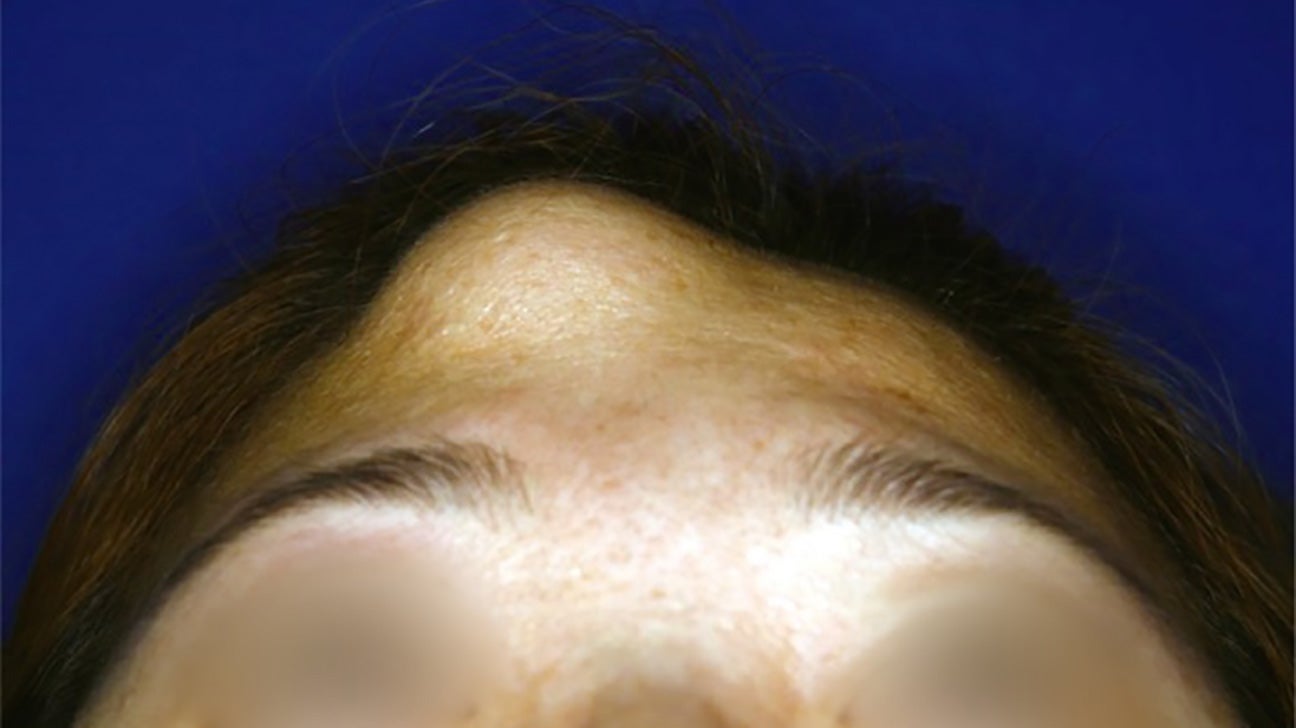
What is an osteoma? An osteoma is a benign bone tumor that typically forms on the skull or facial bones. These growths are usually slow-growing and non-cancerous, meaning they don't spread to other parts of the body. While they can occur at any age, they are most commonly found in young adults. Osteomas often go unnoticed because they rarely cause symptoms. However, if they grow large enough, they can lead to discomfort or cosmetic concerns. Treatment options vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, ranging from observation to surgical removal. Understanding osteomas can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate medical advice.
What is Osteomalacia?
Osteomalacia is a condition that affects bones, making them soft and weak. It’s often caused by a deficiency in vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. Understanding this condition can help in managing and preventing it.
-
Osteomalacia is different from osteoporosis. While both conditions affect bones, osteomalacia involves softening, whereas osteoporosis involves bone thinning.
-
Vitamin D deficiency is a primary cause. Without enough vitamin D, the body can’t absorb calcium effectively, leading to soft bones.
-
Symptoms include bone pain and muscle weakness. These symptoms often start subtly but can become more severe over time.
-
Osteomalacia can affect people of all ages. However, it’s more common in older adults and those with limited sun exposure.
-
The condition can be diagnosed through blood tests. These tests check levels of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate.
Causes of Osteomalacia
Understanding the causes of osteomalacia can help in preventing the condition. Several factors contribute to the development of this bone disorder.
-
Lack of sunlight exposure is a significant cause. Sunlight helps the body produce vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health.
-
Certain medical conditions can lead to osteomalacia. These include celiac disease, kidney disorders, and liver problems.
-
Some medications can cause osteomalacia. Anticonvulsants and certain antacids can interfere with vitamin D metabolism.
-
Dietary deficiencies play a role. A diet low in vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate can lead to osteomalacia.
-
Genetic factors can also contribute. Some inherited disorders affect the body’s ability to process vitamin D.
Symptoms of Osteomalacia
Recognizing the symptoms of osteomalacia is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can vary but often include the following.
-
Bone pain is a common symptom. The pain is usually dull and aching, often affecting the lower back, pelvis, hips, legs, and ribs.
-
Muscle weakness is another symptom. This can make everyday activities difficult and increase the risk of falls.
-
Difficulty walking can occur. The weakness and pain can lead to a waddling gait.
-
Bone fractures are more likely. Softened bones are more prone to breaks and fractures.
-
Fatigue and general discomfort are also common. The overall weakness and pain can lead to a constant feeling of tiredness.
Diagnosing Osteomalacia
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Several methods are used to diagnose osteomalacia.
-
Blood tests are often the first step. These tests measure levels of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate.
-
X-rays can reveal bone abnormalities. They can show slight cracks in the bones, known as Looser’s zones.
-
Bone biopsy is sometimes necessary. A small sample of bone is taken to examine under a microscope.
-
Bone density scans can help. These scans measure the density and strength of bones.
-
Medical history and physical exams are also important. Doctors will consider symptoms and risk factors during diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Osteomalacia
Treating osteomalacia involves addressing the underlying cause and improving bone health. Several treatment options are available.
-
Vitamin D supplements are commonly prescribed. These help increase vitamin D levels in the body.
-
Calcium and phosphate supplements may be needed. These minerals are essential for bone health.
-
Sunlight exposure can help. Spending time in the sun helps the body produce vitamin D naturally.
-
Dietary changes are often recommended. Eating foods rich in vitamin D and calcium can improve bone health.
-
Treating underlying conditions is crucial. Managing diseases like celiac disease or kidney disorders can help prevent osteomalacia.
Preventing Osteomalacia
Prevention is always better than cure. Several steps can be taken to prevent osteomalacia.
-
Ensure adequate sunlight exposure. Spending time outdoors can help maintain healthy vitamin D levels.
-
Eat a balanced diet. Include foods rich in vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate.
-
Take supplements if necessary. Vitamin D and calcium supplements can help prevent deficiencies.
-
Regular exercise is beneficial. Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones and improve overall health.
-
Monitor and manage medical conditions. Regular check-ups can help detect and treat conditions that may lead to osteomalacia.
Interesting Facts About Osteomalacia
Here are some intriguing facts about osteomalacia that you might not know.
-
Osteomalacia was once known as “adult rickets.” Rickets is a similar condition that affects children.
-
The name “osteomalacia” comes from Greek. It means “soft bones.”
-
It’s more common in women. Hormonal changes and pregnancy can increase the risk.
-
Dark-skinned individuals are at higher risk. Melanin reduces the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight.
-
Osteomalacia can be reversible. With proper treatment, bones can regain their strength.
-
It’s a global health issue. Osteomalacia affects people worldwide, particularly in areas with limited sunlight.
Final Thoughts on Osteomas
Osteomas might sound intimidating, but understanding them helps ease concerns. These benign bone growths often appear in the skull or jaw, causing discomfort or cosmetic issues. While they rarely turn cancerous, monitoring them is crucial. Treatments range from watchful waiting to surgical removal, depending on size and symptoms.
Knowing the symptoms, like headaches or facial pain, can prompt early medical advice. Regular check-ups ensure any changes are caught early. If you or someone you know has an osteoma, remember it's usually manageable with proper care.
Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and don't hesitate to seek second opinions if needed. Knowledge empowers you to make the best decisions for your health. Osteomas may be a part of life, but they don't have to control it.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
