Condyloma, commonly known as genital warts, are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts appear on the genital and anal areas, sometimes even inside the body. But what exactly are condyloma, and how do they affect people? Understanding this condition is crucial for prevention and treatment.
In this post, we will explore 30 facts about condyloma, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Whether you're looking to educate yourself or support someone dealing with this condition, these facts will provide valuable insights. Let's dive into the world of condyloma and learn more about this common yet often misunderstood health issue.
What is Condyloma?
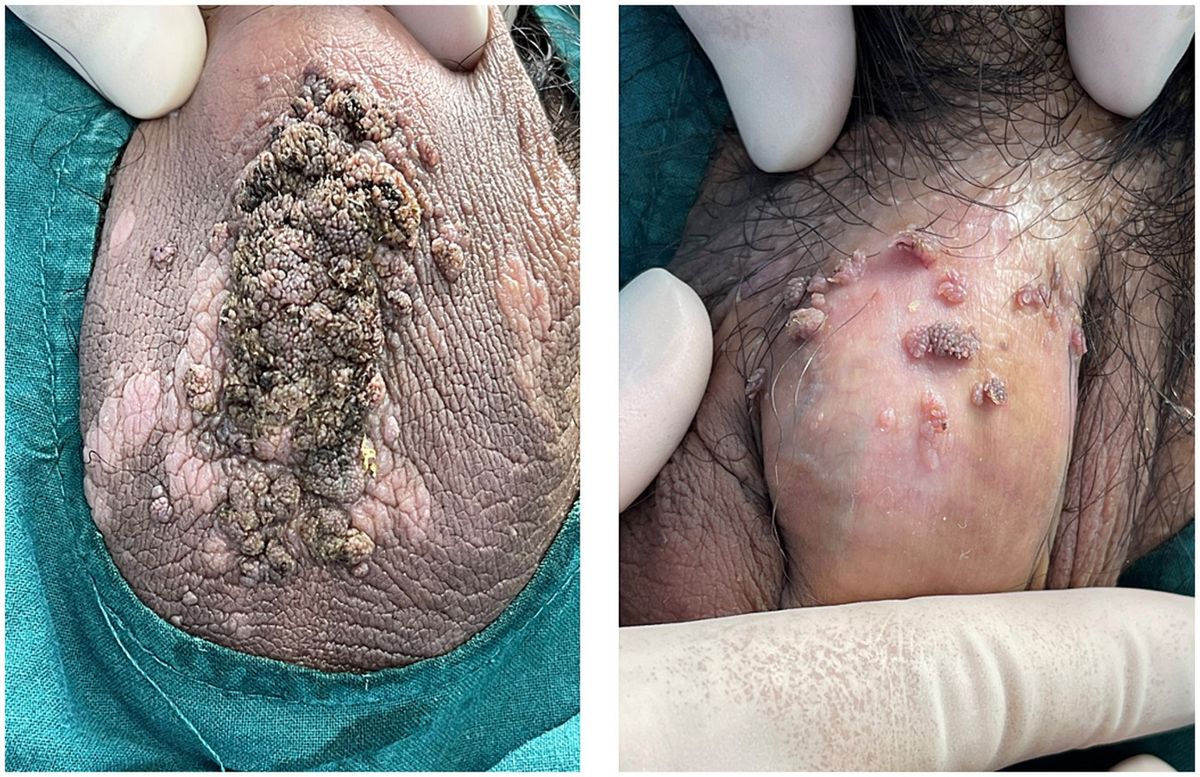
Condyloma, also known as genital warts, is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts appear on the genital and anal areas and can affect both men and women. Understanding more about condyloma can help in prevention and treatment.
- Condyloma is caused by HPV types 6 and 11, which are responsible for about 90% of genital warts cases.
- HPV is the most common STI worldwide, with millions of new cases each year.
- Condyloma can appear as small, flesh-colored or gray swellings in the genital area.
- These warts can cluster together, forming a cauliflower-like shape.
- Condyloma is highly contagious and spreads through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of condyloma is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While some people may not show any symptoms, others might experience noticeable changes.
- Some people with condyloma may experience itching or discomfort in the genital area.
- In some cases, bleeding during intercourse or urination can occur.
- Condyloma can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare provider.
- A biopsy may be performed if the diagnosis is uncertain or if the warts are atypical.
- Women may need a Pap smear to check for HPV-related changes in the cervix.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available for condyloma, ranging from topical medications to surgical procedures. The choice of treatment depends on the size, number, and location of the warts.
- Topical treatments like imiquimod, podophyllin, and sinecatechins can be applied directly to the warts.
- Cryotherapy involves freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen.
- Electrocautery uses an electric current to burn off the warts.
- Laser therapy can be used to remove larger or more stubborn warts.
- Surgical excision may be necessary for extensive or resistant cases.
Prevention and Vaccination
Preventing condyloma involves practicing safe sex and getting vaccinated against HPV. Vaccination is a powerful tool in reducing the incidence of genital warts and other HPV-related conditions.
- Using condoms can reduce the risk of contracting HPV, though it does not eliminate it entirely.
- The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection with HPV types 6 and 11.
- The vaccine is recommended for both boys and girls, ideally before they become sexually active.
- Regular screening and Pap smears for women can help detect HPV-related changes early.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners can also reduce the risk of HPV infection.
Impact on Health
Condyloma can have various impacts on an individual's health, both physically and emotionally. Understanding these effects can help in managing the condition better.
- Genital warts can cause significant emotional distress and embarrassment.
- In rare cases, untreated condyloma can lead to complications like secondary infections.
- Pregnant women with condyloma may experience complications during delivery.
- There is a low risk of condyloma leading to cancer, but certain high-risk HPV types are associated with cancers.
- Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor and manage the condition.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding condyloma. Clearing up these misunderstandings can help in better awareness and prevention.
- Condyloma is not caused by poor hygiene; it is a sexually transmitted infection.
- You cannot get condyloma from toilet seats or swimming pools.
- Having condyloma does not mean a person has been unfaithful; HPV can remain dormant for years.
- Condyloma can affect anyone who is sexually active, regardless of age or gender.
- The HPV vaccine does not treat existing infections but prevents new ones.
Final Thoughts on Condyloma
Condyloma, or genital warts, are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear as small bumps or groups of bumps in the genital area. While they can be uncomfortable and sometimes embarrassing, they're usually not dangerous. Treatment options include topical medications, cryotherapy, and surgical removal. Prevention is key; vaccines like Gardasil can protect against the most common HPV strains that cause warts. Regular screenings and practicing safe sex can also reduce the risk. If you suspect you have condyloma, consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Staying informed and proactive can help manage and prevent the spread of HPV and its symptoms. Remember, it's a common condition, and help is available.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
