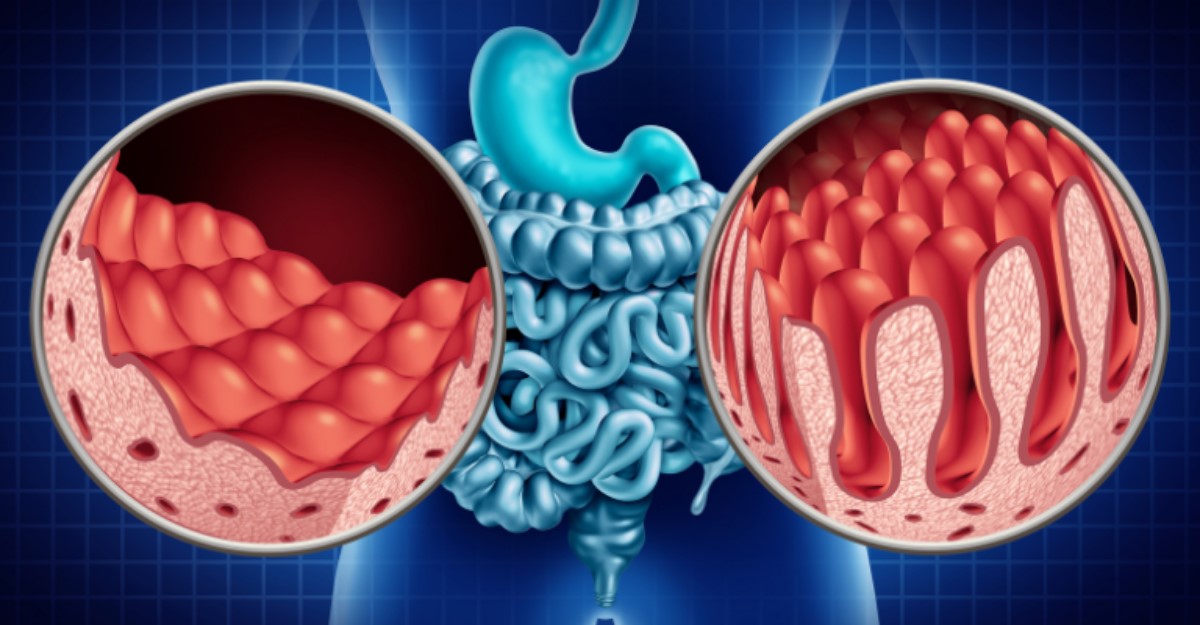
What is Celiac Sprue? Celiac sprue, also known as celiac disease, is a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by consuming gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with celiac disease eats gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the small intestine's villi, tiny finger-like projections that absorb nutrients. This damage leads to malabsorption of essential nutrients, causing various health issues. Symptoms can range from digestive problems like diarrhea and abdominal pain to more subtle signs such as fatigue and anemia. The only effective treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet. Ignoring this condition can result in severe complications, including osteoporosis, neurological disorders, and even certain cancers.
Key Takeaways:
- Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, affecting 1% of the global population. Early diagnosis and strict gluten-free diet are crucial for managing this condition and preventing serious health complications.
- Untreated celiac disease can lead to various complications, including osteoporosis, neurological disorders, and increased cancer risk. Raising awareness and education about celiac disease is essential for early diagnosis and proper management.
What is Celiac Sprue?
Celiac sprue, also known as celiac disease, is a chronic autoimmune disorder. It affects the small intestine and is triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Here are some essential facts to understand this condition better:
-
Definition and Causes: Celiac sprue is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, damaging the villi in the small intestine and interfering with nutrient absorption.
-
Prevalence: About 1% of the global population has celiac disease, though some regions report higher rates.
-
Genetic Predisposition: More common in people with a genetic predisposition, especially those of European, Middle Eastern, Indian, South American, and North African descent.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial for managing celiac disease. Symptoms can vary widely, making diagnosis challenging.
-
Symptoms: Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and nutrient malabsorption. Some individuals may have no symptoms at all.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves serological tests (like anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies) and a small bowel biopsy to confirm intestinal damage.
-
Treatment: The only treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet. Even small amounts of gluten can trigger intestinal damage.
Complications and Associated Conditions
Untreated celiac disease can lead to various complications and increase the risk of other health issues.
-
Complications: If untreated, it can lead to osteoporosis, anemia, malnutrition, neurological disorders, and increased cancer risk.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Higher risk of developing other autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes, thyroid diseases, and rheumatic diseases like Sjögren’s syndrome.
-
Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorption can cause deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, including iron, calcium, and B vitamins.
Extraintestinal Manifestations
Celiac disease doesn't just affect the gut. It can have symptoms and effects throughout the body.
-
Extraintestinal Manifestations: Symptoms can include dermatitis herpetiformis, hepatobiliary signs, and neurological abnormalities.
-
Lactose Intolerance: Some individuals may experience lactose intolerance due to mucosal injury in the small intestine, which heals over time.
-
Malabsorption Syndrome: Classic presentation includes diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal bloating, and steatorrhea.
Neurological and Cancer Risks
Celiac disease can also impact neurological health and increase cancer risks.
-
Neurological Symptoms: Symptoms can include ADHD, headaches, lack of muscle coordination, seizures, ataxia, dementia, neuropathy, myopathy, and multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
-
Small Intestine Cancer: Increased risk of small intestine cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma in untreated individuals.
-
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies: Deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, as well as B vitamins, can occur due to malabsorption.
Other Health Issues
Celiac disease can lead to various other health complications if not managed properly.
-
Gall Bladder Malfunction: Untreated celiac disease can lead to gall bladder malfunction and liver diseases like autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis.
-
Pancreatic Insufficiency: Some individuals may experience pancreatic insufficiency, exacerbating malabsorption issues.
-
Infertility and Miscarriage: Can affect fertility and increase miscarriage risk due to nutrient malabsorption.
-
Liver Failure: Untreated celiac disease can lead to liver failure and other liver-related complications.
-
Long-Term Health Conditions: Early onset osteoporosis or osteopenia, heart disease, and other long-term health conditions are potential complications.
Age and Diagnosis
The age at which celiac disease is diagnosed can significantly impact the risk of developing other conditions.
-
Age of Diagnosis: Early diagnosis (ages 2-4) lowers the chance of developing another autoimmune condition compared to later diagnoses.
-
Undiagnosed or Untreated Celiac Disease: Can lead to a range of serious health problems, including long-term health conditions and other autoimmune disorders.
Prevalence and Family History
Understanding the prevalence and genetic factors can help in early detection and management.
-
Prevalence in Different Populations: Varies across populations. For instance, a mass screening in Italy found a prevalence of 1.6%, while in Finland, it was 1.99%.
-
Global Incidence: A meta-analysis found that the global incidence of celiac disease is significantly increasing, likely due to environmental factors.
-
Family History: Strong familial component, with up to 44% of first-degree relatives having the condition.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity and Economic Impact
Not everyone who reacts to gluten has celiac disease, and the economic impact of undiagnosed celiac disease is significant.
-
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: Up to 6% of Americans have non-celiac gluten sensitivity, which does not damage the small intestine but can cause similar symptoms.
-
Diagnostic Challenges: Often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. The average time to correct diagnosis is 6-10 years.
-
Economic Impact: Undiagnosed celiac disease can significantly increase healthcare costs. Over four years, individuals with undiagnosed celiac disease cost an average of $3,964 more than healthy individuals.
Healing and Awareness
Healing on a gluten-free diet and raising awareness are crucial for managing celiac disease.
-
Healing on Gluten-Free Diet: One in five children with celiac disease does not heal on a gluten-free diet, highlighting the importance of strict adherence.
-
Awareness and Education: Raising awareness about celiac disease is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Sharing fast facts on social media can help spread education among the medical, science, culinary communities, and the general public.
Understanding Celiac Sprue
Celiac sprue, or celiac disease, is a serious autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten. Affecting about 1% of the global population, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications. From abdominal pain and diarrhea to more severe issues like osteoporosis and neurological disorders, the impact is significant. Diagnosis involves serological tests and a small bowel biopsy. The only effective treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet. Ignoring this can result in severe health problems, including increased cancer risks and other autoimmune diseases. Awareness and early diagnosis are crucial for managing this condition. Sharing information about celiac disease can help improve the lives of those affected. Remember, even small amounts of gluten can cause harm, so strict adherence to a gluten-free diet is essential for those diagnosed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


