Fechtner Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood, kidneys, and hearing. Characterized by macrothrombocytopenia and leukocyte inclusions, this condition often overlaps with Alport's syndrome, which impacts kidneys, hearing, and eyes. The syndrome results from mutations in the MYH9 gene, leading to abnormal platelet function and structure. Symptoms can include large platelets, bleeding tendencies, anemia, hearing loss, and progressive renal failure. Diagnosing Fechtner Syndrome involves blood tests, genetic analysis, and microscopic examination of blood cells. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment, which may include corticosteroids, blood transfusions, and genetic counseling.
Understanding Fechtner Syndrome
Fechtner syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the blood and kidneys. It’s an autosomal dominant condition, meaning a single copy of the mutated gene can cause the disorder. Here are 15 key facts about Fechtner syndrome, its symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
Symptoms and Characteristics
Fechtner syndrome presents with a variety of symptoms that can affect multiple body systems. Knowing these symptoms can help in early diagnosis and management.
-
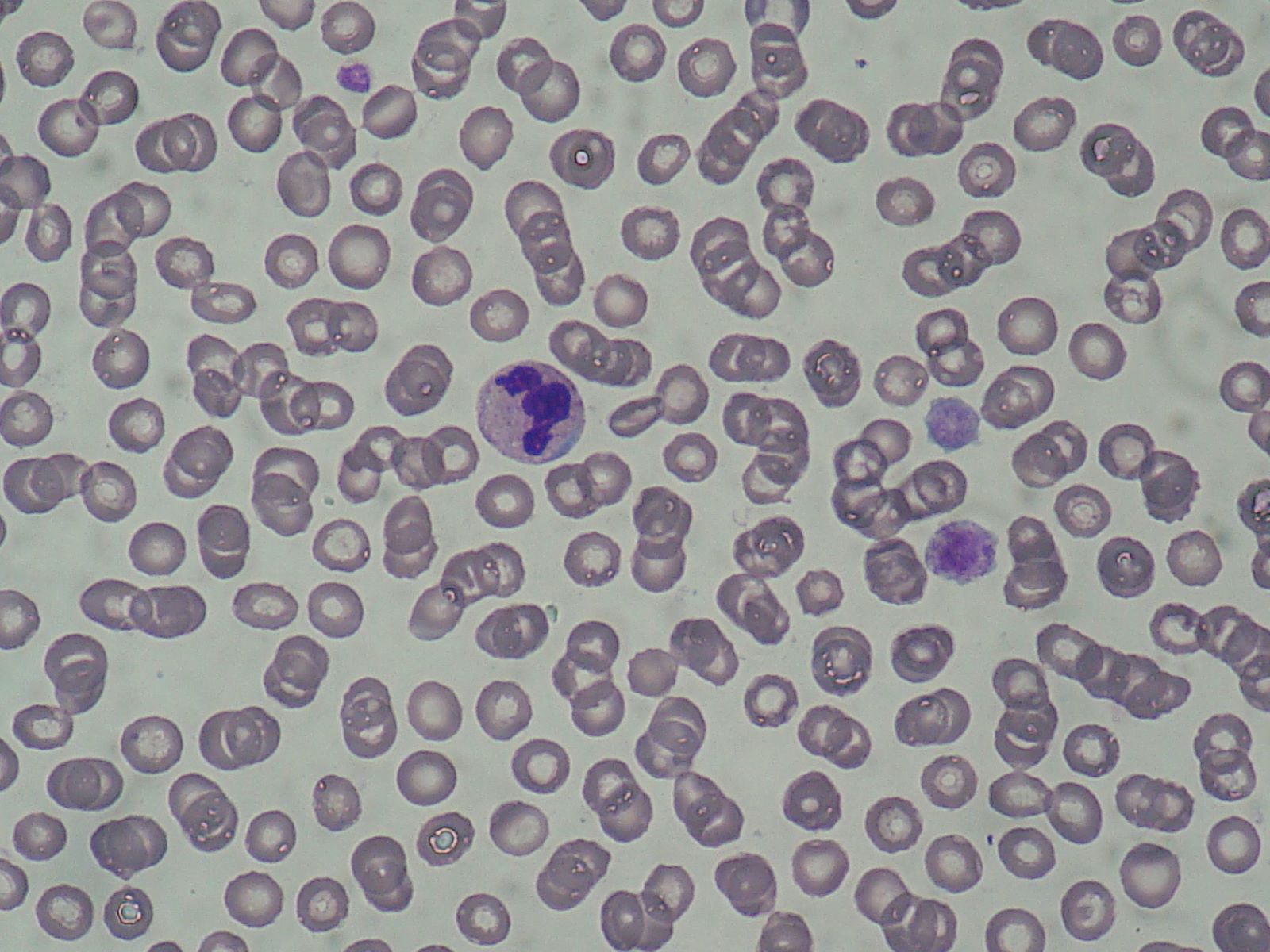
Macrothrombocytopenia: This condition is characterized by larger-than-normal platelets. Despite their size, these platelets can lead to bleeding complications.
-
Leukocyte Inclusions: Abnormal structures within white blood cells are a hallmark of Fechtner syndrome. These inclusions can be observed under a microscope.
-
Hearing Loss: Many patients experience sensorineural hearing loss, which affects the inner ear. This can lead to significant hearing impairment if untreated.
-
Renal Failure: Progressive renal failure is common, often linked with Alport’s syndrome. This can lead to serious kidney damage over time.
-
Bleeding Tendencies: Due to the abnormal platelets, patients may experience frequent bleeding episodes.
-
Anemia: Some individuals with Fechtner syndrome may develop anemia, a condition where there aren’t enough red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body.
Genetic Basis and Diagnosis
Understanding the genetic underpinnings and diagnostic methods is crucial for managing Fechtner syndrome effectively.
-
MYH9 Gene Mutations: The disorder is caused by mutations in the MYH9 gene, which encodes for the heavy chain of non-muscle myosin IIA. This protein is vital for platelet function and structure.
-
Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC test helps assess platelet count and size, which are critical for diagnosing Fechtner syndrome.
-
Peripheral Blood Smear: This test allows doctors to observe leukocyte inclusions and macrothrombocytopenia under a microscope.
-
Electron Microscopy: Confirming the presence of Fechtner inclusions within leukocytes often requires electron microscopy.
-
Genetic Testing: Identifying mutations in the MYH9 gene through genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
Associated Conditions and Complications
Fechtner syndrome often coexists with other conditions, leading to a range of complications.
-
Association with Alport’s Syndrome: Fechtner syndrome is frequently linked with Alport’s syndrome, a hereditary condition affecting the kidneys, hearing, and eyes. This association suggests a common genetic pathway involving collagen-related genes.
-
Ocular Anomalies: Patients may experience eye-related issues such as cataracts and glomerulonephritis, impacting vision.
Management and Treatment
Managing Fechtner syndrome involves addressing its various symptoms and complications. Here are some common approaches.
-
Corticosteroids: These are often used to manage renal failure in patients with Fechtner syndrome.
-
Blood and Platelet Transfusions: In severe cases of thrombocytopenia or bleeding complications, transfusions may be necessary to stabilize the patient.
Fechtner syndrome is a complex genetic disorder with significant clinical implications. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and management is crucial for providing appropriate care to affected individuals. Continued research into this rare condition will help in improving the lives of those affected by it.
Final Thoughts on Fechtner Syndrome
Fechtner syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, presents unique challenges due to its association with macrothrombocytopenia, leukocyte inclusions, and Alport's syndrome. Understanding its symptoms, like large platelets, hearing loss, and renal failure, is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Genetic mutations in the MYH9 gene play a significant role in this condition, making genetic testing essential for accurate identification.
Managing Fechtner syndrome involves addressing bleeding tendencies and renal issues through treatments like corticosteroids, blood transfusions, and genetic counseling. Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals.
Ongoing research aims to uncover more about the molecular mechanisms behind Fechtner syndrome, paving the way for better treatments. Staying informed and proactive in managing this condition can make a significant difference for those living with Fechtner syndrome.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


