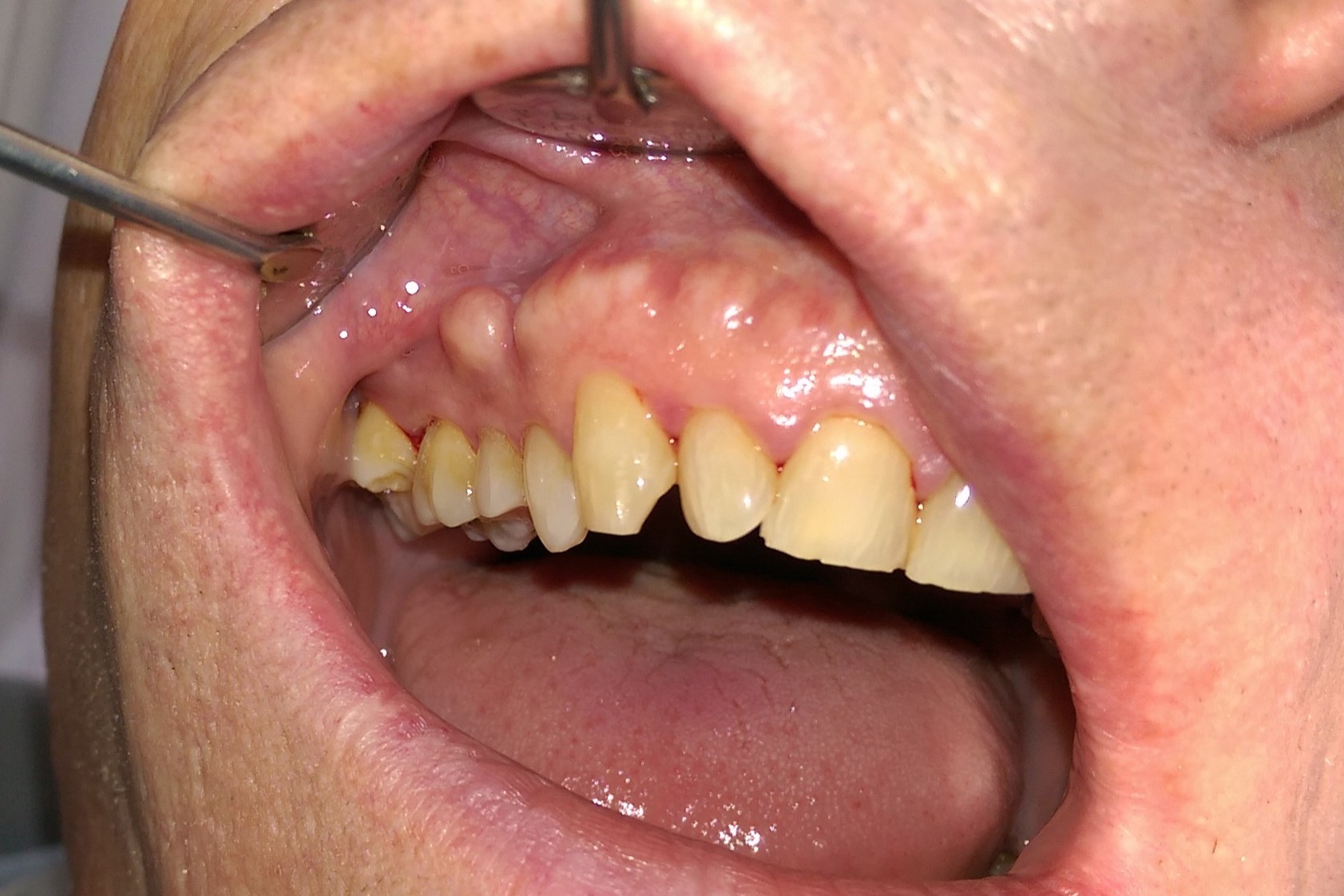
What is exostosis? Exostosis is a condition where new bone grows on top of existing bone, often causing pain or discomfort. This abnormal bone growth can occur in various parts of the body, including the ear canal, jaw, and long bones. Why does it happen? It can be triggered by repetitive stress, chronic irritation, or genetic factors. Who is affected? Athletes, surfers, and people with certain genetic conditions are more prone to developing exostosis. How is it treated? Treatment options range from monitoring the growth to surgical removal if it interferes with daily activities. Why should you care? Understanding exostosis can help in early detection and management, improving quality of life.
What is Exostosis?
Exostosis, also known as osteochondroma, is a benign bone growth that usually forms on the surface of bones. These growths can occur in various parts of the body and are often discovered incidentally during X-rays for other conditions. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about exostosis.
- Exostosis is a common bone condition, particularly in children and adolescents.
- These growths are typically non-cancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body.
- Osteochondromas are the most frequent type of exostosis, accounting for 35-40% of all benign bone tumors.
- Exostosis can develop on any bone but is most commonly found on long bones like the femur, tibia, and humerus.
- The exact cause of exostosis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to genetic factors and bone growth abnormalities.
- Multiple exostoses can occur in a condition known as Hereditary Multiple Exostoses (HME), which is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- HME affects approximately 1 in 50,000 people worldwide.
- Symptoms of exostosis may include pain, swelling, or restricted movement, especially if the growth presses on nerves or muscles.
- Some individuals with exostosis may experience no symptoms at all and may not require treatment.
- Diagnosis of exostosis is usually made through physical examination and imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs.
Treatment and Management of Exostosis
Managing exostosis depends on the size, location, and symptoms caused by the growth. Here are some key facts about treatment options.
- Observation is often the first step in managing exostosis, especially if the growth is asymptomatic.
- Regular monitoring with periodic X-rays may be recommended to track the growth's progression.
- Surgical removal is considered if the exostosis causes significant pain, deformity, or functional impairment.
- The surgical procedure involves excising the bony growth and smoothing the bone surface.
- Recovery from surgery typically involves a period of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to normal activities.
- Complications from surgery are rare but can include infection, nerve damage, or recurrence of the growth.
- Pain management may include over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
- Physical therapy can help improve mobility and strength in the affected area.
- In cases of HME, multiple surgeries may be necessary over a person's lifetime to address various growths.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for individuals with HME to understand the inheritance pattern and potential risks for offspring.
Interesting Facts About Exostosis
Beyond the medical aspects, exostosis has some intriguing characteristics and historical significance.
- Exostosis has been documented in ancient human remains, indicating it has affected humans for thousands of years.
- The condition can also occur in animals, including horses and dogs.
- Surfers are prone to a specific type of exostosis called "surfer's ear," caused by repeated exposure to cold water and wind.
- Surfer's ear involves bony growths in the ear canal, which can lead to hearing loss if left untreated.
- Exostosis can sometimes be mistaken for other bone conditions, such as osteosarcoma, a malignant bone tumor.
- The term "exostosis" comes from the Greek words "ex" meaning "out of" and "osteon" meaning "bone."
- Some exostoses contain cartilage caps, which can be seen on imaging studies.
- The size of an exostosis can vary greatly, from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
- Exostosis is more common in males than females, with a ratio of approximately 1.5:1.
- The growths often stop enlarging once a person reaches skeletal maturity, usually around the age of 18-20.
Prevention and Future Research
While exostosis cannot always be prevented, ongoing research aims to better understand and manage this condition.
- Protective gear, such as earplugs for surfers, can help reduce the risk of developing surfer's ear.
- Early detection and monitoring are crucial for managing exostosis effectively.
- Advances in genetic research may lead to better understanding and treatment of HME.
- Researchers are exploring the role of specific genes and molecular pathways in the development of exostosis.
- New imaging techniques are being developed to improve the accuracy of exostosis diagnosis.
- Minimally invasive surgical techniques are being investigated to reduce recovery time and complications.
- Patient education and awareness are essential for early intervention and management of exostosis.
- Collaboration between orthopedic surgeons, geneticists, and researchers is key to advancing the understanding and treatment of exostosis.
Understanding Exostosis
Exostosis, or bone spurs, can be a real pain, literally. These bony growths often develop due to repetitive stress, injury, or genetic factors. While they might seem harmless at first, they can cause discomfort and even limit movement over time. Early detection and treatment are key to managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help catch exostosis early. Treatments range from physical therapy to surgical removal, depending on the severity. Staying informed about your condition and following medical advice can make a big difference in your quality of life.
Remember, if you experience persistent pain or notice unusual growths, don't ignore them. Seek professional help to get the right diagnosis and treatment plan. Your bones will thank you!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
