Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that forms in the lining of blood vessels and lymph vessels. This type of cancer can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the skin, breast, liver, and spleen. Symptoms often include swelling, skin lesions, and pain in the affected area. Early detection is challenging due to its subtle signs, making it crucial to understand the risk factors and treatment options. Risk factors include prior radiation therapy, chronic lymphedema, and exposure to certain chemicals. Treatment typically involves surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Understanding these facts about angiosarcoma can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical advice.
What is Angiosarcoma?
Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that starts in the lining of blood vessels and lymph vessels. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely treatment.
- Angiosarcoma can develop anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the skin, breast, liver, and spleen.
- This type of cancer is more prevalent in older adults, typically those over 60 years old.
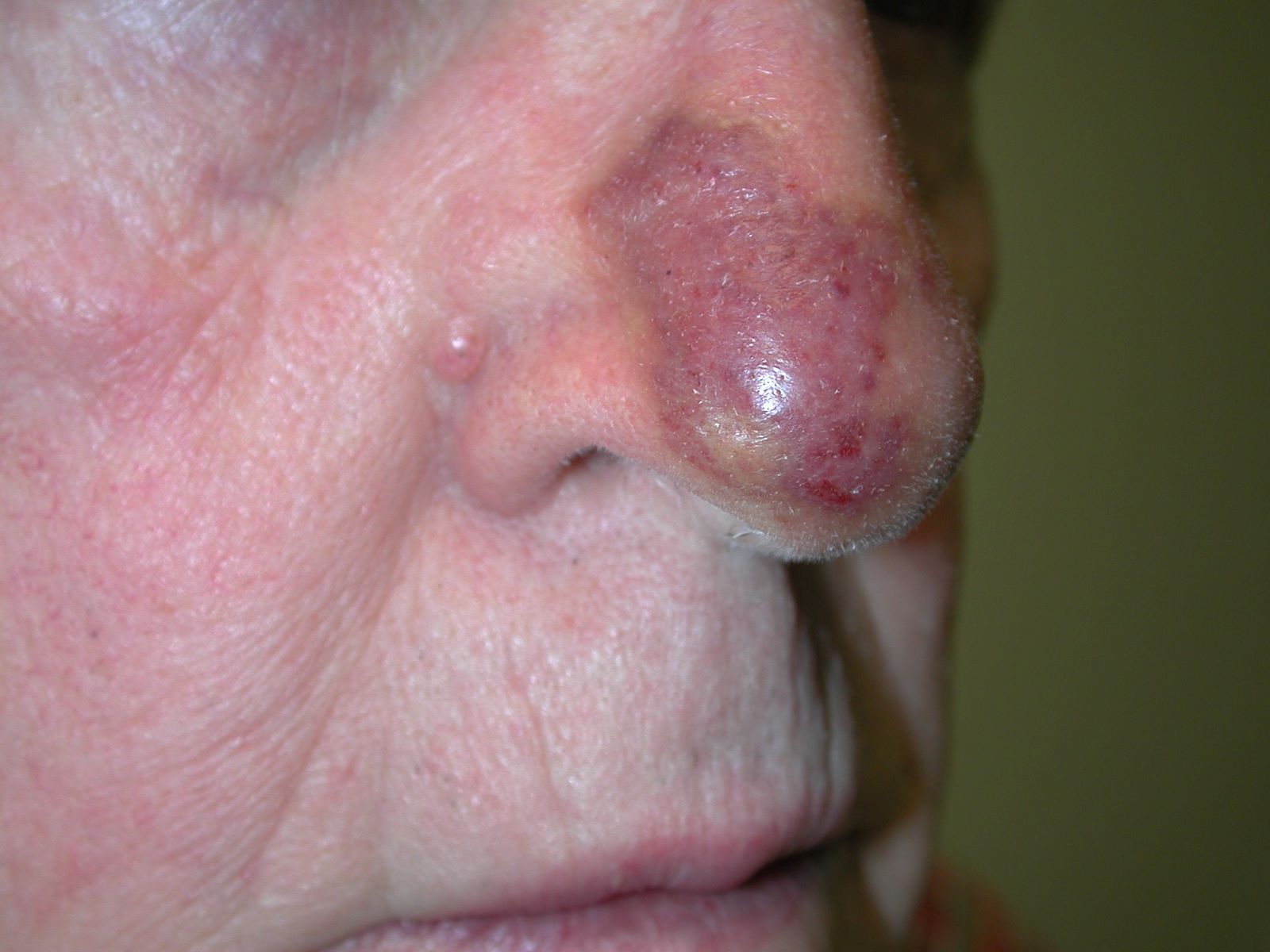
- Angiosarcoma of the skin often appears as a bruise-like lesion that grows over time.
- The exact cause of angiosarcoma is unknown, but it has been linked to radiation exposure and certain chemicals.
- Angiosarcoma can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms often resemble those of other conditions.
Symptoms of Angiosarcoma
Recognizing the symptoms of angiosarcoma can be challenging due to its rarity and the variety of ways it can present itself.
- Common symptoms include swelling, pain, and skin lesions that may bleed.
- In cases where angiosarcoma affects internal organs, symptoms might include abdominal pain or a palpable mass.
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss are also potential signs of angiosarcoma.
- Skin angiosarcoma may appear as a purplish area that looks like a bruise but doesn't heal.
- Angiosarcoma in the liver can cause jaundice and liver dysfunction.
Diagnosis of Angiosarcoma
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of angiosarcoma. Various methods are used to identify this cancer.
- A biopsy is the most definitive way to diagnose angiosarcoma, where a tissue sample is examined under a microscope.
- Imaging tests like MRI, CT scans, and PET scans help determine the extent of the disease.
- Blood tests can provide additional information but are not specific for diagnosing angiosarcoma.
- Pathologists look for specific markers in the tissue that indicate the presence of angiosarcoma.
- Misdiagnosis is common due to the rarity and unusual presentation of angiosarcoma.
Treatment Options for Angiosarcoma
Treatment for angiosarcoma often involves a combination of therapies tailored to the individual patient's needs.
- Surgery is often the first line of treatment to remove the tumor.
- Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to shrink the tumor or kill remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy is another option, especially for angiosarcoma that has spread to other parts of the body.
- Targeted therapy, which uses drugs to target specific cancer cells, is being researched as a treatment for angiosarcoma.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to find more effective treatments for this aggressive cancer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for angiosarcoma varies depending on several factors, including the location and stage of the cancer at diagnosis.
- The overall five-year survival rate for angiosarcoma is relatively low, around 30-40%.
- Early-stage angiosarcoma has a better prognosis compared to advanced-stage disease.
- The location of the tumor significantly impacts survival rates, with skin angiosarcoma having a better outlook than liver angiosarcoma.
- Younger patients tend to have a slightly better prognosis than older patients.
- Ongoing research and new treatments are gradually improving survival rates for angiosarcoma patients.
Risk Factors for Angiosarcoma
Understanding the risk factors associated with angiosarcoma can help in early detection and prevention.
- Previous radiation therapy for other cancers is a known risk factor for developing angiosarcoma.
- Chronic lymphedema, a condition of localized fluid retention, can increase the risk of angiosarcoma.
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as vinyl chloride and arsenic, has been linked to angiosarcoma.
- Genetic factors may play a role, although this is still being studied.
- A history of other cancers can also increase the risk of developing angiosarcoma.
Living with Angiosarcoma
Living with angiosarcoma involves managing symptoms, undergoing treatment, and maintaining quality of life.
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring the disease and managing any side effects of treatment.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support for patients and their families.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help improve overall well-being.
- Pain management is an important aspect of care for angiosarcoma patients.
- Palliative care can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those with advanced angiosarcoma.
Research and Future Directions
Research is ongoing to better understand angiosarcoma and develop more effective treatments.
- Scientists are studying the genetic mutations that cause angiosarcoma to develop targeted therapies.
- Immunotherapy, which uses the body's immune system to fight cancer, is being explored as a potential treatment.
- Advances in imaging technology are helping doctors diagnose angiosarcoma earlier and more accurately.
- Collaboration between researchers and healthcare providers is essential for advancing treatment options.
- Patient participation in clinical trials is crucial for discovering new and better treatments for angiosarcoma.
Final Thoughts on Angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma, a rare and aggressive cancer, demands awareness and understanding. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes. Regular check-ups and being mindful of unusual symptoms are crucial. This cancer can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, liver, and heart. Treatment options range from surgery to radiation and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and location.
Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals plays a vital role in managing this disease. Research continues to advance, offering hope for better treatments and outcomes. Staying informed and proactive can make a significant difference.
Remember, knowledge is power. By understanding angiosarcoma, we can better support those affected and contribute to ongoing efforts to combat this challenging disease. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and support research initiatives. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against angiosarcoma.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.