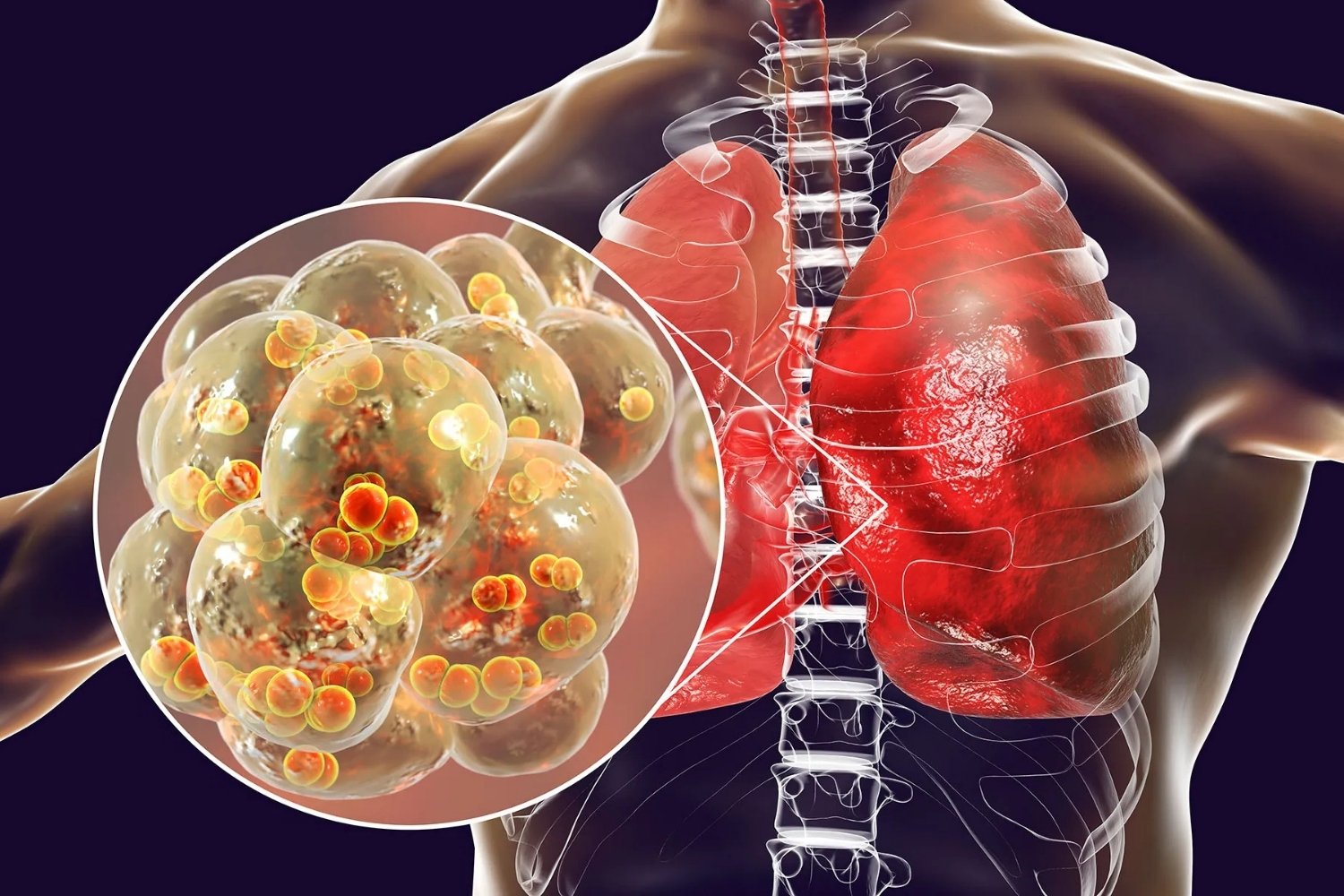
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that affects millions worldwide. Did you know that it can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi? This illness inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms like cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can strike anyone, but it's especially dangerous for infants, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. Vaccines can help prevent some types of pneumonia, and early treatment is crucial for recovery. Understanding the facts about pneumonia can help you protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially life-threatening condition.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can affect anyone, from infants to the elderly. Understanding this illness is crucial for prevention and treatment. Here are some eye-opening facts about pneumonia.
-
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
-
It can be caused by various organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The most common bacterial cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae.
-
Pneumonia can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening. It is most serious for infants, young children, people older than age 65, and those with health problems or weakened immune systems.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Here are some key symptoms and diagnostic methods.
-
Common symptoms include chest pain when breathing or coughing, confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and older), and a cough that may produce phlegm.
-
Other symptoms can include fatigue, fever, sweating, shaking chills, lower than normal body temperature (in adults older than age 65 and people with weak immune systems), nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
-
Pneumonia is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Doctors listen for abnormal lung sounds using a stethoscope.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing pneumonia. Knowing these can help in taking preventive measures.
-
Smoking damages the natural defenses of the lungs, making it easier for pneumonia-causing organisms to infect the lungs.
-
Chronic diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart disease can increase the risk of pneumonia.
-
Hospitalization, especially in intensive care units, can expose individuals to a higher risk of pneumonia, particularly if they are on a ventilator.
Prevention
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some effective ways to prevent pneumonia.
-
Vaccines are available to prevent some types of pneumonia and the flu. These vaccines are especially recommended for children, older adults, and people with chronic health conditions.
-
Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent respiratory infections that can lead to pneumonia.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of pneumonia.
Treatment
Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of pneumonia. Here are some common treatment methods.
-
Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics. The type of antibiotic depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
-
Viral pneumonia usually requires rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Antiviral medications may be prescribed in some cases.
-
Fungal pneumonia is treated with antifungal medications. This type of pneumonia is more common in people with weakened immune systems.
Complications
Pneumonia can lead to serious complications, especially in high-risk groups. Awareness of these complications can prompt timely medical intervention.
-
Bacteremia occurs when bacteria from the lungs enter the bloodstream, potentially causing septic shock and organ failure.
-
Lung abscesses, which are pockets of pus that form in the lungs, can develop if pneumonia is not treated promptly.
-
Pleural effusion, or fluid accumulation around the lungs, can make breathing difficult and may require drainage.
Global Impact
Pneumonia affects millions of people worldwide and remains a significant public health issue.
-
Pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under five years old globally, accounting for approximately 15% of all deaths in this age group.
-
In 2019, pneumonia caused an estimated 2.5 million deaths worldwide, including over 672,000 children.
-
Low- and middle-income countries bear the highest burden of pneumonia-related deaths due to limited access to healthcare and vaccines.
Historical Context
Understanding the history of pneumonia can provide insights into how far medical science has come in combating this disease.
-
The term "pneumonia" comes from the Greek word "pneumon," meaning lung. The disease has been recognized for thousands of years.
-
The discovery of antibiotics in the 20th century revolutionized the treatment of bacterial pneumonia, significantly reducing mortality rates.
-
The first pneumonia vaccine was introduced in the 1980s, providing a powerful tool in preventing pneumococcal pneumonia.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about pneumonia that might surprise you.
-
Pneumonia can be classified into different types based on where it was acquired: community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
-
Walking pneumonia is a milder form of pneumonia that doesn't usually require bed rest or hospitalization. It is often caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
-
Pneumonia can affect animals too. Dogs, cats, and other pets can develop pneumonia, often requiring veterinary care.
Modern Advances
Recent advancements in medical science continue to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of pneumonia.
-
Rapid diagnostic tests are being developed to quickly identify the specific cause of pneumonia, allowing for more targeted treatment.
-
New vaccines are in development to protect against a broader range of pneumonia-causing organisms.
-
Telemedicine is becoming an important tool in managing pneumonia, allowing patients to receive medical advice and monitoring without leaving their homes.
Final Thoughts on Pneumonia
Pneumonia remains a serious health issue affecting millions worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help reduce its impact. Vaccinations, good hygiene, and prompt medical attention are key in preventing and managing this illness. Remember, pneumonia can affect anyone, but certain groups like the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable.
Staying informed and proactive about your health can make a significant difference. If you or someone you know shows signs of pneumonia, don't hesitate to seek medical advice. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a full recovery.
By spreading awareness and knowledge about pneumonia, we can all contribute to a healthier, more informed community. Stay vigilant, stay healthy, and take care of each other.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
