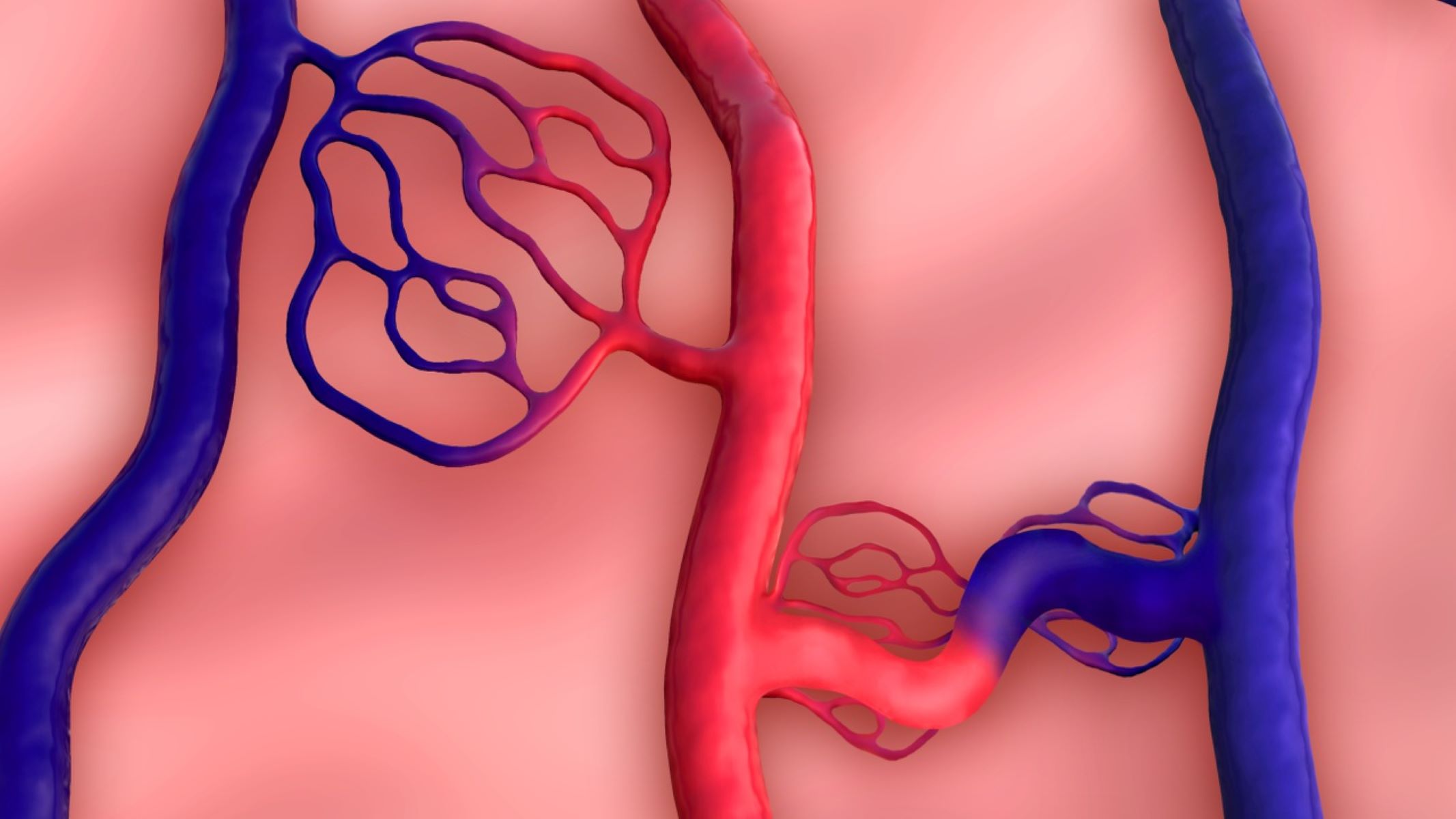
What exactly is an arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? An AVM is a tangled web of abnormal blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This condition can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms vary widely, from headaches and seizures to muscle weakness and vision changes. While the exact cause remains unclear, AVMs are believed to form during embryonic development. Diagnosing and treating AVMs involves a range of imaging tests and medical procedures. Understanding the complexities of AVMs is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing severe complications like stroke or hemorrhage.
What is an Arteriovenous Malformation?
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are complex and unusual connections between arteries and veins. These connections bypass the capillary system, leading to various complications. Let's explore some key facts about AVMs.
-
Definition and Overview: AVMs are abnormal connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary bed, which can lead to high flow rates and serious complications.
-
Symptoms: Symptoms vary based on the AVM's location and size. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, muscle weakness, and changes in vision.
-
Buzzing or Rushing Sound in the Ears: Some people with AVMs hear a constant buzzing or rushing sound due to abnormal blood flow.
-
Headache: AVMs can cause headaches, though no specific type has been identified.
-
Backache: AVMs in the spinal cord can lead to persistent back pain.
-
Seizures: Seizures are a common symptom, especially with brain AVMs.
-
Loss of Sensation: AVMs can cause numbness or loss of sensation in parts of the body.
-
Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness is another symptom, often affecting one side of the body.
-
Changes in Vision: Vision changes can occur if the AVM is near the optic nerves.
-
Facial Paralysis: AVMs in the brain can lead to facial paralysis.
-
Drooping Eyelids: Drooping eyelids may occur if the AVM affects the nerves controlling the eyelids.
-
Problems Speaking: Speech difficulties can arise from AVMs in certain brain areas.
-
Changes in Sense of Smell: AVMs near the olfactory nerves can alter the sense of smell.
-
Problems with Motion: AVMs can cause coordination and movement issues.
-
Dizziness: Dizziness is a common symptom, especially with brain AVMs.
-
Loss of Consciousness: Severe cases can lead to loss of consciousness.
-
Bleeding: AVMs can rupture, causing significant bleeding.
-
Pain: Pain is a common symptom, especially if the AVM is pressing on nerves.
-
Cold or Blue Fingers or Toes: Poor blood flow from AVMs can cause extremities to feel cold or appear blue.
Causes and Pathogenesis
Understanding the causes and development of AVMs helps in managing and treating them effectively.
-
Causes: The exact cause of AVMs is unknown, but they are rarely hereditary.
-
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT): This genetic condition increases the risk of developing AVMs.
-
Pathogenesis: AVMs likely form during embryonic development, bypassing the capillary bed and leading to high flow rates.
-
High Flow Rates: The absence of capillaries in AVMs results in high flow rates, which can weaken vessel walls.
Types of AVMs
AVMs can occur in various parts of the body, each with unique challenges and symptoms.
-
Brain AVMs: The most common type, brain AVMs, can cause significant morbidity and mortality due to hemorrhage risk.
-
Spinal AVMs: Less common but can cause neurological symptoms and back pain.
-
Lung AVMs: Often associated with HHT, lung AVMs can lead to pulmonary hypertension.
Diagnosis and Mistaken Diagnoses
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. AVMs can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, imaging tests, and sometimes genetic testing.
-
Imaging Tests: Common imaging tests include ultrasound, MRI, CT scans, and angiograms.
-
Mistaken Diagnoses: AVMs can be mistaken for capillary malformations or infantile hemangiomas.
Risk Factors and Complications
Certain factors increase the risk of developing AVMs, and they can lead to severe complications.
-
Risk Factors: HHT, trauma, and pregnancy can increase the risk of AVMs.
-
Complications: AVMs can cause stroke, numbness, speech or movement problems, and hydrocephalus.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the AVM's location, size, and symptoms. Various options are available.
-
Surgery: Microsurgical resection involves removing the AVM.
-
Endovascular Embolization: A catheter blocks blood flow to the AVM.
-
Radiosurgery: Radiation is used to shrink the AVM.
-
Medical Observation: Monitoring the AVM for potential rupture without immediate intervention.
Final Thoughts on Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are complex and potentially serious vascular anomalies. They can cause a range of symptoms, from headaches and seizures to more severe complications like stroke. Diagnosing AVMs involves various imaging techniques, and treatment options include surgery, endovascular embolization, and radiosurgery. While the exact cause remains unclear, ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment. Managing symptoms and regular monitoring are crucial for those affected. Family support and lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing the condition. Participation in clinical trials helps advance research and treatment options. With advancements in medical science, there's hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals with AVMs. Stay informed, seek medical advice, and consider genetic counseling if there's a family history of related conditions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


