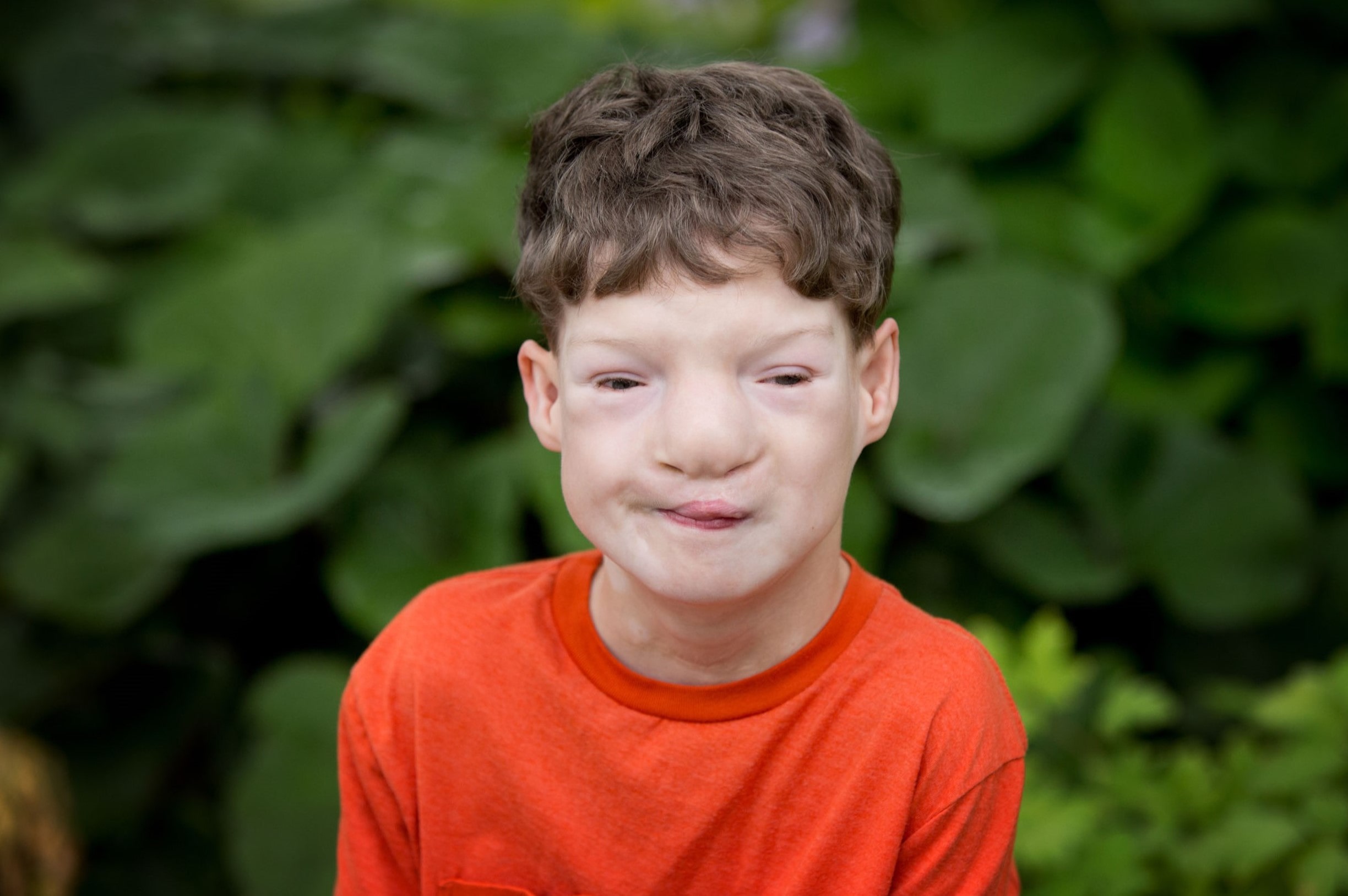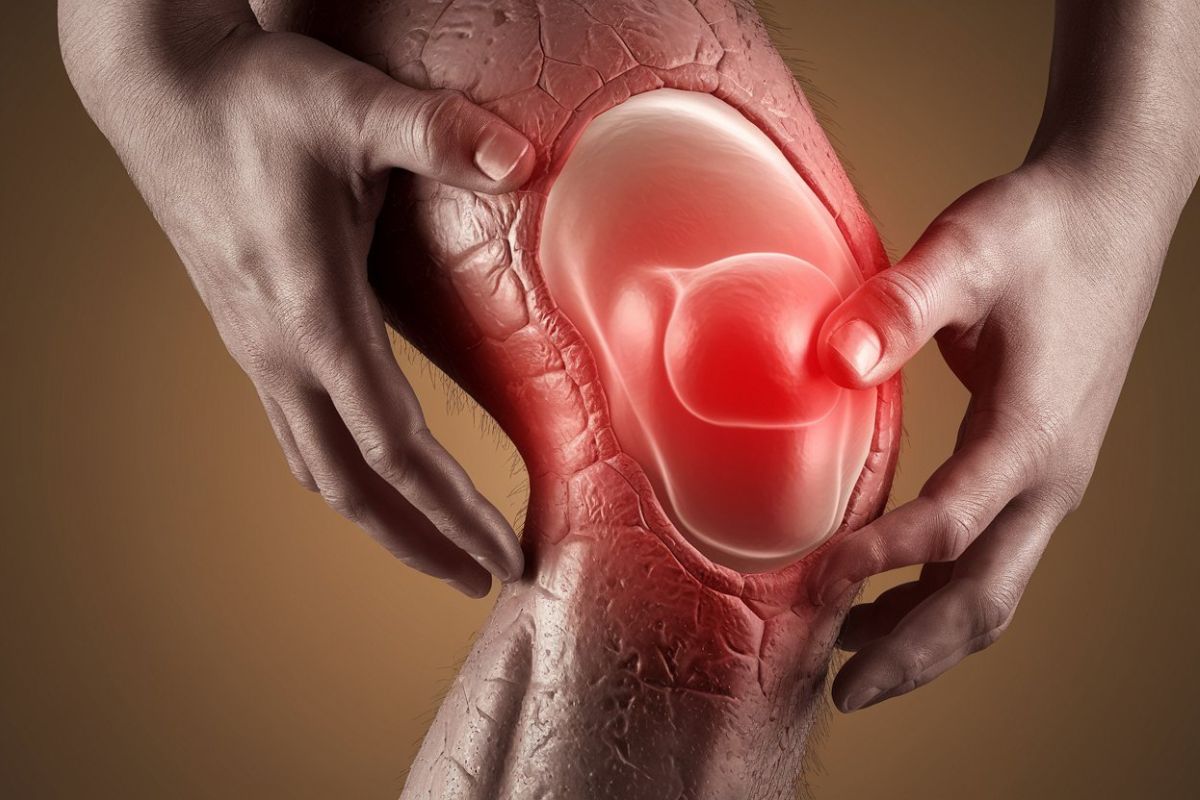
Genitopatellar Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. Characterized by distinctive facial features, genital abnormalities, and knee problems, this condition can significantly impact a person's life. Caused by mutations in the KAT6B gene, it often leads to developmental delays and intellectual disabilities. Symptoms vary widely, making each case unique. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing the condition and improving quality of life. Understanding the complexities of Genitopatellar Syndrome can help families and healthcare providers offer better support and care. Here are 20 facts to help you grasp the essentials of this rare disorder.
What is Genitopatellar Syndrome?
Genitopatellar Syndrome (GPS) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple parts of the body, including the genitals, knees, and other skeletal structures. Understanding this condition can help those affected and their families manage it better.
Genetic Causes of Genitopatellar Syndrome
The syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in specific genes. These genetic changes can lead to various physical and developmental issues.
- Mutations in the KAT6B Gene: GPS is often linked to mutations in the KAT6B gene. This gene plays a crucial role in regulating the development of bones and other tissues.
- Autosomal Dominant Inheritance: The condition follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means a single copy of the mutated gene from one parent can cause the disorder.
- De Novo Mutations: Many cases result from new mutations, known as de novo mutations, which occur spontaneously and are not inherited from parents.
Physical Characteristics of Genitopatellar Syndrome
Individuals with GPS exhibit distinct physical traits. These characteristics can vary in severity from person to person.
- Underdeveloped Kneecaps: One of the hallmark features is underdeveloped or absent kneecaps, leading to mobility issues.
- Genital Abnormalities: Males may have undescended testes, while females might experience underdeveloped genitalia.
- Facial Dysmorphisms: Common facial features include a broad nasal bridge, a high forehead, and widely spaced eyes.
- Joint Contractures: Stiffness in joints, particularly in the knees and elbows, is frequently observed.
- Short Stature: Many affected individuals have a shorter-than-average height due to skeletal abnormalities.
Developmental and Cognitive Aspects
GPS doesn't just affect physical appearance. It can also impact cognitive and developmental milestones.
- Delayed Development: Children with GPS often experience delays in reaching developmental milestones like walking and talking.
- Intellectual Disability: Mild to moderate intellectual disability is common, affecting learning and daily functioning.
- Speech Difficulties: Speech may be delayed or impaired, requiring speech therapy for improvement.
- Behavioral Issues: Some children may exhibit behavioral challenges, including hyperactivity and attention deficits.
Medical Complications Associated with GPS
Managing GPS involves addressing various medical complications that can arise due to the syndrome.
- Heart Defects: Congenital heart defects, such as holes in the heart, may be present and require medical intervention.
- Kidney Problems: Some individuals may have kidney abnormalities, which can lead to urinary issues.
- Hearing Loss: Hearing impairment is another possible complication, necessitating regular hearing checks.
- Respiratory Issues: Respiratory problems, including frequent infections, can occur due to structural anomalies.
Diagnosis and Management
Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for those with GPS.
- Genetic Testing: Confirming the diagnosis often involves genetic testing to identify mutations in the KAT6B gene.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Treatment typically requires a team of specialists, including geneticists, orthopedists, and speech therapists.
- Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help improve mobility and joint function.
- Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct skeletal or genital abnormalities.
Final Thoughts on Genitopatellar Syndrome
Genitopatellar Syndrome, though rare, impacts many lives. Understanding its symptoms like genital abnormalities, patellar hypoplasia, and developmental delays can help in early diagnosis and better management. Families dealing with this condition often face unique challenges, but awareness and support can make a significant difference. Genetic counseling plays a crucial role in providing information and emotional support to affected families.
Medical advancements continue to improve the quality of life for those with Genitopatellar Syndrome. Researchers are constantly working on new treatments and therapies. Staying informed about the latest developments can offer hope and practical solutions.
Remember, every bit of knowledge helps in creating a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with this syndrome. Keep learning, stay compassionate, and spread awareness. Together, we can make a positive impact.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.