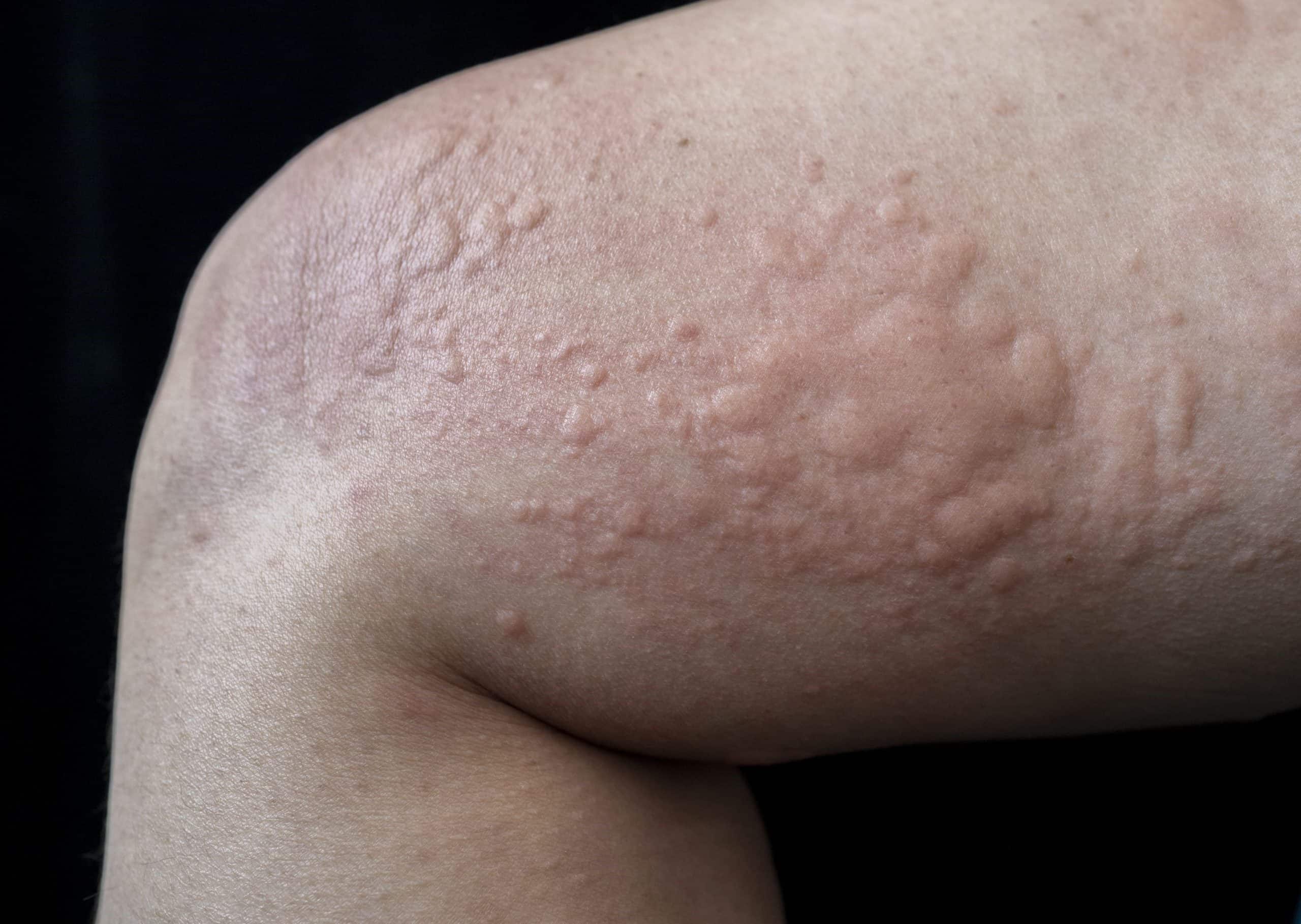
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that causes itchy, red welts. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size. Hives can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, stress, or even exercise. While most cases are acute and resolve within a few days, some people experience chronic urticaria, which can last for months or even years. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of this condition is crucial for managing it effectively. This article will provide 50 facts about urticaria to help you better understand and manage this common yet often misunderstood skin condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Urticaria, or hives, can be triggered by allergies, infections, and stress. It can be managed with antihistamines, lifestyle changes, and home remedies like cold compresses and oatmeal baths.
- Children can also suffer from urticaria, often due to food allergies and viral infections. Keeping a food diary and using antihistamines under medical supervision can help manage the condition effectively.
What is Urticaria?
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size. Understanding urticaria can help manage and treat it effectively.
- Urticaria affects about 20% of people at some point in their lives.
- The condition can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks).
- Stress can trigger or worsen urticaria.
- Urticaria can be caused by allergic reactions, infections, or even physical stimuli like pressure or temperature changes.
- The welts can change shape, move around, disappear, and reappear over short periods.
Symptoms of Urticaria
Recognizing the symptoms of urticaria is crucial for timely treatment. The symptoms can range from mild to severe and may require different approaches to manage.
- Itchy, raised welts are the most common symptom.
- Welts can be red, pink, or flesh-colored.
- Swelling, known as angioedema, can occur around the eyes, lips, hands, feet, and throat.
- The itching can be intense and may interfere with daily activities.
- Symptoms can worsen at night, disrupting sleep.
Causes of Urticaria
Identifying the cause of urticaria can help in managing the condition more effectively. Various factors can trigger hives, and understanding these can aid in prevention.
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings are common triggers.
- Infections, both viral and bacterial, can cause urticaria.
- Physical factors like heat, cold, sunlight, and pressure can trigger hives.
- Autoimmune disorders can lead to chronic urticaria.
- Sometimes, the cause remains unknown, termed idiopathic urticaria.
Diagnosis of Urticaria
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose urticaria and determine its underlying cause.
- A detailed medical history is often the first step in diagnosis.
- Physical examination of the skin helps identify the characteristic welts.
- Allergy tests can pinpoint specific allergens causing the hives.
- Blood tests may be conducted to rule out underlying conditions.
- In some cases, a skin biopsy is performed to exclude other skin disorders.
Treatment Options for Urticaria
Several treatment options are available to manage urticaria. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
- Antihistamines are the most common treatment for urticaria.
- Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe cases.
- Avoiding known triggers can help prevent flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressants are used in chronic cases unresponsive to other treatments.
- Omalizumab, an injectable medication, is effective for chronic urticaria.
Home Remedies for Urticaria
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help alleviate the symptoms of urticaria. These remedies can provide relief and complement conventional treatments.
- Applying a cold compress can reduce itching and swelling.
- Taking an oatmeal bath can soothe irritated skin.
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing can prevent further irritation.
- Avoiding hot showers and opting for lukewarm water can help.
- Using fragrance-free skin care products can reduce irritation.
Complications of Urticaria
While urticaria is usually not life-threatening, it can lead to complications if not managed properly. Understanding these complications can help in taking preventive measures.
- Chronic urticaria can significantly impact the quality of life.
- Severe angioedema can cause difficulty breathing and swallowing.
- Persistent itching can lead to skin infections from scratching.
- Stress and anxiety can worsen the condition, creating a vicious cycle.
- In rare cases, anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction, can occur.
Urticaria in Children
Children can also suffer from urticaria. Recognizing and managing the condition in children requires special attention and care.
- Food allergies are a common cause of urticaria in children.
- Viral infections often trigger hives in young kids.
- Children's skin is more sensitive, making them more prone to hives.
- Antihistamines are generally safe for children but should be used under medical supervision.
- Keeping a food diary can help identify triggers in children.
Urticaria and Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage urticaria more effectively. These changes can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
- Maintaining a healthy diet can boost the immune system.
- Regular exercise can help reduce stress, a known trigger.
- Practicing good skin care can prevent irritation.
- Avoiding known allergens is crucial in managing the condition.
- Staying hydrated can help maintain healthy skin.
Myths and Facts about Urticaria
There are many myths surrounding urticaria. Dispelling these myths can lead to better understanding and management of the condition.
- Myth: Urticaria is contagious. Fact: It is not contagious.
- Myth: Only allergies cause urticaria. Fact: Many factors can trigger it.
- Myth: Urticaria always requires medical treatment. Fact: Mild cases can resolve on their own.
- Myth: Hives are always red. Fact: They can be pink or flesh-colored.
- Myth: Urticaria is a rare condition. Fact: It affects a significant portion of the population.
Final Thoughts on Urticaria
Urticaria, or hives, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its triggers, symptoms, and treatments can help manage this condition better. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, stress, and environmental factors. Symptoms often involve red, itchy welts on the skin, which can be uncomfortable and distressing. Treatments range from antihistamines and corticosteroids to lifestyle changes like avoiding known triggers and reducing stress.
Knowing these facts empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing urticaria. If you or someone you know suffers from hives, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Staying informed and vigilant can make a significant difference in improving quality of life. Remember, while urticaria can be challenging, it’s manageable with the right knowledge and approach. Stay educated, stay prepared, and take control of your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
