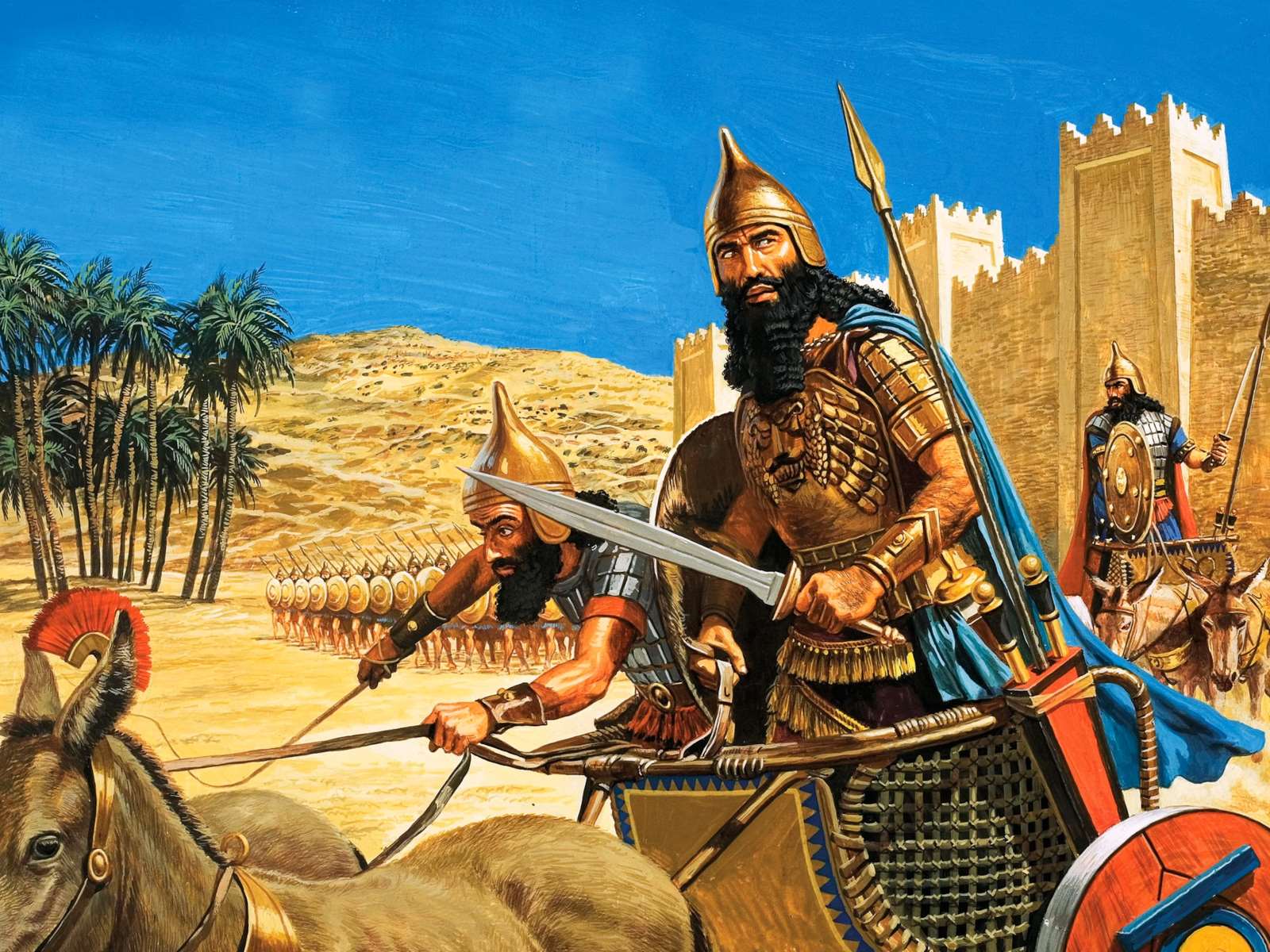
Hammurabi, the sixth king of Babylon, is best known for his famous legal code. However, his reign was also marked by significant military campaigns, including a notable conflict with Assyria. This war was part of Hammurabi's broader strategy to expand Babylonian territory and secure resources. Facing a coalition that included Ashur, Eshnunna, and Elam, Hammurabi demonstrated both military prowess and strategic diplomacy. His ability to counter these threats not only solidified his control over key regions but also ensured Babylon's dominance in Mesopotamia. This article explores the key aspects of Hammurabi's war with Assyria, shedding light on his tactics, challenges, and ultimate success.
Hammurabi's Early Challenges
Hammurabi, the sixth king of Babylon, faced numerous challenges early in his reign. His strategic and military prowess would soon be tested by neighboring powers.
-
Rivalry with Rim-Sin of Larsa
Hammurabi's first major rival was Rim-Sin of Larsa. Rim-Sin controlled the southern part of Babylonia and had conquered Isin, a strategic city. This rivalry set the stage for many of Hammurabi's early military campaigns. -
Strategic Use of Water Resources
Hammurabi employed innovative military strategies, such as manipulating water resources. He dammed a main watercourse and released it suddenly to flood enemy territories. This tactic was used against Rim-Sin, showcasing Hammurabi's ingenuity.
The Coalition Threat
In 1764 BCE, Hammurabi faced a formidable coalition of Ashur, Eshnunna, and Elam. This alliance threatened his access to vital resources and posed a significant challenge to his rule.
-
War with Ashur, Eshnunna, and Elam
Hammurabi countered the coalition's advances through a mix of military strength and strategic diplomacy. His ability to navigate these threats solidified his reputation as a formidable leader. -
Importance of Metal-Producing Areas
The coalition threatened Hammurabi's access to metal-producing areas in Iran. Controlling these resources was crucial for maintaining his military and economic power.
Conquest of Larsa
Hammurabi's conflict with Rim-Sin of Larsa culminated in a decisive siege that would shape the future of Babylonia.
-
Final Siege of Larsa
The siege of Larsa lasted several months and required extensive military resources. Hammurabi's victory marked a turning point, solidifying his control over much of Babylonia. -
Strategic Planning and Resources
The prolonged conflict with Larsa showcased Hammurabi's ability to plan and allocate resources effectively. His victory demonstrated his military acumen and strategic foresight.
Conflict with Mari
In 1761 BCE, Hammurabi turned his attention to Mari, a city-state with strategic importance.
-
War with Mari
Hammurabi's conflict with Zimrilim, the king of Mari, remains somewhat mysterious. It may have been over water rights or an attempt to control Mari's strategic location at trade route crossroads. -
Strategic Location of Mari
Mari's location made it a valuable asset. Controlling it allowed Hammurabi to dominate trade routes and enhance Babylon's economic power.
Eastern Campaigns
Hammurabi's ambitions extended eastward, where he sought to maintain control over key regions.
-
Third Campaign Against Eastern Powers
Between 1757 and 1755 BCE, Hammurabi launched a third campaign eastward. This effort aimed to secure his dominance and prevent rival powers from threatening his rule. -
Maintaining Control Over Eastern Regions
These campaigns were crucial for maintaining stability and control over the eastern territories. Hammurabi's efforts ensured that no rival powers could challenge his dominance.
The Code of Hammurabi
Amidst his military campaigns, Hammurabi also focused on establishing a comprehensive legal code.
-
Creation of the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi, inscribed on a stone stele, contains 282 laws covering various aspects of Babylonian society. It aimed to provide fairness and stability in a society prone to disputes. -
Purpose of the Code
The code sought to establish justice and prevent the strong from oppressing the weak. Clear penalties for crimes and standards for proof streamlined the process of settling disputes.
Legacy of Hammurabi
Hammurabi's reign left a lasting impact on Mesopotamian society and future civilizations.
-
Prologue and Epilogue of the Code
The Code of Hammurabi begins with a prologue describing Hammurabi's royal authority and achievements. The epilogue expresses his hope that the laws would be respected and includes curses for those who disobey. -
Representation on the Legal Code Stele
Hammurabi is depicted receiving the laws from the god Shamash, emphasizing his role as a king of justice chosen by the gods. -
Military Strength and Diplomacy
Hammurabi's military strength was complemented by his diplomatic skills. He negotiated alliances and treaties, maintaining a balance of power in Mesopotamia. -
Economic Impact
His military campaigns expanded Babylon's territory, leading to increased trade and economic activity. The Code of Hammurabi facilitated commerce by establishing clear laws and regulations. -
Social Impact
The code provided a framework for social relationships and family dynamics. It protected the rights of slaves and ensured they could marry and have children without being enslaved. -
Historical Significance
Hammurabi's reign marked a transition from the Amorite dynasty to the Old Babylonian period. His military campaigns and diplomatic maneuvers shaped Mesopotamia's political landscape. -
Archaeological Evidence
The discovery of the Code of Hammurabi on a stone stele in Susa provides tangible proof of his existence and the significance of his legal code. Archaeological findings reveal the extent of his military campaigns. -
Cultural Impact
Hammurabi's reign influenced later legal systems, including those of the Assyrians and Persians. His depiction on the legal code stele remains an iconic representation of justice and divine authority in ancient Mesopotamian culture.
Hammurabi's Legacy in Warfare and Law
Hammurabi's reign wasn't just about military conquests; it was about shaping a civilization. His strategic brilliance in warfare, especially against formidable foes like Assyria, showcased his tactical mind. Yet, his legacy extends beyond the battlefield. The Code of Hammurabi stands as a monumental achievement, laying the groundwork for justice and governance. This blend of military prowess and legal innovation set Babylon apart, influencing future generations. Hammurabi's ability to balance war and law cemented his place in history. His reign marked a turning point, not just for Babylon, but for the entire Mesopotamian region. The impact of his actions, both in war and in law, continues to be felt, reminding us of the enduring power of a well-rounded leader. Hammurabi's story is a testament to the lasting influence of a ruler who understood the importance of both strength and justice.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.