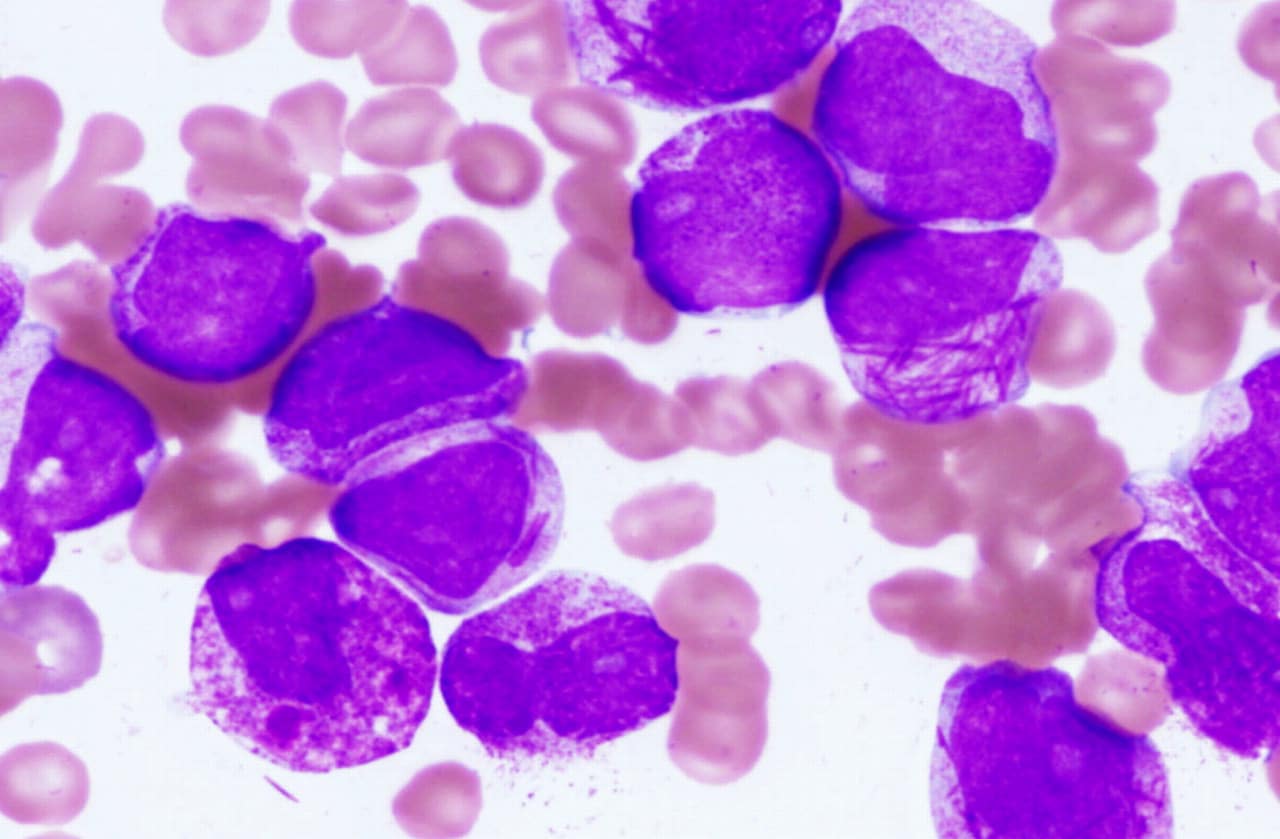
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) is a rare but highly treatable type of blood cancer. It affects the bone marrow, leading to an overproduction of immature white blood cells called promyelocytes. These cells crowd out healthy blood cells, causing symptoms like fatigue, easy bruising, and frequent infections. APL is unique because it often involves a specific genetic mutation, the PML-RARA fusion gene. Treatment typically includes a combination of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide, which has significantly improved survival rates. Understanding APL can help patients and families navigate this challenging diagnosis with more confidence and hope.
What is Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia?
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) is a rare type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) characterized by the accumulation of immature white blood cells called promyelocytes. Here are some fascinating facts about APL:
-
APL is caused by a genetic mutation involving the PML and RARA genes, which leads to the production of an abnormal fusion protein.
-
This type of leukemia accounts for about 10-15% of all AML cases.
-
APL is most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 20 and 50.
-
The disease is slightly more prevalent in males than females.
-
Symptoms of APL can include fatigue, easy bruising, bleeding, and frequent infections.
Diagnosis and Treatment of APL
Diagnosing and treating APL involves a combination of medical tests and therapies. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving patient outcomes.
-
APL is often diagnosed through blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and genetic testing.
-
The presence of the PML-RARA fusion gene is a key diagnostic marker for APL.
-
Treatment typically begins with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) therapy, which helps mature the abnormal promyelocytes.
-
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) is another effective treatment option for APL.
-
Combining ATRA and ATO has significantly improved survival rates for APL patients.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for APL has improved dramatically over the years, thanks to advancements in treatment and early diagnosis.
-
The five-year survival rate for APL patients is now over 80%.
-
Early treatment initiation is critical, as delays can lead to life-threatening complications.
-
APL patients are at high risk for a condition called disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which can cause severe bleeding.
-
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential for managing APL and preventing relapse.
-
Bone marrow transplants may be considered for patients who do not respond to standard treatments.
Research and Advances in APL
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights and potential therapies for APL, offering hope for even better outcomes in the future.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of targeted therapies that specifically attack the PML-RARA fusion protein.
-
Immunotherapy is being investigated as a potential treatment option for APL.
-
Clinical trials are testing new drug combinations to improve treatment efficacy and reduce side effects.
-
Advances in genetic testing have made it easier to identify APL and tailor treatments to individual patients.
-
Scientists are studying the role of epigenetics in APL to develop new therapeutic strategies.
Living with APL
Living with APL can be challenging, but with the right support and care, patients can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Support groups and counseling can help APL patients and their families cope with the emotional impact of the disease.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall well-being.
-
Patients should avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of complications.
-
Regular medical check-ups and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for managing APL.
-
Advances in treatment and supportive care have greatly improved the quality of life for APL patients.
Final Thoughts on Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) stands out due to its unique characteristics and treatment options. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can significantly improve survival rates. APL's link to the PML-RARA gene fusion makes it distinct among leukemias. Treatments like all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide have revolutionized outcomes, turning a once fatal disease into a highly treatable one. Awareness and understanding of APL are crucial for early intervention. Regular check-ups and being vigilant about symptoms can make a big difference. Remember, medical advancements continue to evolve, offering hope and better outcomes for patients. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and support research efforts. Knowledge is power when it comes to battling diseases like APL.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


