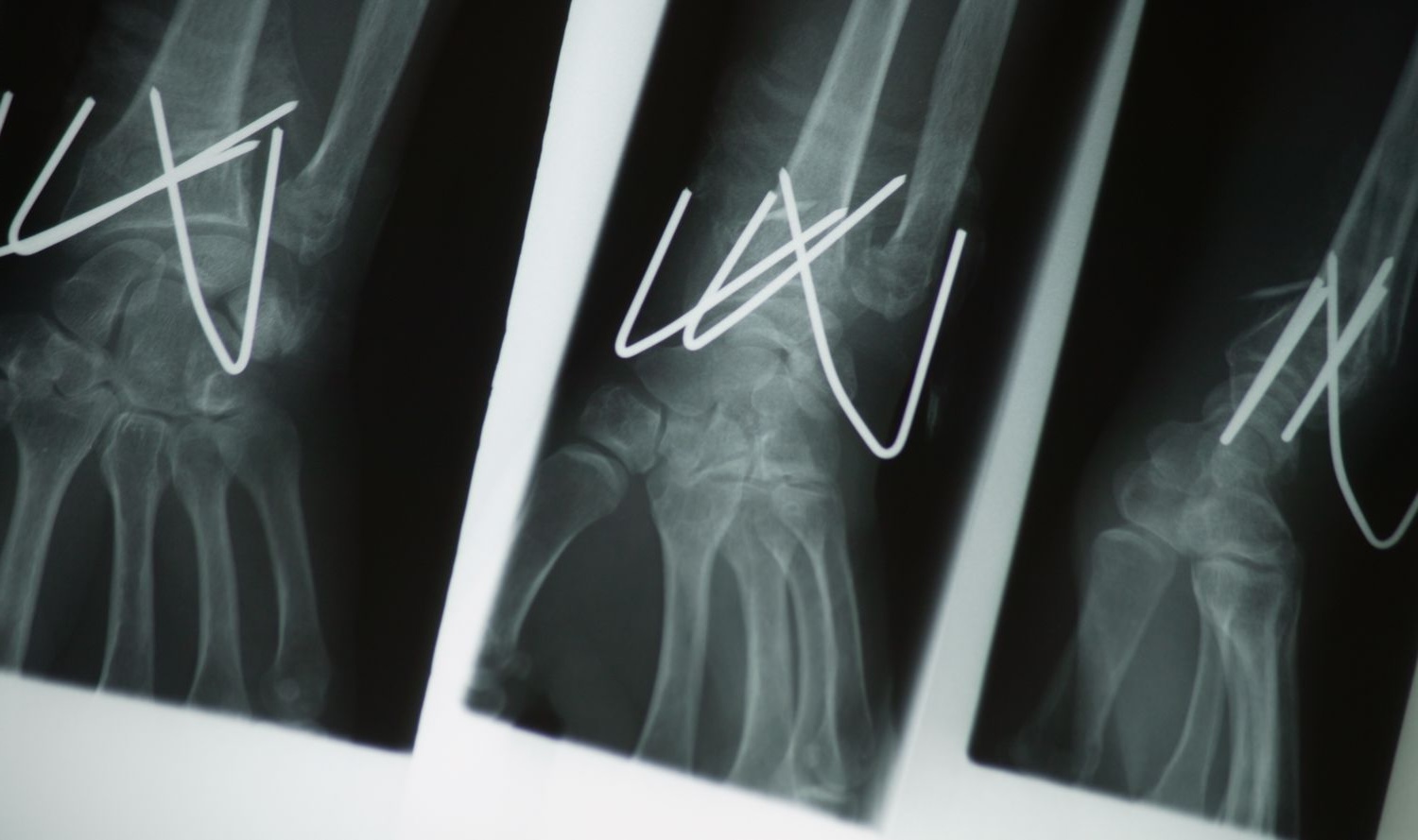
Kirschner wires, often called K-wires, are slender, pointed stainless steel pins used in orthopedic surgery. They play a crucial role in fixing bone fractures, stabilizing bone fragments, and guiding surgical procedures. But what makes these wires so special? K-wires are versatile, easy to use, and can be inserted with minimal surgical trauma. They are commonly used in both human and veterinary medicine. From stabilizing broken bones in children to aiding complex hand surgeries, these wires are indispensable. Understanding their applications, benefits, and limitations can help you appreciate their significance in modern medicine. Let's dive into 30 fascinating facts about Kirschner wires that highlight their importance and versatility.
Key Takeaways:
- Kirschner wire, or K-wire, was invented in 1909 by a German surgeon named Martin Kirschner. It's a thin, strong wire used in orthopedic surgery to stabilize bones and help them heal.
- K-wire is versatile and cost-effective, making it a popular choice in orthopedic surgeries. However, it also comes with risks like infection and wire migration, so proper care is essential.
What is Kirschner Wire?
Kirschner wire, often called K-wire, is a thin, stiff wire used in orthopedic surgery. It stabilizes bone fragments or holds skeletal structures together. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this essential medical tool.
History of Kirschner Wire
Understanding the origins of K-wire can provide insight into its development and importance in medical history.
- Invented in 1909: Martin Kirschner, a German surgeon, introduced K-wire in 1909. His invention revolutionized orthopedic surgery.
- Named After Its Inventor: The wire is named after Martin Kirschner, honoring his contribution to medical science.
- Early Uses: Initially, K-wire was used for skeletal traction and fixation of bone fractures.
- World War I: During World War I, K-wire became widely used for treating soldiers' fractures, proving its effectiveness.
Material and Design
The composition and design of K-wire are crucial for its function in surgeries.
- Made of Stainless Steel: K-wire is typically made from stainless steel, ensuring strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Varying Diameters: K-wires come in different diameters, usually ranging from 0.6 mm to 3.0 mm, to suit various surgical needs.
- Sharp Tips: The wire has sharp tips on both ends, allowing easy insertion into bone.
- Smooth or Threaded: K-wires can be smooth or threaded. Threaded wires provide better grip in bone.
Applications in Surgery
K-wire's versatility makes it a staple in many surgical procedures.
- Fracture Fixation: K-wire is commonly used to fix small bone fractures, especially in the hands and feet.
- Pediatric Orthopedics: In children, K-wire is often used due to its minimal invasiveness and effectiveness.
- Temporary Fixation: Surgeons use K-wire for temporary fixation during complex procedures.
- Arthrodesis: K-wire helps in joint fusion surgeries, known as arthrodesis.
- Osteotomies: It is used in osteotomies, where bones are cut and realigned.
Advantages of Using Kirschner Wire
K-wire offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice in orthopedic surgeries.
- Minimally Invasive: The thin wire causes minimal tissue damage, leading to quicker recovery.
- Cost-Effective: K-wire is relatively inexpensive compared to other fixation devices.
- Versatile: Its wide range of applications makes it a versatile tool in orthopedic surgery.
- Easy to Remove: K-wire can be easily removed once the bone has healed.
- Radiolucent: The wire is radiolucent, meaning it does not interfere with X-rays, allowing clear imaging during and after surgery.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its advantages, K-wire has some challenges and risks associated with its use.
- Infection Risk: There is a risk of infection at the insertion site if proper sterilization is not maintained.
- Wire Migration: K-wire can migrate from its original position, potentially causing complications.
- Skin Irritation: Protruding wires can irritate the skin and surrounding tissues.
- Limited Load-Bearing: K-wire is not suitable for load-bearing bones due to its thin structure.
Innovations and Improvements
Over the years, advancements have been made to enhance the effectiveness and safety of K-wire.
- Coated Wires: Some K-wires are coated with materials to reduce infection risk and improve biocompatibility.
- Bioabsorbable Wires: Research is ongoing into bioabsorbable K-wires that dissolve in the body, eliminating the need for removal.
- Improved Sterilization Techniques: Enhanced sterilization methods have reduced infection rates associated with K-wire use.
- Customizable Lengths: Surgeons can now customize the length of K-wires to better suit specific surgical needs.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about K-wire.
- Used in Veterinary Medicine: K-wire is also used in veterinary surgeries to treat fractures in animals.
- Training Tool: Medical students often practice with K-wire to learn surgical techniques.
- Emergency Situations: In emergencies, K-wire can be used for quick and effective fracture stabilization.
- Global Use: K-wire is used worldwide, making it a universal tool in orthopedic surgery.
The Final Word on Kirschner Wire
Kirschner wires, or K-wires, play a crucial role in orthopedic surgery. These thin, flexible wires help stabilize bone fractures and guide surgical procedures. Invented by Martin Kirschner in 1909, they’ve become a staple in medical toolkits worldwide. K-wires are versatile, used in everything from fixing broken bones to aiding in spinal surgeries. They’re easy to insert and remove, making them a favorite among surgeons.
Despite their benefits, K-wires come with risks like infection and wire migration. Proper sterilization and careful monitoring are essential to minimize these issues. Advances in technology continue to improve their safety and effectiveness.
Understanding the ins and outs of K-wires can help patients feel more at ease when facing surgery. Knowledge is power, and now you’re equipped with the facts about this vital medical tool. Stay informed, stay healthy!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
