom Spectrum: Ranges from silent infection to severe, malaria-like disease with severe hemolysis and occasional death.
-
Sterile Immunity: Slow to develop, with parasite DNA persisting for months to years after recovery, indicating a prolonged immune response.
-
Immunological Responses: Involves both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms, with resistance to B. microti infection being genetically determined and altered by aging.
Blood Transfusion and Pregnancy Risks
Babesiosis can also be transmitted through blood transfusions and from mother to child, highlighting additional risks.
-
Blood Transfusion Risk: Transmission through blood transfusions is a recognized risk, necessitating screening of blood products.
-
Pregnancy and Vertical Transmission: Possible from mother to child during pregnancy or at birth, emphasizing the need for screening pregnant women.
Public Awareness and Preventive Measures
Raising public awareness and implementing preventive measures are key to reducing the incidence of babesiosis.
-
Public Awareness: Educating the public about the risks associated with tick bites and the importance of regular tick checks can help reduce the incidence of the disease.
-
Preventive Measures: Use insect repellents containing 20–30% DEET, treat clothing with permethrin, and wear protective clothing. Regularly check yourself, kids, and pets for ticks.
-
Veterinary Role: Veterinarians advise pet owners on tick control products and educate them about the risks associated with tick bites, helping reduce transmission from animals to humans.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are essential for improving diagnostic tests and treatments for babesiosis.
-
Research and Development: Necessary to improve diagnostic tests and treatments, including developing more sensitive tests and exploring new therapeutic options.
-
Epidemiological Description: Advanced diagnostic tests help in understanding the distribution and prevalence of the disease, crucial for public health interventions.
Global Health Impact
Babesiosis has a significant global health impact, affecting both humans and animals. Continued monitoring and prevention efforts are essential.
-
Global Health Impact: Affects both humans and animals, necessitating continued monitoring and effective prevention strategies.
-
Public Health Threat: Poses a serious threat in highly endemic areas, highlighting the need for continued surveillance and prevention efforts.
-
Economic Impact: Significant economic impact in terms of veterinary medicine and human healthcare, affecting free-living animals worldwide.
Final Thoughts on Babesiosis
Babesiosis is a serious tick-borne disease caused by Babesia parasites. It primarily spreads through tick bites, especially from the blacklegged or deer tick. Symptoms can range from mild flu-like signs to severe hemolytic anemia. Older adults, immunocompromised individuals, and those without a spleen are at higher risk for severe complications. Diagnosis involves blood tests and microscopic examination, while treatment typically includes a combination of atovaquone and azithromycin or clindamycin and quinine. Preventing babesiosis focuses on avoiding tick-infested areas, using repellents, and performing regular tick checks. Public awareness and education are crucial for early detection and prevention. Continued research and improved diagnostic tests are essential for better management of the disease. Understanding babesiosis helps protect both human and animal health, reducing its global impact. Stay vigilant and take preventive measures to keep babesiosis at bay.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.