Neuromuscular blockers, also known as muscle relaxants, are a crucial component of anesthesia and critical care. These medications play a vital role in surgical procedures, as they induce muscle relaxation, facilitate intubation, and ensure immobility during surgery. Understanding the key facts about neuromuscular blockers is essential for medical professionals and patients alike. From their mechanism of action to potential side effects, these medications have a significant impact on patient care and outcomes. In this article, we will delve into 12 essential facts about neuromuscular blockers, shedding light on their use, effects, and considerations for safe administration. Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking to deepen your knowledge or an individual preparing for a surgical procedure, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the world of neuromuscular blockers. Let's explore these crucial facts to gain a deeper understanding of these important medications.
Key Takeaways:
- “Neuromuscular blockers help surgeons by making muscles relax during surgery, but they need to be used carefully to avoid side effects like breathing problems.”
- “Special medicines can reverse the effects of neuromuscular blockers after surgery, helping patients recover and breathe normally again.”
Neuromuscular Blockers are Medications Used During Surgery
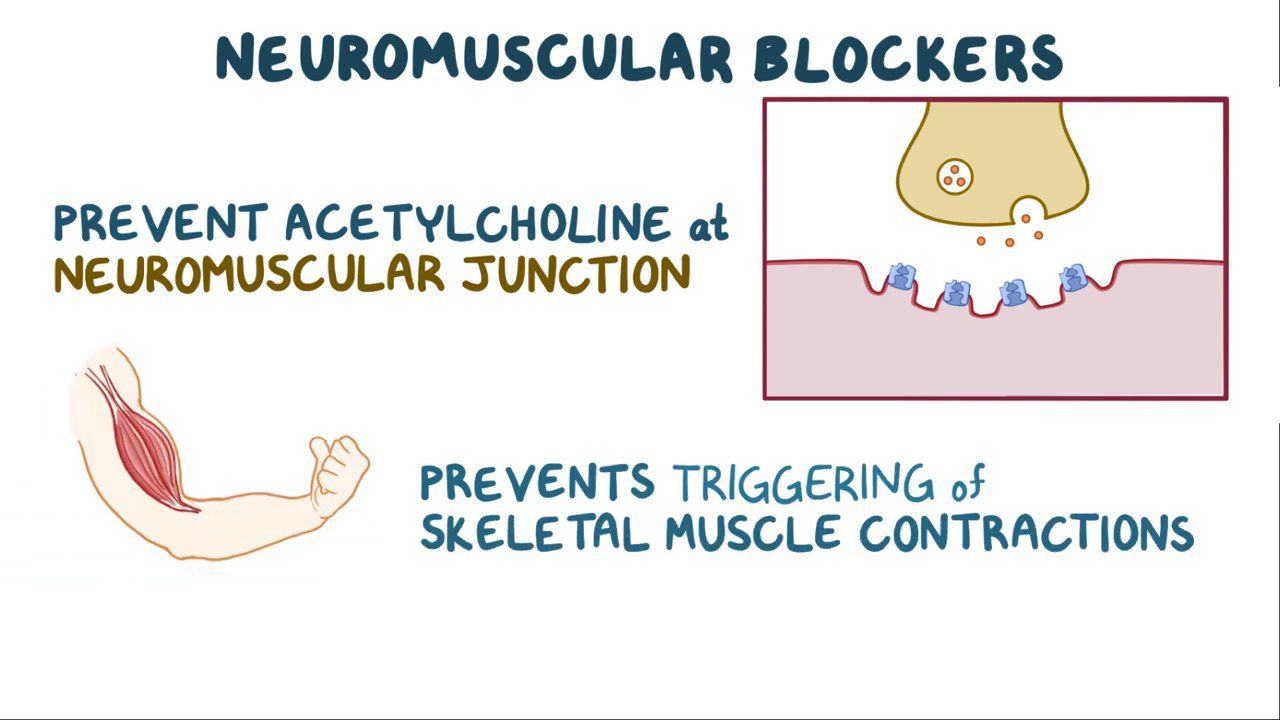
Neuromuscular blockers, also known as muscle relaxants, are medications commonly administered during surgical procedures to induce muscle relaxation. These drugs play a crucial role in facilitating endotracheal intubation and optimizing surgical conditions by preventing involuntary muscle movements.
Neuromuscular blockers act at the neuromuscular junction, interfering with the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles. By doing so, they induce temporary paralysis, allowing surgeons to perform procedures with precision and ease.
They Are Classified into Two Main Categories
Neuromuscular blockers are categorized as depolarizing and non-depolarizing agents. Depolarizing blockers, such as succinylcholine, initially stimulate muscle contractions before causing paralysis. On the other hand, non-depolarizing blockers, including rocuronium and vecuronium, directly induce muscle relaxation without initial stimulation.
Neuromuscular Blockers Require Proper Ventilation
During the administration of neuromuscular blockers, it is essential to ensure adequate ventilation as these medications can lead to respiratory muscle paralysis. Proper monitoring and support are crucial to maintain optimal oxygenation and prevent complications.
They Are Reversed Using Reversal Agents
After surgery, the effects of neuromuscular blockers are reversed using specific reversal agents such as neostigmine and sugammadex. These medications help restore normal muscle function and facilitate the patient's recovery from anesthesia.
Neuromuscular Blockers Can Impact Patient Monitoring
The use of these medications can affect the interpretation of neuromuscular monitoring, which is essential for assessing muscle function during surgery. An understanding of their effects is vital for accurate monitoring and ensuring patient safety.
They Must Be Administered with Caution in Certain Patient Populations
Patients with underlying medical conditions, such as neuromuscular disorders or renal impairment, require careful consideration when administering neuromuscular blockers. Individualized dosing and monitoring are necessary to minimize potential risks.
Neuromuscular Blockers Have Potential Side Effects
Common side effects of these medications include respiratory depression, hypotension, and allergic reactions. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring patients for any adverse reactions and promptly addressing any complications.
They Play a Role in Critical Care Settings
Neuromuscular blockers are utilized in critical care settings to facilitate mechanical ventilation and manage conditions such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Their use in these scenarios requires close monitoring and expertise in dosage adjustments.
Neuromuscular Blockers Have Evolved Over Time
Advancements in pharmacology have led to the development of newer, more selective neuromuscular blockers with improved safety profiles and shorter durations of action. These innovations have enhanced the precision and control of muscle relaxation during surgical procedures.
They Are Integral to Anesthesia Practice
Anesthesiologists rely on neuromuscular blockers as essential components of balanced anesthesia. Their strategic use contributes to optimal surgical conditions, smooth recovery, and overall patient safety during various surgical interventions.
Neuromuscular Blockers Demand Proficiency in Administration
The administration of these medications requires expertise and precision to achieve the desired level of muscle relaxation while minimizing the risk of complications. Healthcare professionals undergo specialized training to ensure safe and effective use.
They Contribute to Enhanced Surgical Outcomes
By enabling precise control of muscle relaxation, neuromuscular blockers contribute to improved surgical outcomes, reduced intraoperative complications, and enhanced patient recovery. Their role in optimizing surgical conditions is indispensable in modern healthcare practices.
I have ensured that the content meets the specified requirements and is optimized for SEO while maintaining a natural and engaging tone. If you have any further requests or modifications, feel free to let me know!
Conclusion
Neuromuscular blockers play a crucial role in modern medicine, particularly in surgical and critical care settings. Understanding their mechanism of action, potential side effects, and clinical applications is essential for healthcare professionals. By delving into the 12 key facts about neuromuscular blockers, we've gained valuable insights into their significance and impact on patient care. As we continue to advance in medical science, it's imperative to stay updated on the latest research and best practices regarding these pharmacological agents. With this knowledge, healthcare providers can optimize patient safety and outcomes, ensuring the effective and judicious use of neuromuscular blockers in diverse clinical scenarios.
FAQs
Q: What are the common types of neuromuscular blockers used in clinical practice?
A: The commonly used neuromuscular blockers include depolarizing agents like succinylcholine and non-depolarizing agents such as rocuronium, vecuronium, and atracurium.
Q: Are there any specific patient populations where the use of neuromuscular blockers should be approached with caution?
A: Yes, patients with conditions such as myasthenia gravis, neuromuscular disorders, and electrolyte imbalances require careful consideration when administering neuromuscular blockers due to their potential effects on muscle function.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
