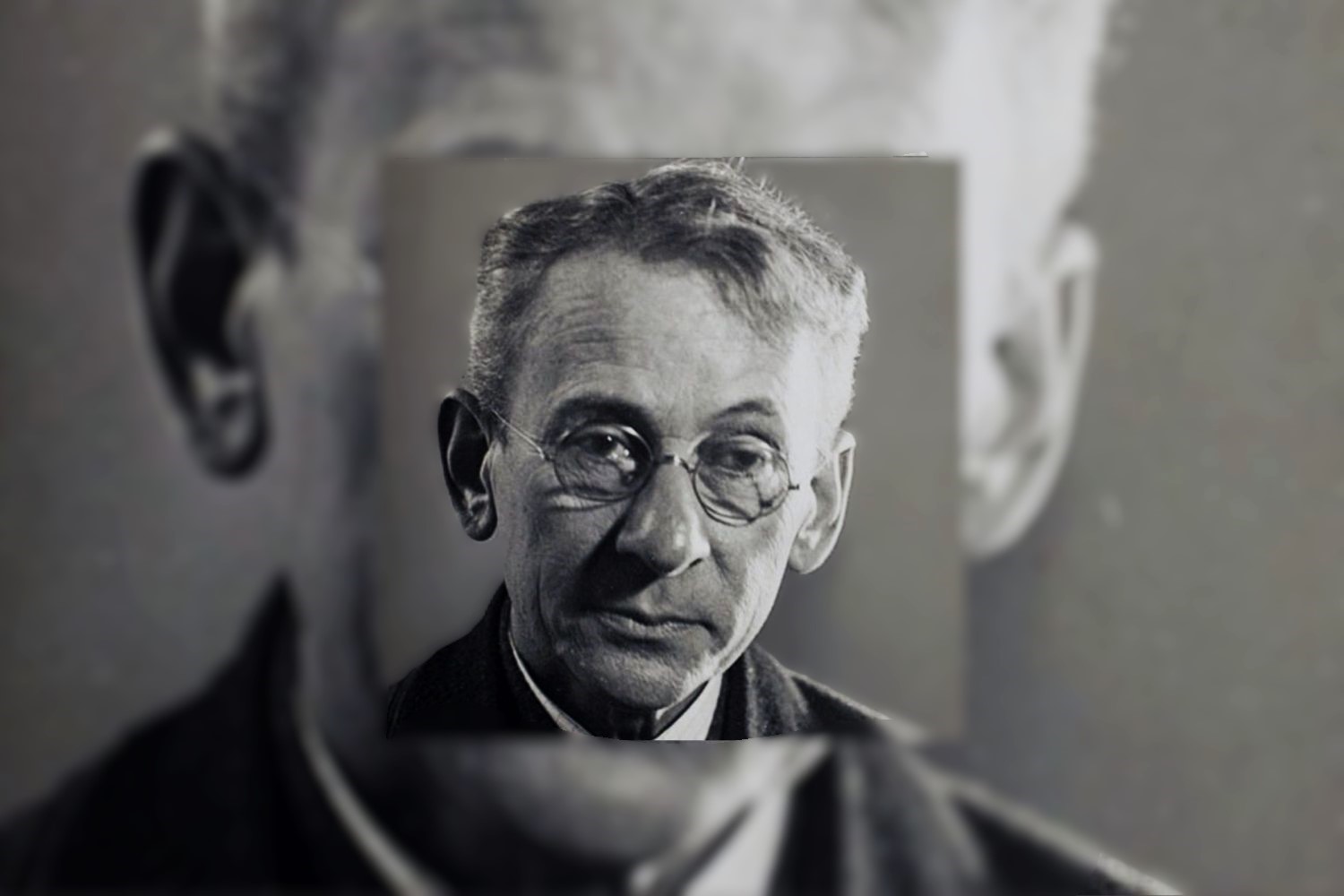
Who was Lewis Hine? Lewis Hine was a pioneering American photographer and sociologist whose work brought significant social change. Born in 1874, Hine used his camera as a tool for social reform, capturing powerful images of child laborers, immigrants, and working-class Americans. His photographs were instrumental in changing child labor laws in the United States. Hine's work documented the harsh realities of early 20th-century life, making him a key figure in the history of documentary photography. His images not only told stories but also sparked movements, proving that a picture is worth more than a thousand words.
Key Takeaways:
- Lewis Hine used his camera to expose the harsh realities of child labor, inspiring change and shaping the future of documentary photography.
- Hine's enduring legacy continues to educate and inspire, impacting fields beyond photography and honoring those who advocate for the welfare of children.
Early Life and Education
Lewis Hine's journey began long before he became a renowned photographer. His early life and education played a significant role in shaping his future work.
- Born on September 26, 1874, in Oshkosh, Wisconsin, Lewis Wickes Hine grew up in a modest family.
- Hine's father died in an accident when Lewis was just 18, forcing him to work to support his family.
- He attended the University of Chicago, Columbia University, and New York University, where he studied sociology.
- Hine initially worked as a teacher at the Ethical Culture School in New York City, where he first picked up a camera.
Career Beginnings
Hine's career took off when he began using photography as a tool for social change. His early work laid the foundation for his later achievements.
- In 1904, Hine started photographing immigrants arriving at Ellis Island, capturing their hopes and struggles.
- His Ellis Island photographs were among the first to humanize immigrants, showing their dignity and resilience.
- Hine's work caught the attention of social reformers, who saw the potential of photography in advocating for change.
- He joined the National Child Labor Committee (NCLC) in 1908, using his camera to expose the harsh realities of child labor.
Child Labor Documentation
Hine's most impactful work involved documenting child labor across the United States. His photographs brought attention to the plight of young workers.
- Hine traveled extensively, often going undercover to gain access to factories, mines, and mills.
- He photographed children as young as five working in dangerous and unhealthy conditions.
- Hine's images showed children operating heavy machinery, working long hours, and suffering from injuries.
- His work led to public outrage and eventually contributed to the passage of child labor laws in the United States.
Techniques and Style
Hine's photographic techniques and style were innovative for his time. He used his skills to convey powerful messages through his images.
- Hine often used natural light to highlight the subjects of his photographs, giving them a sense of realism.
- He employed a large-format camera, which allowed for high-resolution images that captured intricate details.
- Hine's compositions were carefully planned, often focusing on the eyes of his subjects to evoke empathy.
- He wrote detailed captions for his photographs, providing context and enhancing their impact.
Impact on Social Reform
Hine's work had a lasting impact on social reform movements in the United States. His photographs were instrumental in bringing about change.
- His images were used in reports, pamphlets, and exhibitions to raise awareness about child labor.
- Hine's work influenced other photographers and social reformers, inspiring them to use photography as a tool for advocacy.
- The NCLC credited Hine's photographs with helping to secure the passage of the Keating-Owen Child Labor Act of 1916.
- Hine's legacy lives on in the continued use of documentary photography to highlight social issues.
Later Work and Legacy
In his later years, Hine continued to document social issues, leaving behind a rich legacy of impactful photography.
- During World War I, Hine worked for the American Red Cross, documenting relief efforts in Europe.
- He photographed the construction of the Empire State Building, capturing the bravery of the workers.
- Hine's images of the Great Depression highlighted the struggles of American workers and families.
- Despite his contributions, Hine struggled financially in his later years and died in relative obscurity in 1940.
Recognition and Influence
Hine's work has been recognized and celebrated posthumously. His influence on photography and social reform remains significant.
- In 1946, the Museum of Modern Art in New York held a retrospective exhibition of Hine's work.
- Hine's photographs are now part of major collections, including the Library of Congress and the George Eastman Museum.
- His work has inspired generations of photographers, including Dorothea Lange and Walker Evans.
- Hine is often credited with helping to establish documentary photography as a legitimate art form.
Personal Life
Hine's personal life was marked by dedication to his work and a commitment to social justice.
- He married Sara Ann Rich in 1904, and they had one son, Corydon.
- Hine was known for his modesty and humility, often putting the needs of his subjects above his own.
- He faced significant risks while documenting child labor, including threats from factory owners and managers.
- Hine's passion for social justice was evident in his lifelong commitment to using photography as a tool for change.
Enduring Legacy
Hine's legacy endures through his powerful images and the impact they had on society. His work continues to inspire and educate.
- Hine's photographs are used in educational materials to teach students about the history of child labor and social reform.
- His work has been the subject of numerous books, documentaries, and exhibitions.
- Hine's influence extends beyond photography, impacting fields such as sociology, history, and social work.
- The Lewis Hine Award, established by the National Child Labor Committee, honors individuals who have made significant contributions to the welfare of children.
The Lasting Impact of Lewis Hine
Lewis Hine's work left a lasting mark on society. His photographs didn't just capture moments; they sparked change. By highlighting child labor's harsh realities, he pushed for reforms that improved countless lives. Hine's dedication to social justice and his ability to use photography as a tool for change remain inspiring.
His images continue to educate and motivate new generations. They remind us of the power of visual storytelling and the importance of standing up for what's right. Hine's legacy lives on in the laws that protect workers today and in the hearts of those who fight for social justice.
Lewis Hine showed that one person can make a difference. His work proves that art and activism can go hand in hand, creating a better world for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.