Cerebellar agenesis is a rare congenital disorder where the cerebellum, a part of the brain crucial for motor coordination, learning, memory, language, and behavior, is either partially or completely absent. This condition can stem from genetic mutations or environmental factors like prematurity and perinatal hemorrhage. Patients often face a broad spectrum of challenges, including motor disorders, cognitive impairments, language disabilities, and behavioral issues. Diagnosis typically involves MRI scans, which reveal the extent of cerebellar absence. While some individuals experience severe symptoms, others may lead relatively normal lives with appropriate support and rehabilitation. Understanding cerebellar agenesis is vital for providing optimal care and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Cerebellar Agenesis is a rare condition where the cerebellum is missing or underdeveloped, affecting motor skills and cognitive functions. It requires comprehensive management and ongoing support for affected individuals.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and implications of Cerebellar Agenesis is crucial for providing optimal care. Ongoing research aims to improve diagnostic and treatment methods, contributing to a better understanding of this complex condition.
What is Cerebellar Agenesis?
Cerebellar agenesis is a rare congenital disorder where the cerebellum, a part of the brain responsible for motor coordination and other functions, is either partially or completely absent. This condition can have a wide range of effects on an individual's abilities and development.
-
Definition: Cerebellar agenesis is a condition where the cerebellum is missing or underdeveloped, affecting motor coordination and cognitive functions.
-
Prevalence: This condition is extremely rare, occurring in fewer than 1 in 100,000 births.
-
Causes: It can be caused by genetic mutations, such as those affecting the PTF1A gene, or by environmental factors like prematurity and pre/perinatal hemorrhage.
Development and Diagnosis
Understanding how cerebellar agenesis develops and how it is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
-
Developmental Timeline: The cerebellum starts developing from the ninth gestational week and continues beyond birth, making it susceptible to malformations.
-
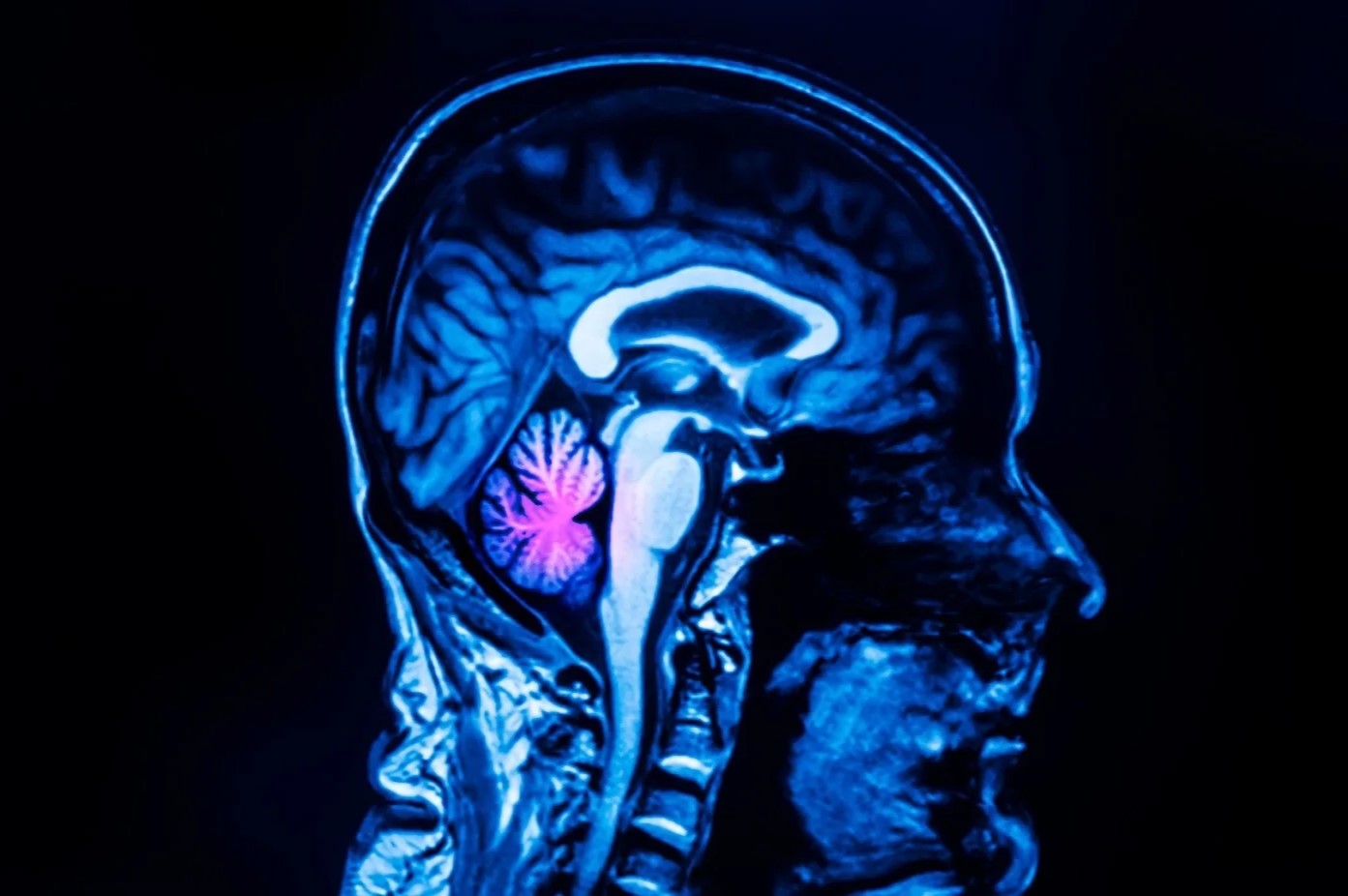
MRI Findings: MRI scans are crucial for diagnosing cerebellar agenesis, showing a complete absence of the cerebellum with small residual vermis.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is often made prenatally through ultrasound or postnatally through MRI, along with a detailed clinical evaluation.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
The symptoms of cerebellar agenesis can vary widely, affecting motor skills, cognitive functions, language, and behavior.
-
Clinical Presentation: Patients often present with a broad spectrum of disabilities, including motor disorders, cognitive impairments, language disabilities, and behavioral disorders.
-
Motor Disorders: Common motor disorders include ataxia (lack of coordination), dysarthria (speech difficulties), dysmetria (impaired ability to judge distance), and dysdiadochokinesia (difficulty with rapid alternating movements).
-
Cognitive Impairments: Cognitive impairments can range from mild to severe, affecting learning, memory, and executive functions.
-
Language Disabilities: Patients may experience delays in language acquisition, particularly in comprehension, and may have difficulties with speech articulation and fluency.
-
Behavioral Disorders: Behavioral issues, such as autism or autistic-like behavior, can also occur, often associated with severe impairments in social and communication skills.
Prognosis and Rehabilitation
The prognosis for cerebellar agenesis varies, and rehabilitation can play a crucial role in improving outcomes.
-
Prognosis: The prognosis depends on the extent and location of the agenesis, with some patients experiencing severe symptoms and others leading relatively normal lives.
-
Rehabilitation: Early intervention through physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help mitigate symptoms and improve functional outcomes.
-
Historical Cases: Historical cases, like that of H.C. in 1939, show that some individuals can lead normal lives despite the condition.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Both genetic and environmental factors can contribute to the development of cerebellar agenesis.
-
Genetic Factors: Mutations in genes such as PTF1A have been linked to cerebellar agenesis, highlighting the importance of genetic research.
-
Environmental Factors: Factors like prematurity and pre/perinatal hemorrhage can also play a role, emphasizing the need for careful prenatal care.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for families with a history of cerebellar agenesis, helping them understand the risks and management options.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand cerebellar agenesis and improve diagnostic and treatment methods.
-
Research Directions: Studies focus on understanding the mechanisms of compensation within the nervous system and improving neuroimaging techniques.
-
MRI in Diagnosis: Advanced neuroimaging techniques like diffusion tensor tractography help assess the integrity of brain connections, aiding in diagnosis.
-
Clinical Studies: Clinical studies have shown a wide range of symptoms in patients, from mild motor impairments to severe cognitive and behavioral deficits.
Impact on Daily Life
Cerebellar agenesis can significantly impact daily life, but with the right support, individuals can achieve better outcomes.
-
Cognitive Development: Cognitive development can be significantly impacted, with some patients experiencing mild intellectual disability and others more severe impairments.
-
Language Development: Language development may be delayed, particularly in comprehension, and patients may have difficulties with speech articulation and fluency.
-
Motor Skills: Motor skills are often severely impaired, affecting an individual's ability to perform daily activities.
-
Family Support: Family support is crucial for managing the condition, with early intervention and ongoing support improving quality of life.
Rehabilitation and Support
Rehabilitation programs and family support play a vital role in managing cerebellar agenesis.
-
Rehabilitation Programs: These programs should include physical therapy to improve motor coordination, occupational therapy to enhance daily functioning, and speech therapy to address communication difficulties.
-
Family Support: Educating families about the condition and its management helps provide optimal care and support for the affected individual.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: Early detection through ultrasound and MRI allows for better planning and preparation for the birth of a child with cerebellar agenesis.
Conclusion
Cerebellar agenesis is a complex condition that requires comprehensive management. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and implications is crucial for providing optimal care to affected individuals. Continued research and improved diagnostic tools will help in better managing this condition and improving the quality of life for those affected.
-
Compensation Mechanisms: The brain's ability to compensate for lost cerebellar functions is a significant area of research, although this compensation is not always perfect.
-
Behavioral Correlates: Behavioral correlates include a range of neuropsychological and psychiatric impairments, with severity varying widely.
-
Research and Future Directions: Ongoing research aims to better understand cerebellar agenesis and improve diagnostic and treatment methods, contributing to a better understanding of this complex condition.
Final Thoughts on Cerebellar Agenesis
Cerebellar agenesis is a rare condition where the cerebellum is partially or completely absent. This impacts motor coordination, cognitive functions, language, and behavior. Causes range from genetic mutations to environmental factors like prematurity. Symptoms vary widely, from severe motor disorders to mild cognitive impairments. Diagnosis often involves MRI scans, revealing the extent of cerebellar absence. Rehabilitation, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, is crucial for improving quality of life. Family support and genetic counseling play vital roles in managing the condition. Despite its challenges, some individuals with cerebellar agenesis lead relatively normal lives. Ongoing research aims to better understand and manage this complex disorder. Understanding cerebellar agenesis helps in providing optimal care and improving the lives of those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.