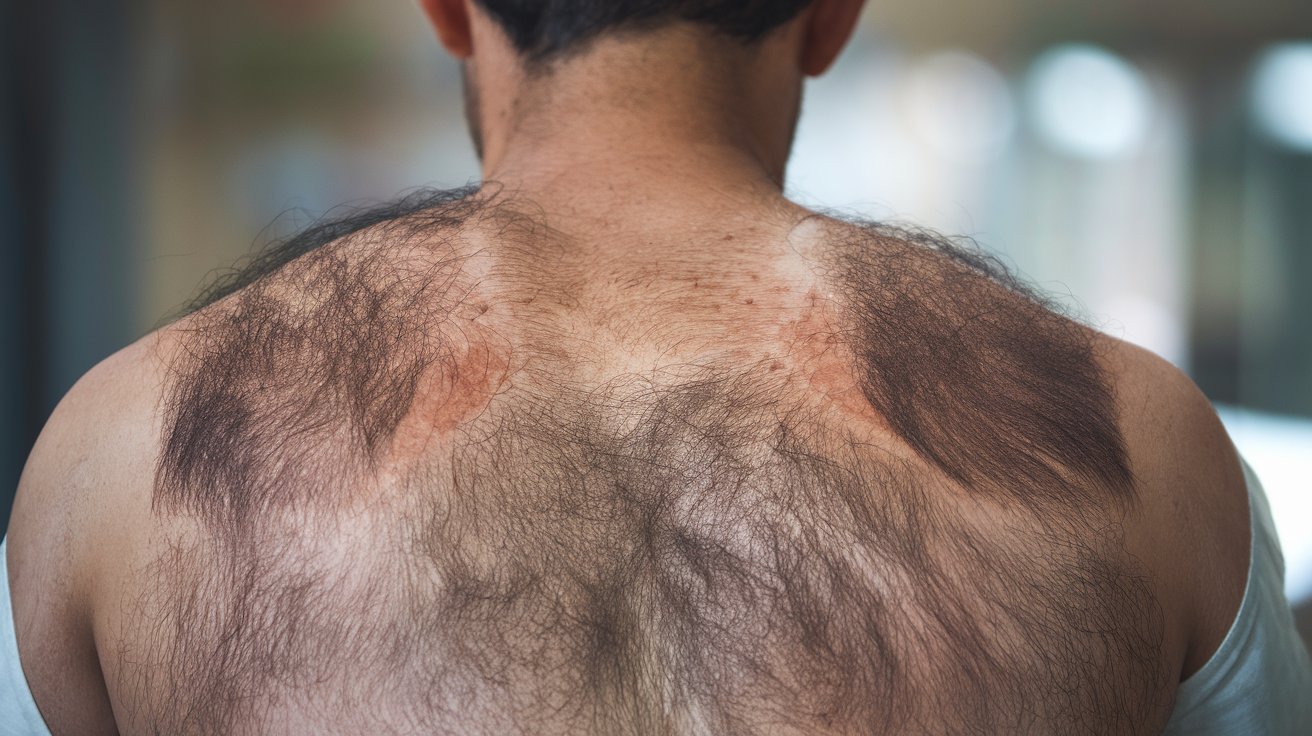
What is Becker's Nevus? Becker's nevus, also called Becker's melanosis, is a rare skin condition featuring pigmented lesions, often found on the chest, back, or shoulders. Affecting about 0.3% to 1% of people, it appears more frequently in males, typically during puberty. These lesions can range in color from light brown to black and may have a rough or hairy texture. While the exact cause remains unclear, hormonal changes and genetic factors are believed to play significant roles. Diagnosis usually involves a clinical examination, and treatment focuses on cosmetic improvement through topical treatments, laser therapy, or surgical excision.
What is Becker's Nevus?
Becker's nevus, also known as Becker's melanosis, is a rare skin condition that often appears as a pigmented lesion. Let's explore some key facts about this condition.
-
Definition and Overview: Becker's nevus is a benign skin condition that looks like a mole or patch of skin discoloration. It was first described by dermatologist Alfred Becker.
-
Prevalence: This condition is relatively rare, affecting about 0.3% to 1% of the population. It is more common in males, with a male-to-female ratio of about 3:1.
-
Age of Onset: Becker's nevus usually appears during puberty, typically between the ages of 10 and 20, but it can also show up in adults.
Symptoms and Appearance
Understanding the symptoms and appearance of Becker's nevus can help in identifying the condition early.
-
Symptoms: The main symptom is a pigmented lesion that can vary in size and color, from light brown to dark brown or black. These lesions often have a hairier texture than the surrounding skin and may be thicker.
-
Location: The most common areas for Becker's nevus are the chest, back, and shoulders. However, it can also appear on the arms, legs, and other parts of the body.
-
Appearance: Lesions can appear as a single patch or multiple patches. They may be irregularly shaped and can have a rough or hairy texture.
Causes and Genetic Factors
The exact causes of Becker's nevus are not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute.
-
Causes: While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to be related to hormonal changes during puberty and genetic factors.
-
Genetic Factors: There is evidence that Becker's nevus may be linked to mutations in genes involved in melanocyte development and function.
-
Hormonal Influence: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly androgens, are thought to play a significant role in the development of Becker's nevus. Many cases appear during puberty when androgen levels rise.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing Becker's nevus effectively.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made based on clinical examination. The appearance and location of the lesion are key diagnostic features. A biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions like melanoma, though this is rare.
-
Differential Diagnosis: Other conditions that may need to be ruled out include melanoma, neurofibromatosis type 1, and other pigmented lesions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Becker's nevus focuses on cosmetic improvement rather than complete removal.
-
Topical Treatments: Creams or ointments containing hydroquinone, retinoids, or corticosteroids may be used to lighten the skin.
-
Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can help reduce the size and color of the lesions.
-
Surgical Excision: In some cases, surgical excision may be considered, especially if the lesion is large or cosmetically bothersome.
-
Photodynamic Therapy: This involves using a light-sensitive medication and a specific wavelength of light to target the melanocytes.
Laser Therapy Techniques
Several laser techniques can be used to treat Becker's nevus effectively.
-
Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser: This laser is effective for breaking up melanin and reducing the appearance of the lesion.
-
Alexandrite Laser: Often used for its ability to target melanin and reduce pigmentation.
-
Pulsed Dye Laser: Useful for treating the vascular component of the lesion, if present.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of approach for managing Becker's nevus.
-
Hydroquinone Creams: These creams help lighten the skin by inhibiting melanin production.
-
Retinoid Creams: Derivatives of vitamin A, retinoids promote cell turnover and can help reduce pigmentation.
-
Corticosteroid Creams: These creams can reduce inflammation and swelling associated with the lesion.
Surgical Excision and Photodynamic Therapy
For larger or more cosmetically significant lesions, surgical options may be considered.
-
Surgical Excision: Typically reserved for cases where the lesion is large or cosmetically significant. The procedure involves removing the affected area and suturing the skin closed.
-
Photodynamic Therapy: Involves applying a light-sensitive medication to the affected area and then exposing it to a specific wavelength of light. This treatment targets the melanocytes responsible for the pigmentation.
Psychological and Family Impact
Becker's nevus can have a significant psychological impact, especially if it is large or in a visible location.
-
Psychological Impact: Cosmetic treatments can help improve self-esteem and confidence.
-
Family History: There is a higher incidence of Becker's nevus in families with a history of the condition, suggesting a possible genetic component.
Hormonal and Genetic Influences
Hormonal fluctuations and genetic factors play a significant role in the development of Becker's nevus.
-
Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes during puberty are a significant factor in the development of Becker's nevus.
-
Androgen Influence: Androgens, such as testosterone, are believed to play a role in the development of Becker's nevus. Many cases appear during puberty when androgen levels rise.
-
Melanocyte Development: Becker's nevus is thought to involve abnormalities in melanocyte development. Melanocytes are the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives color to skin.
-
Genetic Mutations: While the exact genetic mutations responsible for Becker's nevus are not fully understood, there is evidence that mutations in genes involved in melanocyte development and function may contribute to the condition.
Clinical Presentation and Histopathological Features
The clinical presentation of Becker's nevus can vary widely, and histopathological examination can provide additional insights.
-
Clinical Presentation: Lesions may appear as single patches or multiple patches and can range in size from small to large.
-
Histopathological Features: Examination of biopsy samples typically shows hyperpigmentation with an increase in melanin-containing cells. There may also be an increase in hair follicles within the affected area.
Treatment Outcomes and Risks
Understanding the potential outcomes and risks of various treatments is crucial for managing Becker's nevus effectively.
-
Treatment Outcomes: Topical treatments and laser therapy are often effective for reducing pigmentation and improving cosmetic appearance. Surgical excision may be necessary for larger lesions.
-
Surgical Risks: Surgical excision carries risks such as scarring, infection, and potential complications related to anesthesia. These risks should be carefully weighed against the benefits of surgical intervention.
-
Laser Therapy Risks: Laser therapy also carries risks such as temporary changes in skin color, blistering, or scarring. These risks should be discussed with a healthcare provider before undergoing treatment.
-
Topical Treatment Risks: Topical treatments generally have fewer risks compared to surgical or laser therapies but may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
Understanding Becker's Nevus
Becker's nevus, a rare skin condition, often appears during puberty and is more common in males. These pigmented lesions, usually on the chest, back, or shoulders, can vary in size and color. Hormonal changes and genetic factors play significant roles in its development. Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination, sometimes followed by a biopsy to rule out other conditions.
Treatment focuses on cosmetic improvement. Options include topical treatments, laser therapy, surgical excision, and photodynamic therapy. Each method has its own risks and benefits, so discussing these with a healthcare provider is crucial.
The psychological impact of Becker's nevus shouldn't be underestimated. Cosmetic treatments can boost self-esteem and confidence. Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic and hormonal influences, leading to more effective treatments in the future. Understanding and managing Becker's nevus can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.