Tryptophan is more than just a word you hear around Thanksgiving. This essential amino acid plays a crucial role in our bodies. But what exactly is tryptophan, and why is it important? Tryptophan helps produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. It also aids in the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep-wake cycles. Foods like turkey, chicken, eggs, and cheese are rich in tryptophan. Ever wondered why you feel sleepy after a big turkey dinner? Tryptophan might be the reason! But there's more to this amino acid than just making you drowsy. From its impact on mental health to its role in protein synthesis, tryptophan is a fascinating nutrient worth knowing about. Ready to learn 34 intriguing facts about tryptophan? Let's dive in!
What is Tryptophan?
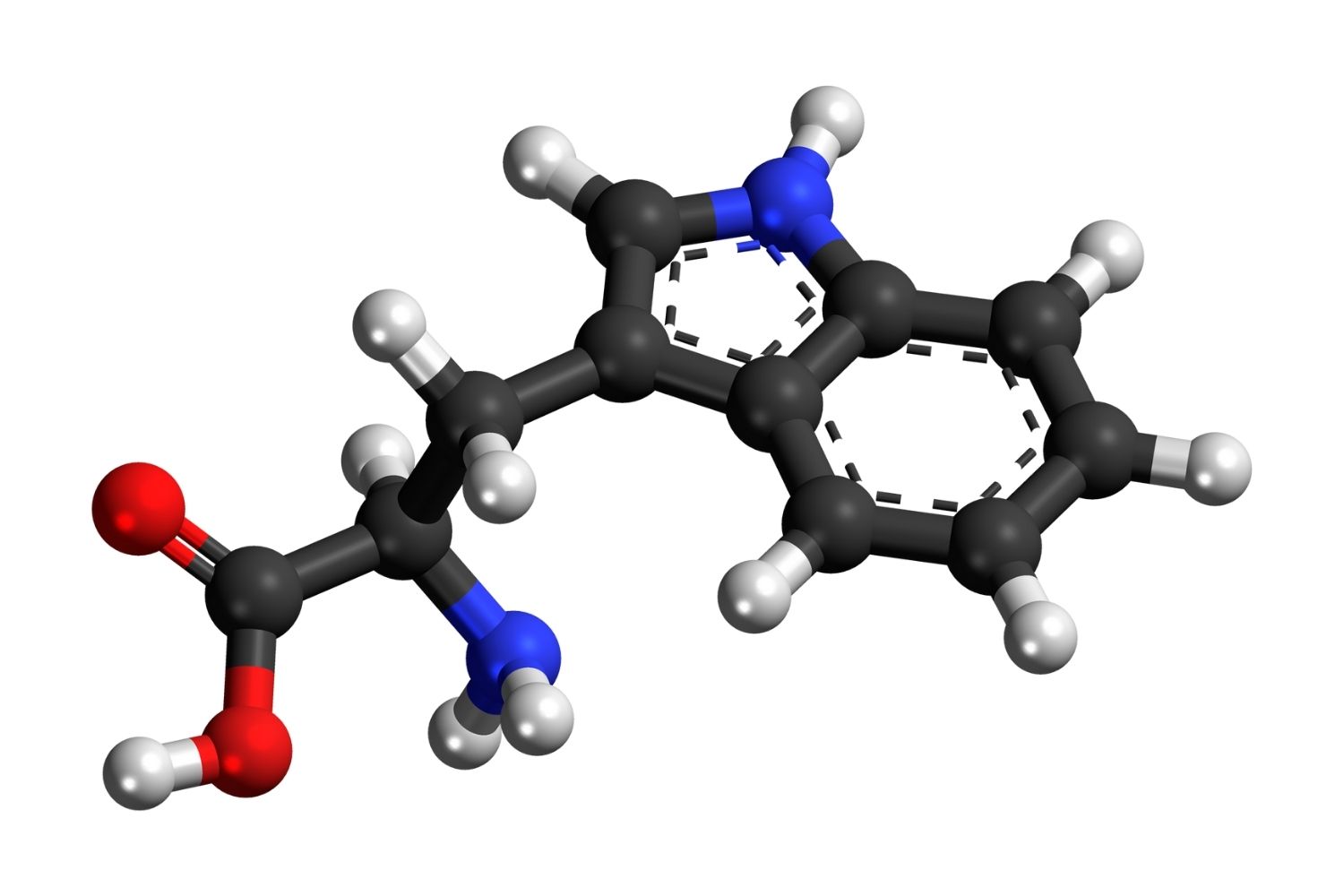
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the human body. It is a building block for proteins and is vital for producing important molecules like serotonin and melatonin.
-
Tryptophan cannot be produced by the body. This amino acid must be obtained through diet, as the human body lacks the ability to synthesize it.
-
It is found in many protein-rich foods. Common sources include turkey, chicken, milk, cheese, yogurt, eggs, fish, peanuts, and pumpkin seeds.
-
Tryptophan is a precursor to serotonin. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, sleep, and appetite.
-
It also helps produce melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, making tryptophan important for good sleep.
-
Tryptophan is used in the production of niacin. Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is essential for energy production and DNA repair.
How Tryptophan Affects Mood and Sleep
Tryptophan's role in producing serotonin and melatonin makes it a key player in mood regulation and sleep patterns.
-
Low levels of tryptophan can lead to mood disorders. Insufficient tryptophan can result in decreased serotonin levels, potentially causing depression and anxiety.
-
It can improve sleep quality. Consuming tryptophan-rich foods can enhance sleep by increasing melatonin production.
-
Tryptophan supplements are available. These supplements can help people with sleep disorders or mood issues, though they should be used under medical supervision.
-
It may help with seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Increased serotonin production from tryptophan can alleviate symptoms of SAD, a type of depression related to seasonal changes.
-
Tryptophan can reduce aggression. Higher serotonin levels from tryptophan intake can lead to reduced aggression and irritability.
Tryptophan in Diet and Nutrition
Incorporating tryptophan into your diet can have numerous health benefits. Here are some interesting facts about its dietary sources and nutritional impact.
-
Turkey is often cited as a top source. The myth that turkey makes you sleepy is partly due to its tryptophan content, though other factors like large meal size play a role.
-
Dairy products are rich in tryptophan. Milk, cheese, and yogurt are excellent sources, making them good bedtime snacks for better sleep.
-
Nuts and seeds are also good sources. Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds provide a healthy dose of tryptophan.
-
Soy products contain tryptophan. Tofu, tempeh, and soy milk are great options for vegetarians and vegans.
-
Oats and bananas have tryptophan. These foods can be easily incorporated into breakfast for a morning mood boost.
Tryptophan and Physical Health
Beyond mood and sleep, tryptophan has several other health benefits that contribute to overall well-being.
-
It supports immune function. Tryptophan helps produce proteins that are crucial for a healthy immune system.
-
Tryptophan aids in weight management. By regulating appetite through serotonin production, it can help control food cravings.
-
It can improve cognitive function. Adequate tryptophan levels are linked to better memory and learning abilities.
-
Tryptophan may reduce pain sensitivity. Higher serotonin levels can lower the perception of pain, providing relief for chronic pain sufferers.
-
It supports cardiovascular health. Tryptophan helps maintain healthy blood vessels and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Interesting Facts About Tryptophan
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about this essential amino acid.
-
Tryptophan was discovered in 1901. It was first isolated by Frederick Hopkins, a British biochemist.
-
It is one of the 20 standard amino acids. These amino acids are the building blocks of proteins in the human body.
-
Tryptophan has a unique structure. It contains an indole functional group, which is rare among amino acids.
-
It is used in animal feed. Tryptophan supplements are added to animal feed to ensure proper growth and health.
-
Tryptophan can be measured in the blood. Blood tests can determine tryptophan levels, which can help diagnose certain health conditions.
Myths and Misconceptions About Tryptophan
There are several myths surrounding tryptophan, especially related to its effects on sleep and mood.
-
Turkey doesn't make you sleepy. While turkey contains tryptophan, the amount is not enough to cause drowsiness on its own.
-
Tryptophan is not a sedative. It helps produce melatonin, which regulates sleep, but it doesn't act as a direct sedative.
-
You can't overdose on tryptophan from food. The body regulates amino acid levels, making it difficult to consume too much tryptophan through diet alone.
-
Tryptophan supplements are not a cure-all. They can help with mood and sleep issues, but they are not a substitute for a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
-
Not all protein-rich foods are high in tryptophan. While many protein sources contain tryptophan, the levels can vary significantly.
Tryptophan in Research and Medicine
Ongoing research continues to uncover new benefits and applications of tryptophan in medicine.
-
It is being studied for its role in cancer treatment. Some research suggests that tryptophan metabolism may affect tumor growth and immune response.
-
Tryptophan may help with inflammatory diseases. Its role in immune function makes it a potential treatment for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
-
It is being explored for its effects on gut health. Tryptophan metabolism in the gut can influence the microbiome and overall digestive health.
-
Tryptophan research is ongoing. Scientists continue to study its various roles in the body, aiming to unlock more health benefits and therapeutic uses.
The Final Scoop on Tryptophan
Tryptophan, an essential amino acid, plays a vital role in our bodies. It helps produce serotonin, which affects mood, sleep, and even appetite. Foods like turkey, chicken, cheese, and nuts are rich in tryptophan, making them great additions to your diet. While tryptophan supplements can help with sleep disorders and mood issues, it's always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
Understanding tryptophan's impact on your health can help you make better dietary choices. Whether you're looking to improve your sleep, boost your mood, or just stay healthy, knowing about tryptophan is a step in the right direction. So, next time you enjoy a turkey sandwich or a handful of nuts, remember you're not just satisfying your hunger—you're also giving your body a little extra support.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
