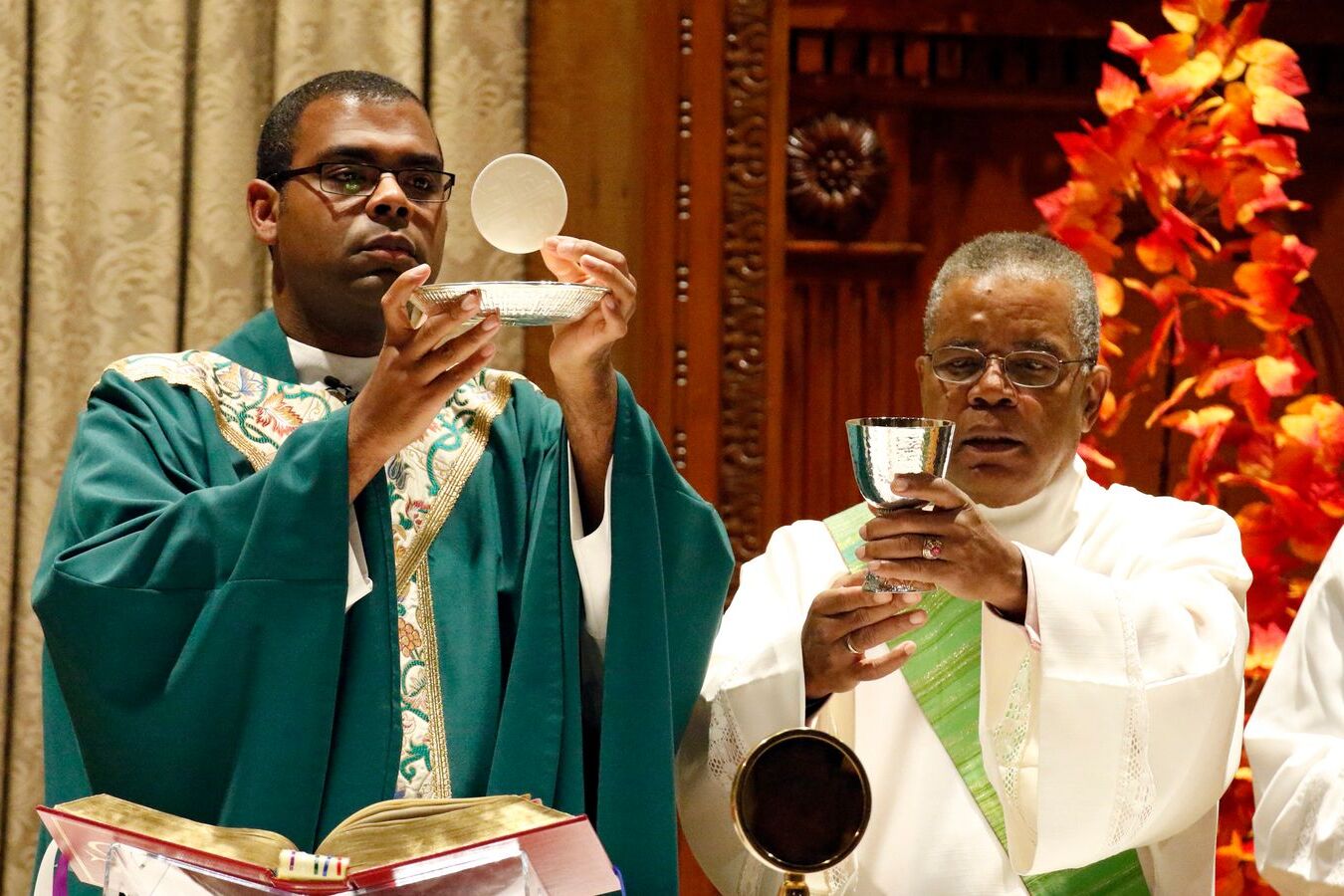
Liturgy is a term often heard in religious contexts, but what does it really mean? Simply put, liturgy refers to the set forms of public worship, especially in Christian traditions. It encompasses rituals, prayers, and ceremonies that have been passed down through generations. These practices not only shape the worship experience but also connect believers to their faith's history. Whether it's the solemnity of a Catholic Mass, the vibrant praise in a Pentecostal service, or the structured prayers in an Anglican church, liturgy plays a crucial role. Understanding liturgy can deepen one's appreciation for these traditions and highlight the rich tapestry of religious expression. Ready to dive into some fascinating facts about liturgy? Let's get started!
What is Liturgy?
Liturgy refers to the customary public worship performed by a religious group. It’s a communal response to the sacred through activities reflecting praise, thanksgiving, supplication, or repentance. Here are some fascinating facts about liturgy.
-
Liturgy Originates from Greek
The word "liturgy" comes from the Greek term "leitourgia," meaning "public service" or "work of the people." It was initially used to describe any public duty or service performed for the state. -
Ancient Roots
Liturgy has ancient roots, dating back to early Jewish worship practices. These rituals influenced Christian liturgical traditions, especially in the structure of services. -
Different Forms
There are various forms of liturgy, including the Roman Catholic Mass, Eastern Orthodox Divine Liturgy, Anglican Holy Communion, and Protestant worship services. Each has unique elements and traditions. -
Liturgical Calendar
Many Christian denominations follow a liturgical calendar, marking seasons like Advent, Christmas, Lent, Easter, and Pentecost. This calendar helps structure worship throughout the year. -
Sacred Texts
Liturgy often involves reading from sacred texts. In Christianity, this includes the Bible, while in Judaism, it includes the Torah. These readings are central to worship services.
Elements of Liturgy
Liturgy comprises various elements that create a cohesive worship experience. These elements can vary significantly between different religious traditions.
-
Prayers
Prayers are a fundamental part of liturgy. They can be spontaneous or scripted, and they often include praise, confession, thanksgiving, and intercession. -
Hymns and Songs
Music plays a crucial role in liturgy. Hymns, psalms, and contemporary worship songs help congregants express their faith and emotions. -
Sermons
A sermon or homily is a key element in many liturgical services. It involves a religious leader interpreting sacred texts and offering guidance to the congregation. -
Sacraments
Sacraments like baptism and communion are vital in many Christian liturgies. They are seen as outward signs of inward grace and are performed with specific rituals. -
Creeds and Confessions
Reciting creeds and confessions of faith, such as the Nicene Creed or the Apostles' Creed, is common in many liturgical traditions. These statements summarize core beliefs.
Historical Development
Liturgy has evolved over centuries, influenced by cultural, theological, and historical factors. Understanding its development provides insight into its current practices.
-
Early Christian Worship
Early Christian worship was simple, often held in homes. It included readings from scripture, prayers, hymns, and the Eucharist. -
Constantine's Influence
Emperor Constantine's conversion to Christianity in the 4th century significantly impacted liturgy. Public worship became more elaborate, with the construction of grand churches. -
Medieval Liturgy
During the medieval period, liturgy became more formalized. The Roman Catholic Mass developed intricate rituals, and the use of Latin became widespread. -
Reformation Changes
The Protestant Reformation in the 16th century brought significant changes to liturgy. Reformers like Martin Luther and John Calvin simplified worship and emphasized scripture. -
Vatican II
The Second Vatican Council (1962-1965) brought major liturgical reforms in the Roman Catholic Church. It allowed for the use of vernacular languages and encouraged active participation by the laity.
Cultural Variations
Liturgy varies widely across different cultures and religious traditions. These variations reflect the diversity of human expression in worship.
-
Eastern Orthodox Liturgy
Eastern Orthodox liturgy is known for its rich symbolism and elaborate rituals. The Divine Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom is the most commonly celebrated service. -
Anglican Liturgy
Anglican liturgy combines elements of Catholic and Protestant traditions. The Book of Common Prayer is a central text, guiding worship practices. -
Jewish Liturgy
Jewish liturgy includes daily prayers, Sabbath services, and special rituals for holidays. The Siddur is the traditional Jewish prayer book used in these services. -
Islamic Liturgy
Islamic liturgy involves daily prayers (Salah), Friday congregational prayers (Jumu'ah), and special prayers during Ramadan and other Islamic holidays. -
Hindu Liturgy
Hindu liturgy, or puja, involves rituals performed at home or in temples. It includes offerings, prayers, and recitations from sacred texts like the Vedas.
Modern Adaptations
Liturgy continues to adapt to contemporary contexts, reflecting changes in society and culture. These adaptations ensure that worship remains relevant and meaningful.
-
Contemporary Worship
Many churches have adopted contemporary worship styles, incorporating modern music, multimedia, and informal settings to engage congregants. -
Inclusive Language
Some liturgical traditions have adopted inclusive language to reflect gender equality and diversity. This includes using gender-neutral terms for God and inclusive language in prayers. -
Ecumenical Services
Ecumenical services bring together different Christian denominations for joint worship. These services emphasize unity and shared beliefs. -
Online Worship
The rise of technology has led to the development of online worship services. Virtual liturgies allow people to participate in worship from anywhere in the world. -
Environmental Liturgy
Some communities have developed liturgies focused on environmental stewardship. These services emphasize the connection between faith and care for creation.
Symbolism in Liturgy
Symbols play a significant role in liturgy, conveying deeper meanings and connecting worshippers to their faith.
-
Cross and Crucifix
The cross and crucifix are central symbols in Christian liturgy, representing the sacrifice of Jesus Christ and the hope of resurrection. -
Candles
Candles symbolize the presence of God and the light of Christ. They are often used in liturgical services to create a sacred atmosphere. -
Vestments
Clergy often wear special vestments during liturgical services. These garments symbolize their role and the sacredness of the worship. -
Incense
Incense is used in many liturgical traditions to symbolize prayers rising to heaven. It also creates a sense of mystery and reverence. -
Water
Water is a powerful symbol in liturgy, representing purification, renewal, and baptism. It is often used in rituals to signify spiritual cleansing.
Liturgy and Community
Liturgy fosters a sense of community and belonging among worshippers. It brings people together in shared expressions of faith and devotion.
-
Communal Worship
Liturgy is inherently communal, involving the participation of the entire congregation. This shared experience strengthens bonds within the community. -
Rituals of Passage
Liturgy often includes rituals marking significant life events, such as baptisms, weddings, and funerals. These rituals provide support and meaning during important transitions. -
Feasts and Festivals
Many liturgical traditions celebrate feasts and festivals, such as Christmas, Easter, Passover, and Ramadan. These celebrations bring communities together in joy and reflection. -
Pilgrimages
Pilgrimages to sacred sites are an important aspect of liturgical practice in many religions. These journeys foster spiritual growth and communal solidarity. -
Charitable Acts
Liturgy often inspires acts of charity and service. Many religious communities engage in social justice initiatives, reflecting their faith in action.
Educational Role of Liturgy
Liturgy serves an educational purpose, teaching worshippers about their faith and traditions. It helps transmit religious knowledge and values across generations.
-
Catechesis
Catechesis involves religious instruction, often integrated into liturgical services. It helps prepare individuals for sacraments and deepens their understanding of faith. -
Scripture Readings
Regular readings from sacred texts during liturgy educate worshippers about their religious heritage and moral teachings. -
Liturgical Music
Liturgical music often includes hymns and songs that convey theological truths and spiritual insights. Singing these songs helps embed religious teachings in the hearts of worshippers. -
Visual Arts
Visual arts, such as stained glass windows, icons, and religious paintings, play an educational role in liturgy. They depict biblical stories and saints, inspiring devotion and learning. -
Homilies and Sermons
Homilies and sermons provide opportunities for religious leaders to teach and inspire their congregations. They offer interpretations of scripture and practical guidance for living out one's faith.
Final Thoughts on Liturgy
Liturgy, with its rich history and deep significance, offers a fascinating glimpse into the spiritual practices of various faiths. From the intricate rituals of the Catholic Mass to the simple yet profound ceremonies in other traditions, liturgy serves as a bridge connecting believers to the divine. Understanding these practices not only enriches our knowledge but also fosters greater appreciation for the diverse ways people express their faith. Whether you're a devout practitioner or just curious, exploring liturgy can be a rewarding journey. Remember, every ritual, chant, and prayer has a story to tell, reflecting centuries of devotion and tradition. So next time you witness or participate in a liturgical service, take a moment to reflect on its historical roots and spiritual depth. It’s a testament to the enduring power of faith and community.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.