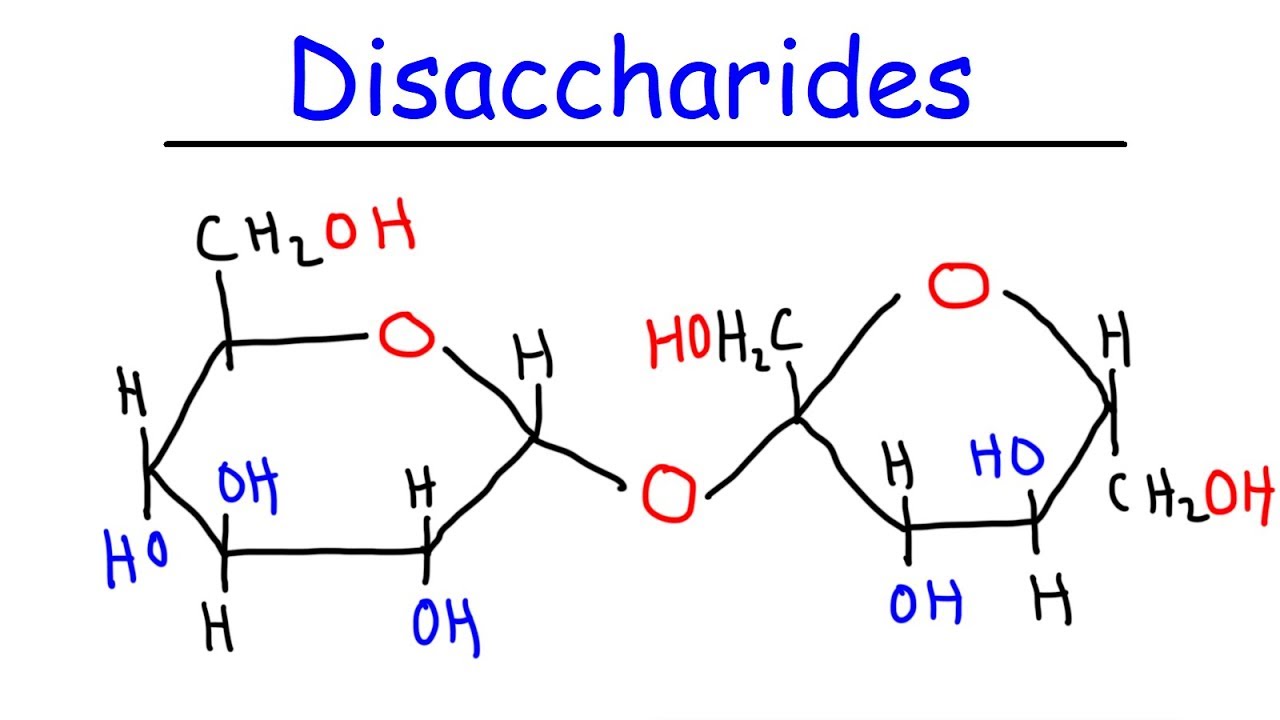
What is a disaccharide? A disaccharide is a type of carbohydrate made up of two sugar molecules bonded together. These sugars, also known as monosaccharides, combine through a process called dehydration synthesis. Common examples include sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose (malt sugar). Disaccharides play a crucial role in our diet, providing a quick source of energy. They are found in many foods we consume daily, from fruits and vegetables to dairy products and grains. Understanding disaccharides can help you make better dietary choices and appreciate the science behind your favorite treats.
What is a Disaccharide?
Disaccharides are a type of carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides join together. They play a crucial role in nutrition and biology. Here are some fascinating facts about disaccharides.
-
Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides. These simple sugars link through a glycosidic bond.
-
Common disaccharides include sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Each has unique properties and functions in the body.
-
Sucrose is table sugar. It's made from glucose and fructose and is widely used as a sweetener.
-
Lactose is found in milk. This sugar consists of glucose and galactose.
-
Maltose is a product of starch digestion. Formed from two glucose molecules, it appears during the breakdown of starch.
How are Disaccharides Formed?
The formation of disaccharides involves a specific chemical process. Understanding this process helps explain their structure and function.
-
Disaccharides form through a dehydration reaction. This process removes a water molecule when two monosaccharides bond.
-
The bond between monosaccharides is called a glycosidic bond. This bond can be alpha or beta, affecting the disaccharide's properties.
-
Enzymes catalyze the formation of disaccharides. Specific enzymes help link monosaccharides together.
-
Hydrolysis breaks down disaccharides. Adding water reverses the dehydration reaction, splitting the disaccharide into monosaccharides.
Functions of Disaccharides in the Body
Disaccharides play several roles in human health and nutrition. Their functions extend beyond just providing sweetness.
-
Disaccharides are a quick energy source. The body easily breaks them down into glucose for energy.
-
Lactose aids calcium absorption. This sugar helps the body absorb calcium from dairy products.
-
Maltose supports digestion. It appears during starch digestion, helping break down complex carbohydrates.
-
Sucrose provides a rapid energy boost. This sugar is quickly metabolized, offering immediate energy.
Interesting Facts About Specific Disaccharides
Each disaccharide has unique characteristics and uses. Here are some intriguing details about the most common ones.
-
Sucrose is the most common disaccharide in the human diet. Found in many foods, it's a primary sweetener.
-
Lactose intolerance affects many people. Some individuals lack the enzyme lactase, needed to digest lactose.
-
Maltose is less sweet than sucrose. Its mild sweetness makes it useful in brewing and baking.
-
Sucrose is derived from sugar cane and sugar beets. These plants are the primary sources of table sugar.
-
Lactose is unique to mammalian milk. No other natural source contains this sugar.
-
Maltose is often found in germinating grains. It's a key ingredient in malted beverages.
Health Implications of Disaccharides
Disaccharides can impact health in various ways. Their effects depend on how they are consumed and metabolized.
-
Excessive sucrose intake can lead to obesity. High sugar consumption is linked to weight gain and related health issues.
-
Lactose intolerance can cause digestive problems. Symptoms include bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
-
Maltose is generally well-tolerated. It rarely causes adverse reactions.
-
Moderation is key with sucrose. Balancing sugar intake helps maintain overall health.
Disaccharides in Food and Industry
Disaccharides are not just important in nutrition; they also have various industrial applications.
-
Sucrose is used in food preservation. It helps extend the shelf life of jams and jellies.
-
Lactose is used in pharmaceuticals. It acts as a filler in many medications.
-
Maltose is essential in brewing beer. It ferments to produce alcohol.
-
Sucrose is a common ingredient in baked goods. It adds sweetness and texture.
-
Lactose is used in infant formula. It mimics the sugar found in breast milk.
-
Maltose is used in the production of malt vinegar. This vinegar is popular in cooking and as a condiment.
Fun Facts About Disaccharides
Beyond their scientific and nutritional importance, disaccharides have some fun and quirky aspects.
-
Sucrose crystals can grow to impressive sizes. With the right conditions, they form large, beautiful crystals.
-
Lactose is less sweet than sucrose. It has only about 16% of the sweetness of table sugar.
-
Maltose was first discovered in 1872. French chemist Anselme Payen identified this sugar.
-
Sucrose is used in making rock candy. This treat showcases the crystalline structure of sugar.
Final Thoughts on Disaccharides
Disaccharides play a crucial role in our daily lives. From sucrose sweetening our coffee to lactose in dairy products, these sugars are everywhere. They provide energy, aid in digestion, and even have industrial uses. Understanding their structure and function helps us make informed dietary choices. Remember, while they offer benefits, moderation is key to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Next time you enjoy a sweet treat or a glass of milk, you'll know the science behind it. Keep exploring the world of carbohydrates and how they impact your health. Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to what we consume. So, stay curious and keep learning about the fascinating world of disaccharides.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
