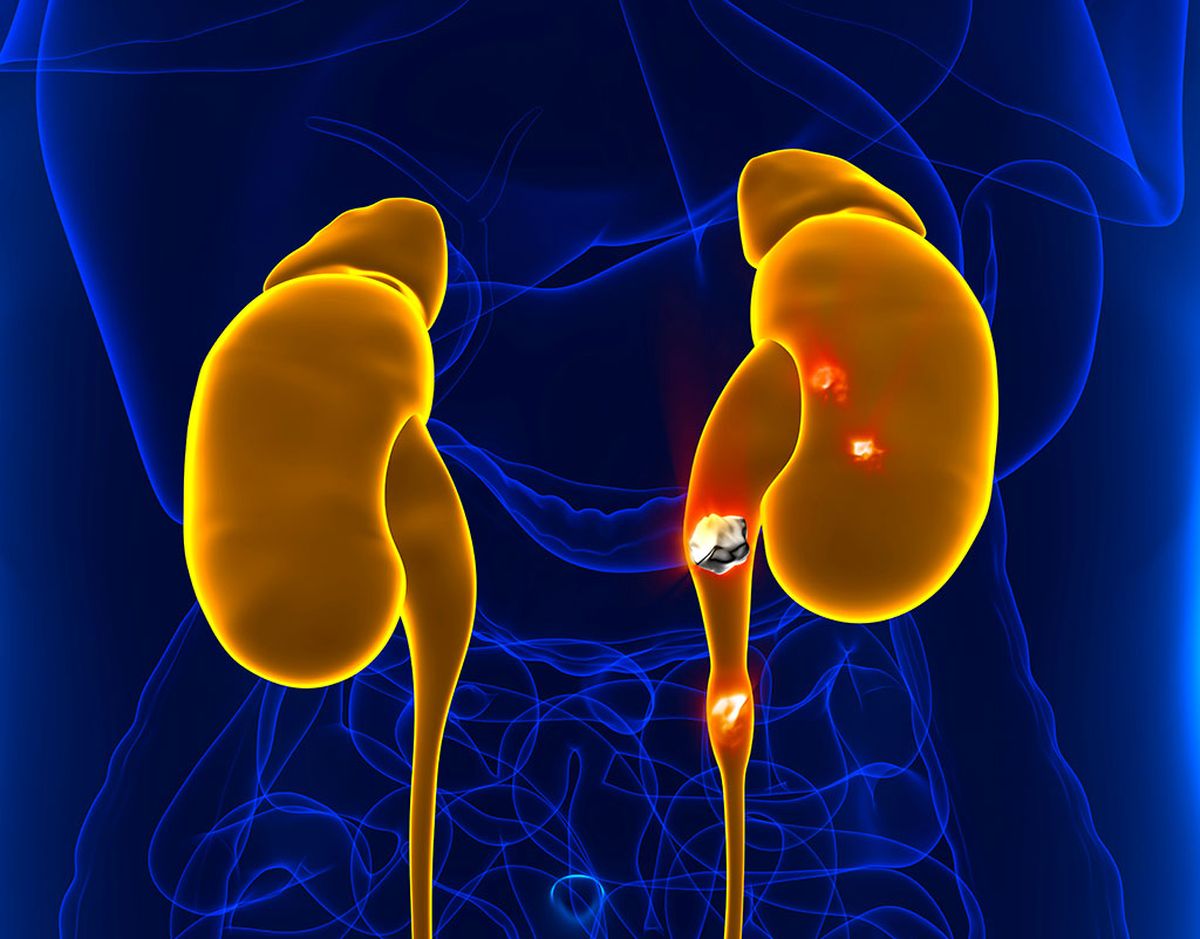
Lithiasis might sound like a complex medical term, but it simply refers to the formation of stones in the body. These stones, also known as calculi, can develop in various organs like the kidneys, gallbladder, or urinary tract. Kidney stones are perhaps the most well-known type, causing intense pain when they pass through the urinary system. Gallstones form in the gallbladder and can lead to severe abdominal pain and digestive issues. Understanding lithiasis can help you recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment. This article will break down 37 essential facts about lithiasis, making it easier to grasp this common yet often misunderstood condition.
What is Lithiasis?
Lithiasis refers to the formation of stones or calculi in the body, often found in organs like the kidneys, gallbladder, or urinary tract. These stones can cause significant discomfort and health issues if not treated properly. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about lithiasis.
Types of Lithiasis
There are various types of lithiasis, each affecting different parts of the body. Understanding these types can help in better diagnosis and treatment.
- Kidney Stones: These are the most common type of lithiasis, formed from minerals and salts in the kidneys.
- Gallstones: These stones form in the gallbladder, often composed of cholesterol or bilirubin.
- Bladder Stones: These develop in the bladder, usually due to concentrated urine.
- Ureteral Stones: These stones travel from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters.
- Pancreatic Stones: Rare but painful, these form in the pancreas and can block digestive enzymes.
Causes of Lithiasis
Several factors contribute to the formation of stones in the body. Knowing these causes can help in prevention.
- Dehydration: Lack of sufficient water intake can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of stone formation.
- Diet: High intake of salt, sugar, and protein can contribute to stone formation.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can alter the chemical balance in the urine, leading to stones.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like hyperparathyroidism and urinary tract infections can increase the risk.
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in the likelihood of developing stones.
Symptoms of Lithiasis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment and relief.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen is a common symptom.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can indicate the presence of stones.
- Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often in small amounts.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms often accompany severe pain.
- Fever and Chills: Indicate an infection, which can occur with lithiasis.
Diagnosis of Lithiasis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various methods are used to identify the presence of stones.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds are commonly used to detect stones.
- Urine Tests: These tests can identify high levels of stone-forming substances.
- Blood Tests: Help in detecting high levels of calcium or uric acid.
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): A special dye is injected to highlight the urinary tract on X-rays.
- Cystoscopy: A thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder to look for stones.
Treatment Options for Lithiasis
Various treatments are available depending on the type and size of the stones.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help small stones pass naturally.
- Medications: Pain relievers and medications to relax the ureters can ease the passage of stones.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): Uses sound waves to break stones into smaller pieces.
- Ureteroscopy: A thin scope is used to remove or break up stones in the ureter or kidney.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A surgical procedure to remove large kidney stones.
Prevention of Lithiasis
Preventing the formation of stones can save a lot of pain and trouble. Here are some effective preventive measures.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute substances in the urine that form stones.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing salt, sugar, and protein intake can lower the risk.
- Maintain Healthy Weight: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can prevent obesity-related stones.
- Monitor Calcium Intake: While calcium is essential, excessive intake can lead to stone formation.
- Avoid Oxalate-Rich Foods: Foods like spinach, beets, and nuts can contribute to stone formation.
Interesting Facts about Lithiasis
Here are some lesser-known yet intriguing facts about lithiasis.
- Ancient History: Evidence of kidney stones has been found in Egyptian mummies.
- Gender Differences: Men are more likely to develop kidney stones than women.
- Recurrence: Once you've had a stone, there's a 50% chance of developing another within five years.
- Size Matters: Stones can range from a grain of sand to the size of a golf ball.
- Silent Stones: Some stones cause no symptoms and are discovered incidentally during imaging tests.
- Dietary Myths: Contrary to popular belief, drinking milk does not increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Global Prevalence: Lithiasis affects people worldwide, with varying prevalence based on diet and climate.
Final Thoughts on Lithiasis
Lithiasis, or kidney stones, can be a real pain—literally. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments helps manage this condition better. Staying hydrated is key. Drinking plenty of water can prevent stones from forming. Diet also plays a role. Reducing salt and animal protein intake can lower risk. Recognizing symptoms early, like severe pain or blood in urine, means getting medical help sooner. Treatments range from medication to break up stones to surgery for larger ones. Prevention is always better than cure. Regular check-ups and lifestyle changes make a big difference. Knowledge is power. The more you know about lithiasis, the better you can handle it. Stay informed, stay healthy, and keep those kidneys stone-free.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
