Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the bones and muscles. Characterized by distinctive facial features, joint deformities, and muscle weakness, this condition presents unique challenges for those affected. Named after the doctors who first described it in 1938, Freeman and Sheldon, the syndrome is also known as "whistling face syndrome" due to the puckered appearance of the lips. Caused by mutations in the MYH3 gene, it can vary widely in severity. Understanding the symptoms and treatments available can help families and caregivers provide better support. Let's explore 20 intriguing facts about Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome to shed light on this complex condition.
What is Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome?
Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome (FSS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the bones and muscles. It is also known as "whistling face syndrome" due to the characteristic facial appearance of individuals with this condition. Here are some intriguing facts about this unique syndrome.
-
Rare Genetic Disorder: FSS is extremely rare, with only about 100 cases reported worldwide. This makes it one of the least understood genetic conditions.
-
Facial Characteristics: People with FSS often have a distinctive facial appearance, including a small mouth, pursed lips, and a "whistling" expression.
-
Inheritance Pattern: FSS can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner. This means it can be passed down from just one parent or both.
-
Caused by Mutations: Mutations in the MYH3 gene are responsible for FSS. This gene is crucial for muscle development.
Physical Manifestations of Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome
The physical traits of FSS are quite distinctive and can affect various parts of the body. Here are some key physical manifestations.
-
Joint Contractures: Individuals with FSS often have joint contractures, which means their joints are permanently bent or fixed in one position.
-
Scoliosis: Many people with FSS develop scoliosis, a condition where the spine curves sideways.
-
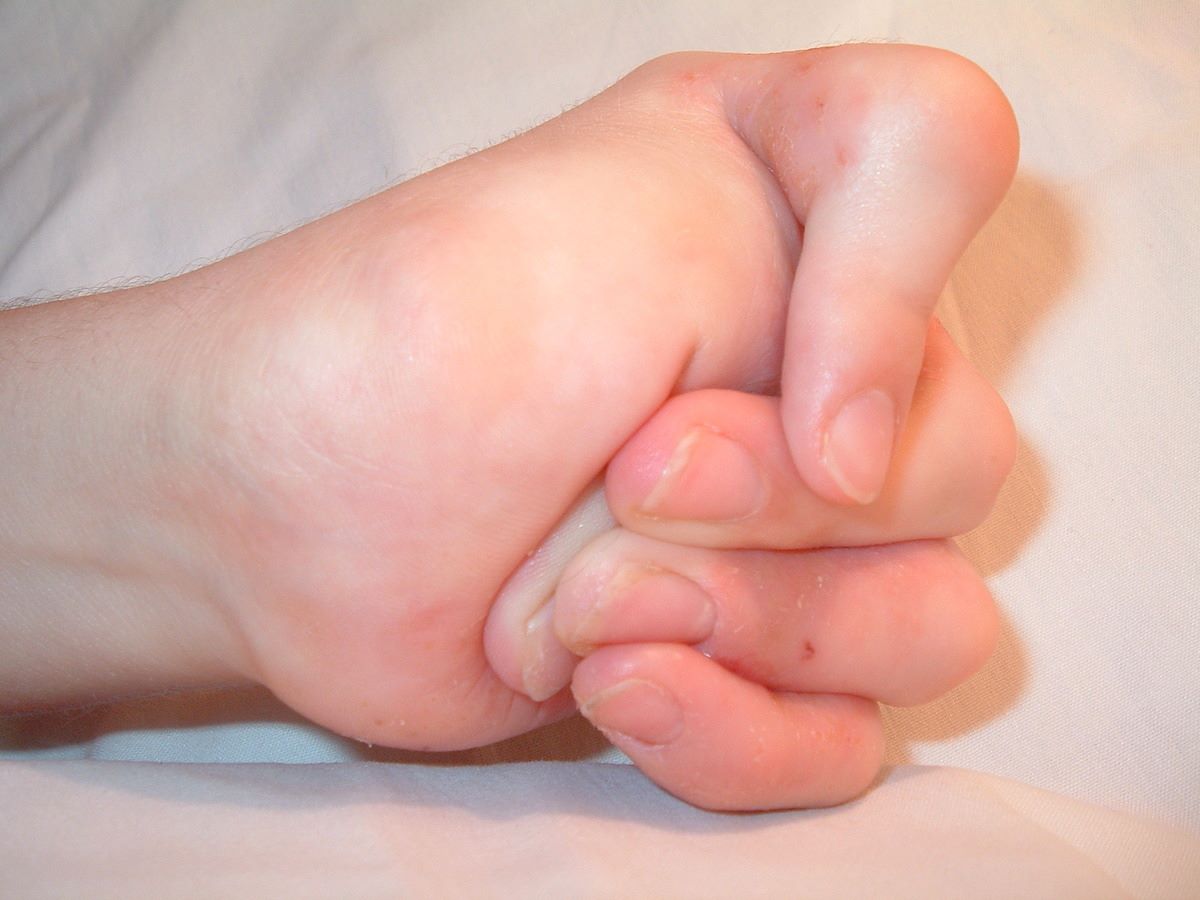
Clubfoot: Clubfoot, a condition where the foot is twisted out of shape or position, is common in those with FSS.
-
Small Chin: A small chin, also known as micrognathia, is another characteristic feature.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with FSS
Living with FSS comes with its own set of challenges. These can range from physical limitations to social and emotional hurdles.
-
Speech Difficulties: Due to the small mouth and other facial abnormalities, individuals with FSS often face challenges with speech.
-
Feeding Issues: The small mouth and jaw can also make feeding difficult, especially in infants.
-
Respiratory Problems: Some individuals may experience respiratory issues due to the structural abnormalities in their face and throat.
-
Social Stigma: The distinctive facial features can sometimes lead to social stigma and emotional challenges.
Medical Management and Treatment
While there is no cure for FSS, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgical Interventions: Surgery can help correct some of the physical abnormalities, such as clubfoot and joint contractures.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can improve mobility and reduce the severity of joint contractures.
-
Speech Therapy: Speech therapy can assist individuals in overcoming speech difficulties.
-
Nutritional Support: Specialized feeding techniques and nutritional support can help manage feeding issues.
Research and Future Directions
Research on FSS is ongoing, with scientists striving to understand the condition better and develop more effective treatments.
-
Genetic Research: Researchers are studying the MYH3 gene to understand how its mutations lead to FSS.
-
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are being conducted to test new treatments and therapies for FSS.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries are being established to collect data and improve our understanding of the condition.
-
Support Groups: Support groups and organizations are working to provide resources and support for individuals with FSS and their families.
Final Thoughts on Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome
Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome (FSS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects muscle and bone development. Understanding FSS helps in recognizing its symptoms early, leading to better management. Key features include facial abnormalities, joint deformities, and scoliosis. Early intervention with physical therapy and surgeries can improve quality of life. Genetic counseling is crucial for families affected by FSS.
Raising awareness about Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome can lead to better support systems and research funding. Connecting with support groups provides emotional and practical help for those living with FSS. Knowledge is power, and staying informed about the latest treatments and therapies can make a significant difference.
Remember, every bit of information shared contributes to a broader understanding and better care for those with Freeman–Sheldon Syndrome. Keep learning, stay supportive, and spread awareness.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.