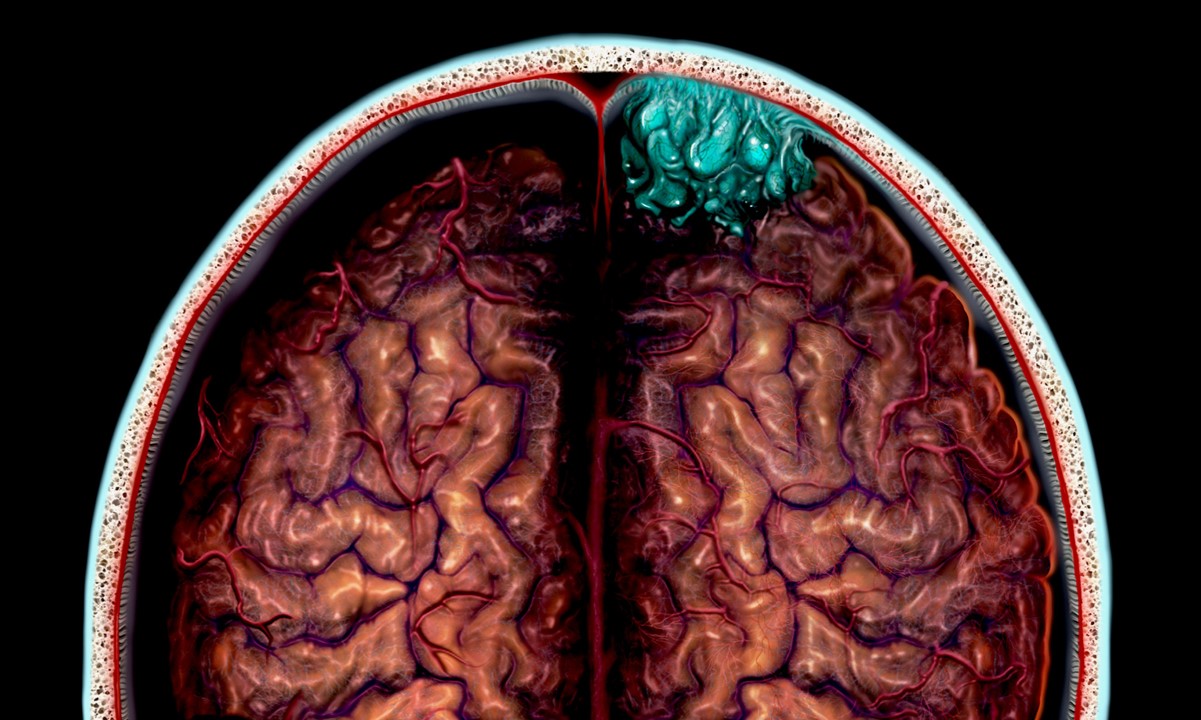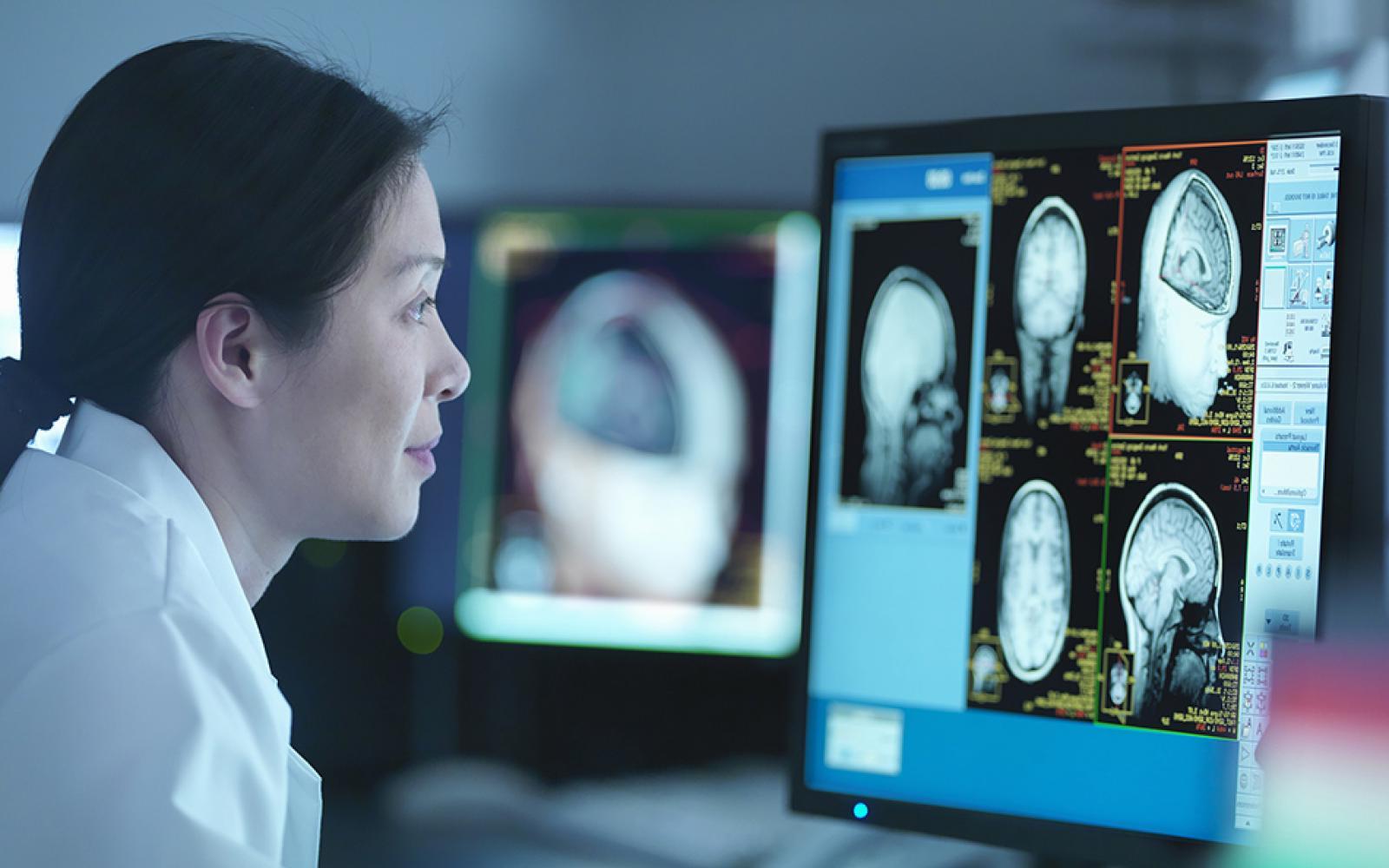
What is a benign astrocytoma? It's a type of brain tumor that originates from astrocytes, a kind of glial cell in the brain. Unlike malignant tumors, benign astrocytomas grow slowly and are less aggressive. These tumors can appear in various parts of the brain, often causing symptoms like headaches, seizures, and cognitive changes. Diagnosis usually involves imaging studies and a biopsy. Treatment often includes surgical removal, sometimes followed by radiation therapy. Understanding benign astrocytomas is crucial for effective management and improving patient outcomes. Let's dive into 20 essential facts about this condition to better grasp its nature and treatment options.
What is Benign Astrocytoma?
Benign astrocytoma, also known as low-grade astrocytoma, is a type of brain tumor that originates from astrocytes, a type of glial cell in the brain. These tumors are generally slow-growing and less aggressive compared to their malignant counterparts. Here are 20 key facts about benign astrocytoma:
-
Definition: Benign astrocytoma is a type of glioma, which is a tumor that arises from glial cells in the brain. It is characterized by its slow growth and non-invasive nature.
-
Prevalence: Benign astrocytomas are relatively rare, accounting for about 10% of all primary brain tumors. They are more common in adults than in children.
Where Do Benign Astrocytomas Occur?
These tumors can develop in various parts of the brain, but some areas are more commonly affected than others.
- Location: These tumors can occur in various parts of the brain, but they are most commonly found in the cerebral hemispheres, particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes.
Symptoms of Benign Astrocytoma
The symptoms of benign astrocytoma can vary widely depending on the location of the tumor. Here are some common symptoms:
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in the face or limbs, and cognitive changes such as memory loss or difficulty with speech and language.
How is Benign Astrocytoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging studies and biopsy to confirm the presence and type of tumor.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging studies like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans, as well as biopsy to confirm the presence and type of tumor. MRI is particularly useful for visualizing the tumor's extent and relationship to surrounding brain structures.
Understanding the Histopathology
Histopathological examination of biopsy tissue reveals the characteristic features of astrocytoma.
- Histopathology: Histopathological examination of biopsy tissue reveals the characteristic features of astrocytoma, including the presence of astrocytes with varying degrees of atypia and mitotic activity. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies these tumors based on their histological grade, with low-grade astrocytomas being classified as Grade I or II.
WHO Classification System
The WHO classification system categorizes gliomas into four grades based on their histological features and clinical behavior.
- WHO Classification: The WHO classification system categorizes gliomas into four grades based on their histological features and clinical behavior. Grade I gliomas are typically benign and include pilocytic astrocytomas, while Grade II gliomas include low-grade astrocytomas like those discussed here.
Treatment Options for Benign Astrocytoma
Treatment for benign astrocytoma often involves surgical resection of the tumor. Here are some common treatment options:
- Treatment Options: Treatment for benign astrocytoma often involves surgical resection of the tumor. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while preserving surrounding brain tissue. In some cases, radiation therapy may be recommended, especially if the tumor is not completely resectable or if there is a high risk of recurrence.
Advances in Surgical Techniques
Modern neurosurgical techniques have significantly evolved over the years.
- Surgical Techniques: Surgical techniques for removing benign astrocytomas have evolved significantly over the years. Modern neurosurgical techniques include the use of microsurgical instruments, intraoperative imaging, and awake craniotomy to minimize the risk of complications and improve outcomes.
Role of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is sometimes used in conjunction with surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is sometimes used in conjunction with surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. However, it is generally reserved for cases where the tumor is not completely resectable or in patients with a high risk of recurrence based on histological features or clinical factors.
Chemotherapy and Benign Astrocytoma
Chemotherapy is not typically used for treating benign astrocytomas due to their slow growth rate and low mitotic activity.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is not typically used for treating benign astrocytomas due to their slow growth rate and low mitotic activity. However, in some cases where the tumor is malignant or there is evidence of aggressive behavior, chemotherapy may be considered.
Prognosis for Patients
The prognosis for patients with benign astrocytoma is generally favorable, especially if the tumor is completely resected.
- Prognosis: The prognosis for patients with benign astrocytoma is generally favorable, especially if the tumor is completely resected. Recurrence rates are lower compared to higher-grade gliomas, and patients can often achieve long-term survival with appropriate treatment.
Dealing with Recurrent Tumors
If a benign astrocytoma recurs, it is often classified as a higher-grade glioma.
- Recurrent Tumors: If a benign astrocytoma recurs, it is often classified as a higher-grade glioma (Grade III or IV). Recurrent tumors may require more aggressive treatment strategies, including a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Genetic Factors in Development
Genetic alterations play a significant role in the development of gliomas, including benign astrocytomas.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic alterations play a significant role in the development of gliomas, including benign astrocytomas. Common genetic mutations include those in the IDH1 and IDH2 genes, which are often associated with lower-grade gliomas.
Importance of Molecular Markers
Molecular markers such as IDH1/IDH2 mutations and 1p/19q codeletion status can help in diagnosing and subclassifying gliomas.
- Molecular Markers: Molecular markers such as IDH1/IDH2 mutations and 1p/19q codeletion status can help in diagnosing and subclassifying gliomas. These markers are increasingly used in clinical practice to guide treatment decisions.
Quality of Life for Patients
The quality of life for patients with benign astrocytoma can vary significantly depending on the location and extent of the tumor.
- Quality of Life: The quality of life for patients with benign astrocytoma can vary significantly depending on the location and extent of the tumor. Early intervention and effective treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
Importance of Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms and complications associated with benign astrocytoma.
- Supportive Care: Supportive care plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms and complications associated with benign astrocytoma. This includes pain management, seizure control, and rehabilitation services to address any functional deficits.
Ongoing Research and Development
Ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of glioma biology and develop more effective treatments.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of glioma biology and develop more effective treatments. This includes the use of immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and innovative surgical techniques.
Importance of Patient Education
Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and potential outcomes is essential for informed decision-making.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and potential outcomes is essential for informed decision-making. Patient education programs can help patients and their families navigate the complexities of brain tumor management.
Multidisciplinary Care Approach
The management of benign astrocytoma often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals.
- Multidisciplinary Care: The management of benign astrocytoma often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving neurosurgeons, neurologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, and other healthcare professionals. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive care tailored to individual patient needs.
Final Thoughts on Benign Astrocytoma
Benign astrocytoma, a type of brain tumor, is slow-growing and less aggressive. It starts in astrocytes, a kind of glial cell. Though rare, it can cause symptoms like headaches, seizures, and cognitive changes. Diagnosis involves MRI and biopsy. Treatment often includes surgery, sometimes followed by radiation. Chemotherapy is less common. Prognosis is generally good if the tumor is fully removed. Recurrence can happen, sometimes leading to more aggressive treatment. Genetic factors and molecular markers play a role in diagnosis and treatment. Quality of life varies but can improve with early intervention. Supportive care is crucial. Ongoing research aims to find better treatments. Patient education and multidisciplinary care are essential for managing this condition. Understanding benign astrocytoma helps in providing optimal care and improving patient outcomes.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.