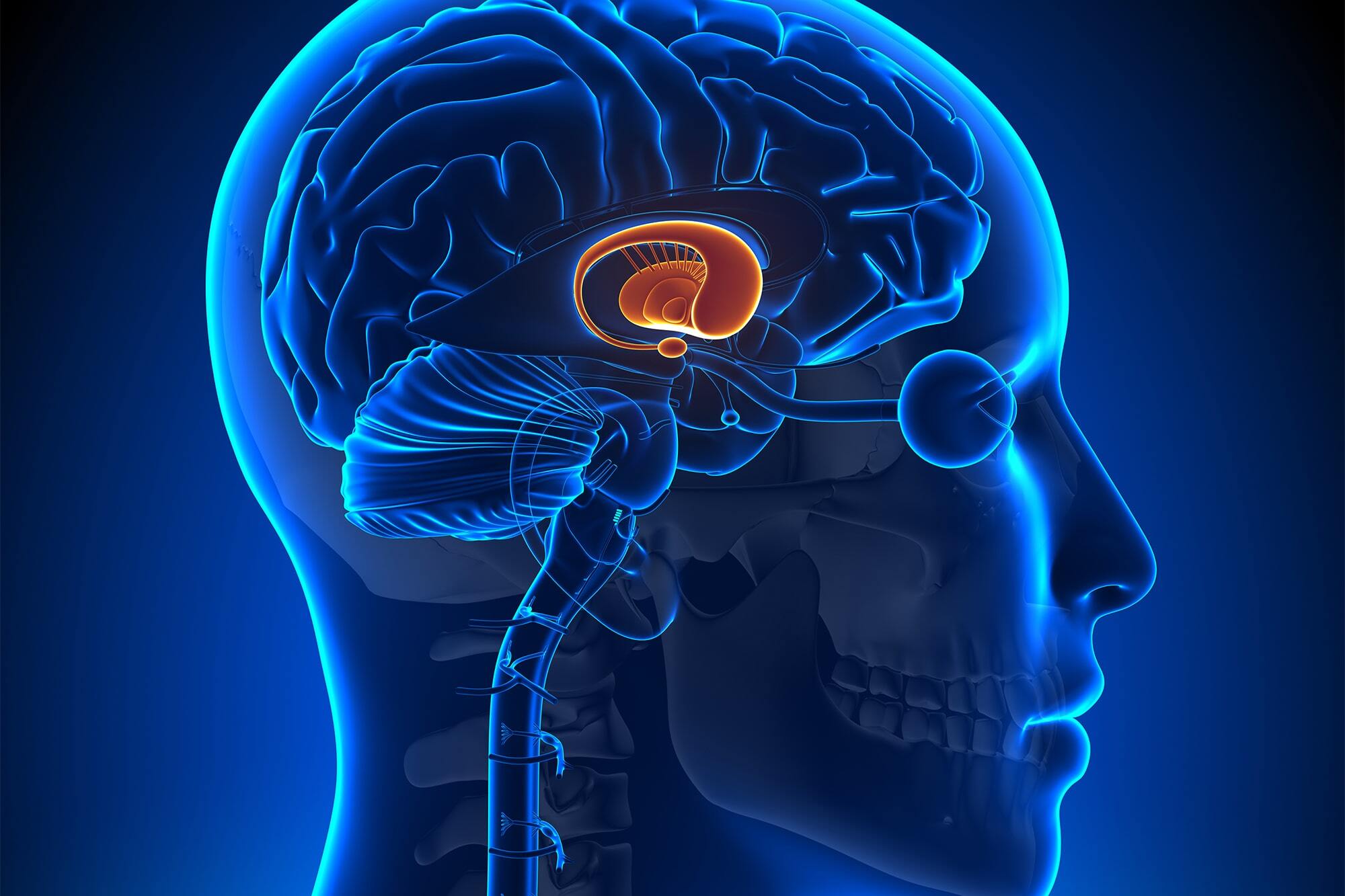
What are Basal Ganglia Diseases? Basal ganglia diseases involve dysfunction in a group of subcortical nuclei located at the base of the forebrain. These nuclei, including the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra, play a crucial role in motor control, learning, executive functions, and emotional behaviors. When these structures malfunction, it can lead to various movement disorders and neurological conditions. Examples include Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, dystonia, and chorea. Understanding these diseases is essential for developing effective treatments and improving the quality of life for those affected. Let's dive into 20 key facts about these complex conditions.
Understanding the Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei located deep within the brain. They play a crucial role in controlling movement, learning new motor skills, and regulating emotions. When these structures malfunction, it can lead to various neurological conditions.
-
Definition and Structure: The basal ganglia consist of the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These nuclei work together to modulate motor functions and behaviors.
-
Primary Functions: They are involved in motor control, motor learning, executive functions, and emotional behaviors. They also play a role in reward and reinforcement mechanisms.
The Role of Basal Ganglia in Movement
The basal ganglia ensure that our movements are smooth and coordinated. They are essential for both voluntary movements and the learning of new motor skills.
-
Motor Control: These structures modulate the activity of motor regions in the cortex, ensuring smooth and coordinated movements.
-
Motor Learning: They are crucial for acquiring new motor skills through practice and repetition, which often happens unconsciously.
Cognitive and Emotional Functions
Beyond movement, the basal ganglia also influence cognitive tasks and emotional responses. They help us make decisions, solve problems, and regulate our emotions.
-
Executive Functions: Attention, decision-making, and problem-solving are influenced by the basal ganglia, making them critical for daily life activities.
-
Emotional Behaviors: They are involved in regulating emotions and forming emotional responses, closely linked to the limbic system.
Reward and Reinforcement Mechanisms
The basal ganglia are key players in how we form habits and respond to rewards. They help us learn what actions are beneficial and which ones to avoid.
-
Reward and Reinforcement: They play a significant role in associating actions with rewards or punishments, aiding in habit formation and the regulation of addictive behaviors.
-
Dopamine’s Role: Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, is crucial for the basal ganglia's functioning. Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra signal unexpected rewards or their absence, essential for learning and motivation.
Common Basal Ganglia Disorders
When the basal ganglia malfunction, it can lead to several movement disorders. These conditions can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
-
Basal Ganglia Disorders: Dysfunction can lead to movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, dystonia, and chorea, resulting from damage or disruptions in their circuitry.
-
Parkinson’s Disease: This neurodegenerative disorder is characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to symptoms like tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability.
-
Huntington’s Disease: An inherited disorder caused by a CAG expansion in the huntingtin gene, leading to neurodegeneration in the striatum and cortex. Symptoms include chorea, bradykinesia, dystonia, and cognitive impairments.
-
Dystonia: Characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, leading to abnormal postures and movements. It can result from basal ganglia dysfunction and is often associated with other neurological conditions.
-
Chorea: This movement disorder involves brief, involuntary movements affecting the trunk, face, and arms. Commonly seen in Huntington’s disease, it can also occur in other conditions affecting the basal ganglia.
Hyperkinetic and Hypokinetic Disorders
Basal ganglia disorders can be classified based on whether they cause excessive or insufficient movement. Understanding these classifications helps in diagnosing and treating these conditions.
-
Hyperkinetic Disorders: Conditions like chorea and dystonia result from insufficient output from the basal ganglia to the thalamus, leading to uncontrolled or involuntary movements.
-
Hypokinetic Disorders: Disorders like Parkinson’s disease arise from excessive output from the basal ganglia to the thalamus, limiting voluntary movement and causing symptoms like bradykinesia and rigidity.
Basal Ganglia Circuitry and Working Memory
The basal ganglia's complex circuitry involves pathways that either promote or inhibit movement. They also play a role in regulating what information enters our working memory.
-
Basal Ganglia Circuitry: The direct pathway (Go pathway) promotes movement, while the indirect pathway (NoGo pathway) inhibits it. These pathways interact to regulate motor functions and behaviors.
-
Working Memory: The basal ganglia gate what enters and what doesn’t enter working memory. The direct pathway allows information into the prefrontal cortex (PFC), while the indirect pathway closes the gate to the PFC, regulating working memory focus.
Addiction and Clinical Significance
The basal ganglia's role in reward and reinforcement makes them crucial in understanding addiction. Dysfunction in these structures can lead to compulsive behaviors and addiction.
-
Addiction: Dysfunction in the basal ganglia can lead to compulsive behaviors and addiction, as they play a role in associating certain actions with rewards or punishments.
-
Clinical Significance: Basal ganglia diseases encompass movement disorders resulting from either excessive or insufficient output to the thalamus. These disorders can significantly impact motor functions, cognitive abilities, and emotional well-being.
Research and Treatment
Ongoing research aims to understand the mechanisms behind basal ganglia diseases better. Developing effective treatments is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
- Research and Treatment: Current treatments include pharmacological interventions, deep brain stimulation, and behavioral therapies aimed at managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Understanding Basal Ganglia Diseases
Basal ganglia diseases impact motor control, cognitive functions, and emotional behaviors. These conditions, like Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease, arise from dysfunction in the basal ganglia's complex circuitry. Dopamine plays a crucial role in these processes, and its imbalance can lead to significant symptoms. Movement disorders such as dystonia and chorea highlight the importance of these brain structures in our daily lives.
Research continues to uncover the intricacies of these diseases, aiming to develop better treatments. Current options include medications, deep brain stimulation, and behavioral therapies. Understanding the basal ganglia's role in motor learning, executive functions, and emotional regulation is key to improving patient outcomes. By grasping these facts, we can appreciate the importance of ongoing research and the need for effective management strategies for those affected by basal ganglia diseases.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.