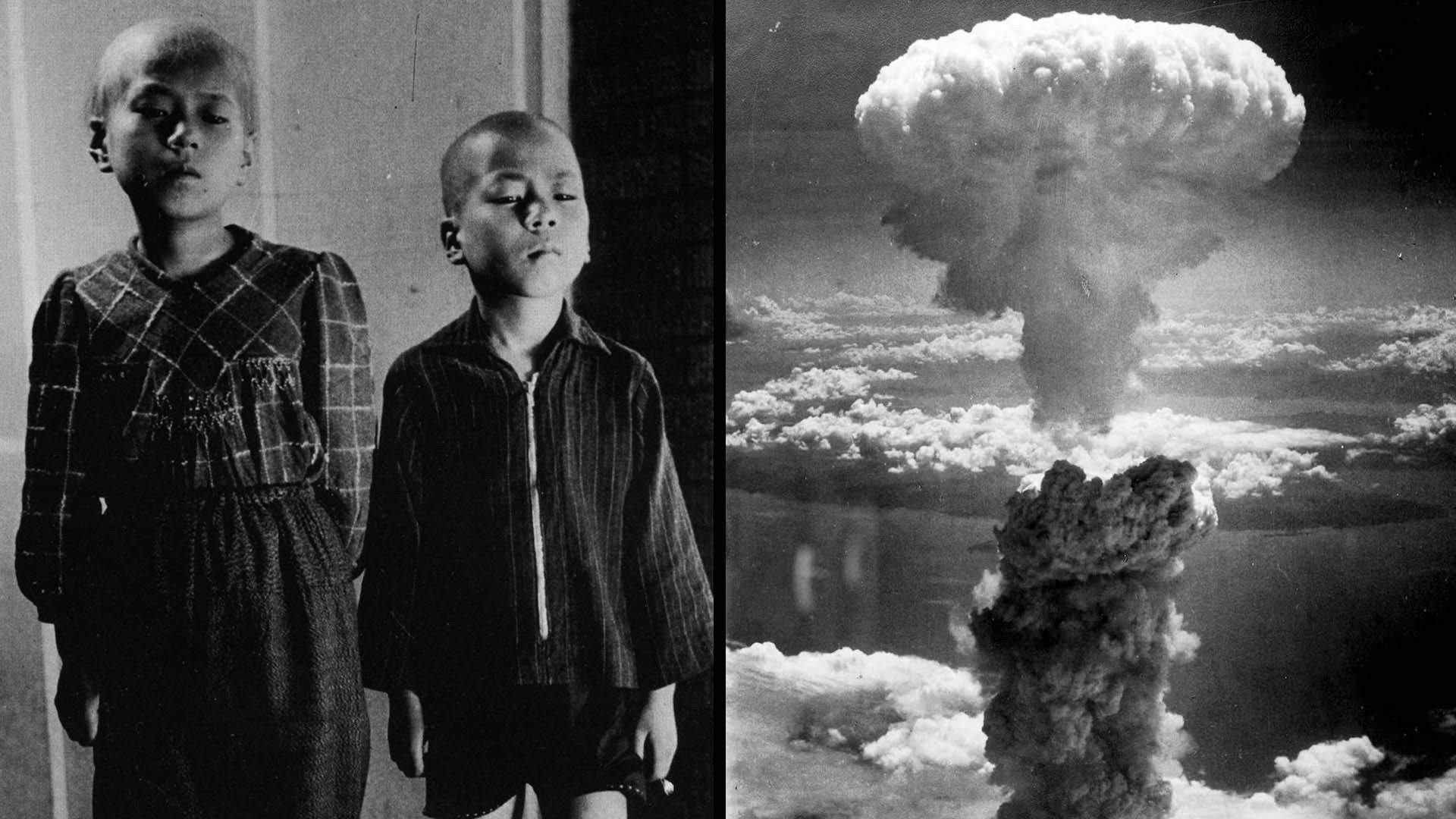
Hiroshima and Nagasaki are names that echo through history, symbols of the devastating power of nuclear weapons. On August 6 and 9, 1945, these Japanese cities were the targets of atomic bombs dropped by the United States during World War II, marking the first and only use of such weapons in warfare. These events led to the immediate surrender of Japan and the end of the conflict. However, the impact of the bombings extends far beyond their historical significance. They have left a lasting legacy on global politics, ethics, and the push for nuclear disarmament. Understanding the facts about Hiroshima and Nagasaki is crucial for comprehending the full scope of their influence on the world stage, human rights, and the ongoing efforts to ensure such a tragedy never occurs again.
The Atomic Bombings
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II remain some of the most significant events in modern history. These bombings not only ended the war but also ushered in the nuclear age.
-
Hiroshima was bombed on August 6, 1945. The bomb, nicknamed "Little Boy," was dropped by the B-29 bomber Enola Gay. It exploded approximately 600 meters above the city, causing massive destruction.
-
Nagasaki was bombed three days later on August 9, 1945. The bomb, called "Fat Man," was dropped by the B-29 bomber Bockscar. Unlike Hiroshima, Nagasaki's terrain limited the bomb's damage somewhat.
The Immediate Impact
The immediate effects of the bombings were catastrophic, leading to immense loss of life and widespread destruction.
-
Hiroshima's population was around 350,000 before the bombing. Approximately 70,000-80,000 people were killed instantly, with tens of thousands more dying from radiation exposure and injuries in the following weeks.
-
Nagasaki had a population of about 263,000. The bombing resulted in the immediate deaths of 40,000-75,000 people. Like Hiroshima, many more succumbed to injuries and radiation sickness later.
The Long-Term Consequences
The long-term effects of the bombings were profound, affecting survivors and their descendants for generations.
-
Radiation exposure caused severe health issues. Survivors, known as hibakusha, suffered from leukemia, cancer, and other radiation-induced illnesses. These health problems persisted for decades.
-
Genetic damage was a significant concern. Studies showed increased rates of birth defects and other genetic disorders among the children of survivors.
The Political and Social Repercussions
The bombings had far-reaching political and social consequences, influencing international relations and public opinion.
-
Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945. The bombings played a crucial role in Japan's decision to surrender, effectively ending World War II.
-
The bombings sparked global debates on nuclear weapons. The ethical and moral implications of using such weapons have been hotly debated ever since.
Memorials and Remembrance
Both cities have established memorials to honor the victims and promote peace.
-
Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park was created in 1954. The park includes the Atomic Bomb Dome, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the Peace Memorial Museum.
-
Nagasaki Peace Park was established in 1955. It features the Peace Statue and the Atomic Bomb Museum, both dedicated to remembering the tragedy and advocating for nuclear disarmament.
Cultural Impact
The bombings have left an indelible mark on global culture, inspiring countless works of art, literature, and film.
-
John Hersey's "Hiroshima" is a seminal work. Published in 1946, this book provides a detailed account of six survivors' experiences, bringing the human cost of the bombings to a global audience.
-
The bombings influenced numerous films and documentaries. Movies like "Grave of the Fireflies" and "Barefoot Gen" depict the harrowing experiences of those affected, ensuring the events are not forgotten.
Reflecting on Hiroshima and Nagasaki's Legacy
Hiroshima and Nagasaki stand as stark reminders of war's devastating power and the human capacity for both destruction and resilience. These cities, once scenes of unimaginable devastation, have been reborn as symbols of peace and hope. Their stories teach us the importance of remembering history's darker chapters, not to dwell in the past, but to forge a future where such tragedies are never repeated. Efforts in education, memorialization, and nuclear disarmament continue to draw inspiration from these events. As we look back, let's also look forward, committing to peace and understanding, ensuring the lessons of Hiroshima and Nagasaki guide humanity towards a brighter, more harmonious world. Their legacy, deeply woven into the fabric of modern history, challenges us to reflect, learn, and act with wisdom and compassion.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.