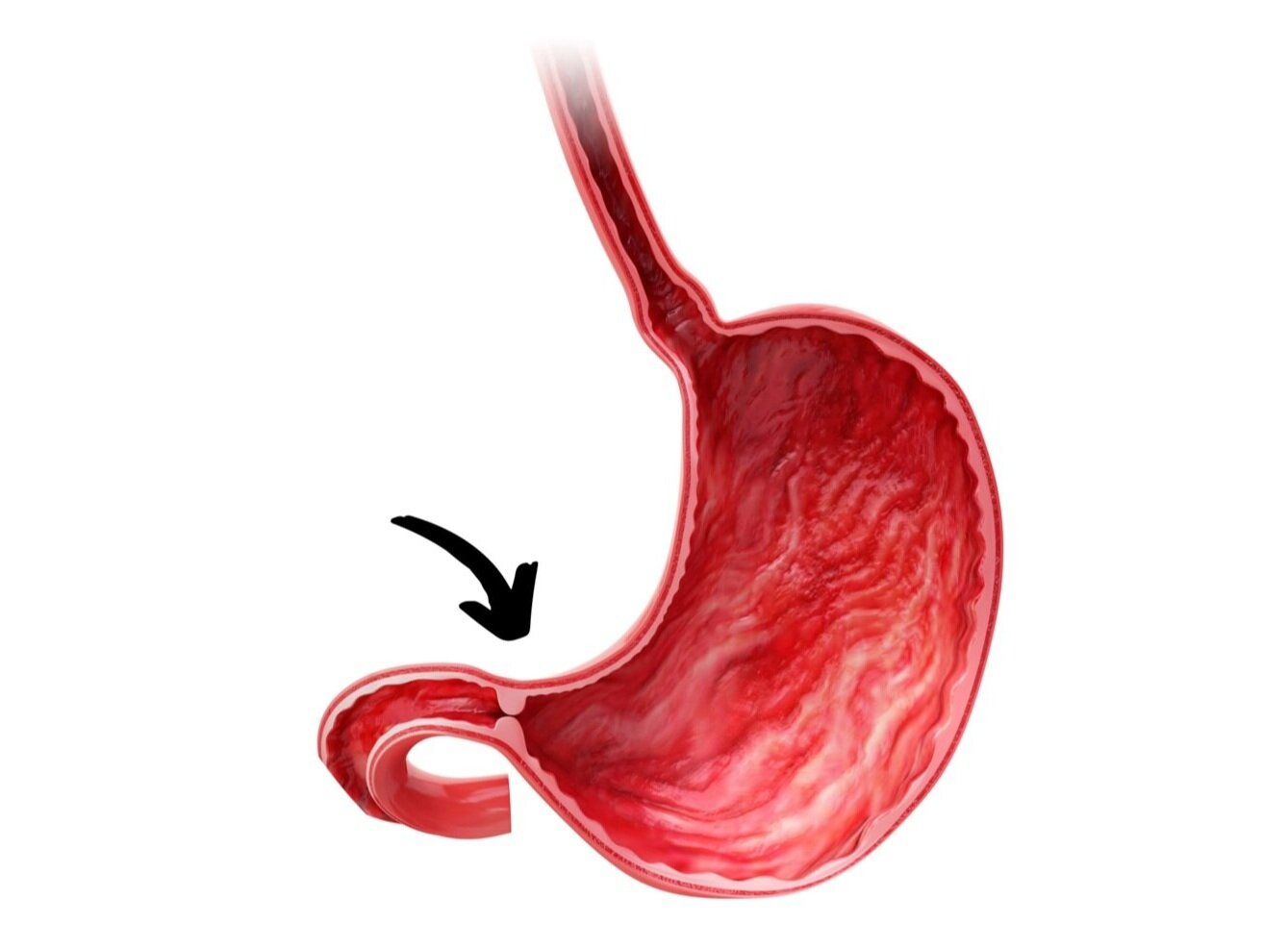
What is pyloric stenosis? Pyloric stenosis is a condition where the passage between the stomach and the small intestine thickens, causing a blockage. This can lead to severe vomiting, dehydration, and weight loss in infants. The exact cause remains unknown, but it often runs in families. Symptoms usually appear within the first few weeks of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications. Surgery, known as pyloromyotomy, is the most common treatment and has a high success rate. Understanding the signs and seeking prompt medical attention can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively.
What is Pyloric Stenosis?
Pyloric stenosis is a condition that affects infants, causing severe vomiting due to the narrowing of the pylorus, the passage between the stomach and small intestine. This condition can lead to dehydration and weight loss if not treated promptly.
- Pyloric stenosis typically appears in infants between 2 to 8 weeks old.
- The condition is more common in boys than girls, with a ratio of about 4:1.
- Symptoms often include projectile vomiting, which can be forceful enough to travel several feet.
- Infants with pyloric stenosis may show signs of hunger soon after vomiting.
- Dehydration is a significant risk, often indicated by fewer wet diapers and a sunken soft spot on the head.
- The exact cause of pyloric stenosis is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors may play a role.
- Pyloric stenosis can sometimes be detected through a physical exam, where a doctor feels an olive-shaped mass in the abdomen.
- Ultrasound is the most common imaging test used to diagnose pyloric stenosis.
- Blood tests may reveal an electrolyte imbalance due to prolonged vomiting.
- The definitive treatment for pyloric stenosis is a surgical procedure called pyloromyotomy.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how pyloric stenosis is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment.
- Infants may exhibit visible waves of peristalsis, the muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
- Weight loss or poor weight gain is a common symptom due to the inability to keep food down.
- Babies might become lethargic or less active as the condition progresses.
- A barium swallow X-ray can also be used to diagnose pyloric stenosis, showing the narrowed pylorus.
- In some cases, the condition can be misdiagnosed as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Treatment and Recovery
Once diagnosed, treatment is usually straightforward and highly effective.
- Pyloromyotomy involves making an incision in the muscles of the pylorus to widen the passage.
- The surgery is typically performed laparoscopically, resulting in smaller incisions and quicker recovery.
- Most infants can start feeding within hours after surgery.
- Full recovery usually occurs within a few days, with most babies discharged from the hospital within 48 hours.
- Post-surgery, infants generally have a normal feeding pattern and gain weight appropriately.
Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for infants who undergo treatment for pyloric stenosis is excellent.
- There are usually no long-term complications after a successful pyloromyotomy.
- The condition rarely recurs after surgery.
- Infants treated for pyloric stenosis typically reach developmental milestones on time.
- Follow-up visits with a pediatrician ensure that the infant is recovering well and gaining weight.
- Parents are advised to monitor their baby's feeding and weight gain closely after surgery.
Interesting Facts
Here are some additional interesting facts about pyloric stenosis.
- Pyloric stenosis has been recognized for centuries, with descriptions dating back to ancient medical texts.
Final Thoughts on Pyloric Stenosis
Pyloric stenosis is a condition that affects infants, causing severe vomiting and requiring prompt medical attention. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options can make a significant difference in a child's health. Early detection is key, as it allows for timely intervention and a smoother recovery process.
Parents should watch for signs like projectile vomiting, dehydration, and weight loss. If these symptoms appear, seeking medical advice is crucial. Treatment usually involves a surgical procedure called pyloromyotomy, which has a high success rate and allows most babies to recover fully.
Awareness and education about pyloric stenosis can help parents and caregivers act quickly, ensuring the best possible outcome for affected infants. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to your child's health. Stay informed and proactive.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
