Tinel's Sign is a medical term often mentioned in discussions about nerve injuries and conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. But what exactly is it? Tinel's Sign is a way to detect irritated nerves. When a doctor taps over a nerve, a tingling sensation or "pins and needles" feeling may occur in the area the nerve supplies. This reaction helps diagnose nerve problems. Named after French neurologist Jules Tinel, this test is simple yet effective. Knowing about Tinel's Sign can help you understand more about your body and how doctors diagnose nerve issues. Ready to learn 50 fascinating facts about Tinel's Sign? Let's get started!
What is Tinel's Sign?
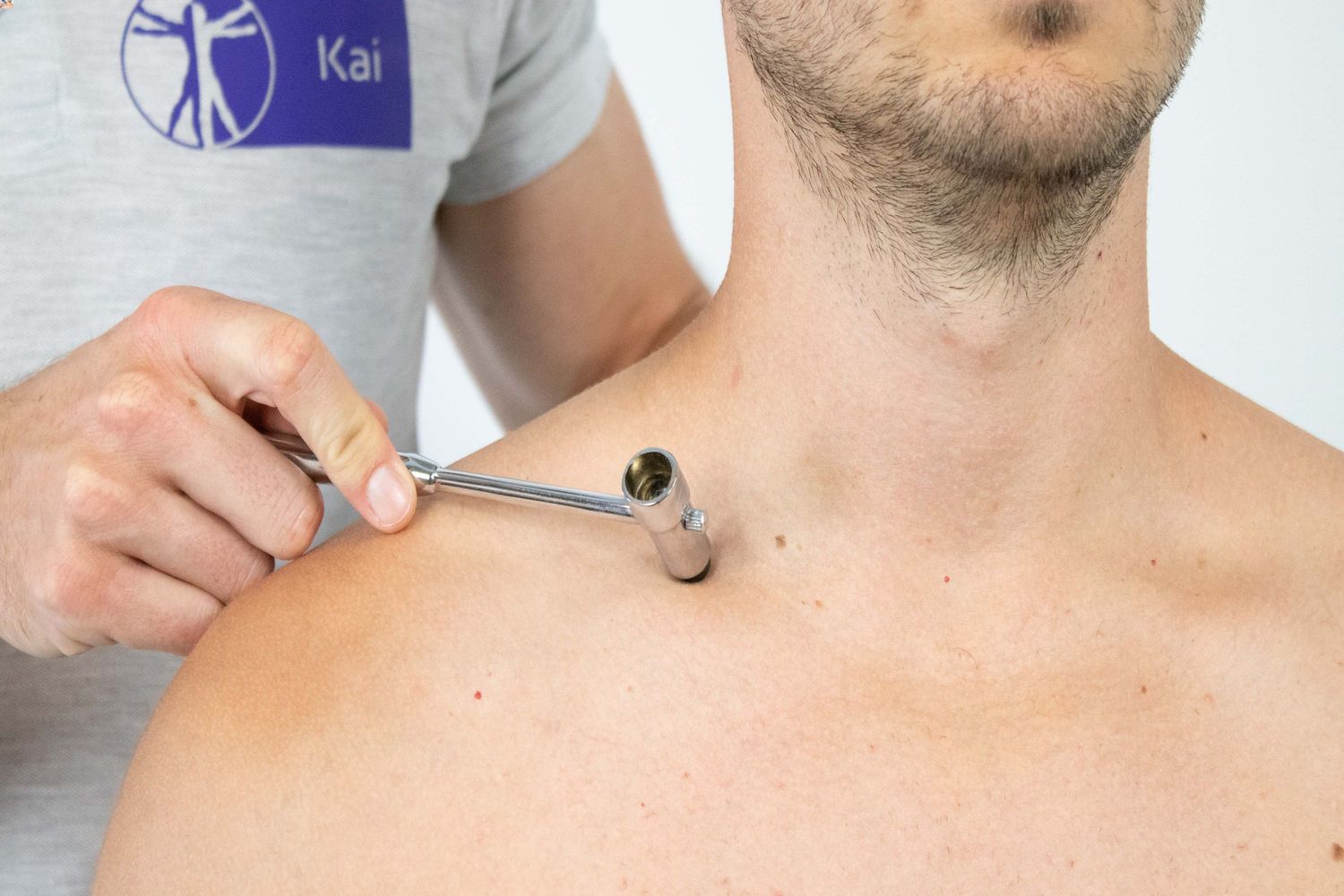
Tinel's sign is a medical test used to detect irritated nerves. Named after French neurologist Jules Tinel, it involves tapping over a nerve to elicit a tingling sensation. This test helps diagnose conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and other nerve compression disorders.
- Tinel's sign is named after Jules Tinel, a French neurologist who described it in 1915.
- The test involves tapping over a nerve to elicit a tingling sensation, known as paresthesia.
- Paresthesia felt during the test indicates nerve irritation or damage.
- Tinel's sign is commonly used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
- It can also help identify cubital tunnel syndrome, another nerve compression disorder.
- The test is performed by gently tapping over the suspected nerve with a reflex hammer or fingers.
- A positive Tinel's sign means the patient feels tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.
- Negative Tinel's sign means no tingling sensation is felt, suggesting no nerve irritation.
- The test can be performed on various nerves, including the median nerve and ulnar nerve.
- Tinel's sign is a non-invasive and simple test, making it easy to perform in a clinical setting.
Historical Background of Tinel's Sign
Understanding the history behind Tinel's sign gives insight into its development and significance in medical diagnostics. Jules Tinel's work during World War I led to the identification of this useful diagnostic tool.
- Jules Tinel first described the sign while treating soldiers with nerve injuries during World War I.
- His observations were published in a paper titled "Le signe du fourmillement dans les lésions des nerfs" in 1915.
- Tinel's work focused on nerve regeneration and the symptoms associated with nerve healing.
- The test was initially used to monitor the progress of nerve recovery in injured soldiers.
- Tinel's sign has since become a standard diagnostic tool in neurology and orthopedics.
How Tinel's Sign is Used in Diagnosis
Tinel's sign plays a crucial role in diagnosing various nerve-related conditions. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals.
- Tinel's sign helps diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome by tapping over the median nerve at the wrist.
- For cubital tunnel syndrome, the test involves tapping over the ulnar nerve at the elbow.
- It can also be used to detect tarsal tunnel syndrome by tapping over the posterior tibial nerve at the ankle.
- The test is useful in identifying nerve entrapment in different parts of the body.
- Tinel's sign can help differentiate between nerve injury and other causes of pain or numbness.
- It is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies and electromyography.
- A positive Tinel's sign can guide further imaging studies, like MRI or ultrasound, to pinpoint the exact location of nerve compression.
- The test is also helpful in post-surgical evaluations to assess nerve healing and recovery.
- Tinel's sign can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment interventions for nerve compression disorders.
Limitations and Considerations
While Tinel's sign is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has its limitations. Understanding these can help healthcare professionals use the test more effectively.
- A positive Tinel's sign is not always definitive for nerve compression; other conditions can cause similar symptoms.
- The test may produce false positives in patients with heightened sensitivity or anxiety.
- False negatives can occur if the nerve irritation is mild or the tapping is not performed correctly.
- Tinel's sign should be interpreted in the context of the patient's overall clinical picture and other diagnostic findings.
- The test may be less reliable in patients with chronic nerve compression, where nerve damage is more extensive.
- Tinel's sign is less effective in diagnosing deeply located nerves due to the difficulty in accessing them through tapping.
- The test's sensitivity and specificity can vary depending on the examiner's technique and experience.
- Tinel's sign is more useful in early-stage nerve compression, where symptoms are more likely to be elicited.
- It should be used as part of a comprehensive assessment rather than a standalone diagnostic tool.
Interesting Facts About Tinel's Sign
Beyond its clinical applications, Tinel's sign has some intriguing aspects that highlight its significance in medical history and practice.
- Tinel's sign is sometimes referred to as the "Tinel-Hoffmann sign" in honor of German neurologist Paul Hoffmann, who independently described a similar test.
- The test is a classic example of a "provocative test", designed to provoke symptoms to aid in diagnosis.
- Tinel's sign is often taught in medical schools as a fundamental clinical skill for diagnosing nerve disorders.
- The test can be performed by healthcare professionals across various specialties, including neurology, orthopedics, and physical therapy.
- Tinel's sign has been adapted for use in veterinary medicine to diagnose nerve injuries in animals.
- The test's simplicity and non-invasiveness make it a preferred initial diagnostic tool in resource-limited settings.
- Tinel's sign has been featured in numerous medical textbooks and clinical guidelines as a key diagnostic maneuver.
- The test's effectiveness can vary based on the patient's anatomy and the location of the nerve compression.
- Tinel's sign is often used in sports medicine to diagnose nerve injuries in athletes.
- The test can be performed in various positions, such as sitting, standing, or lying down, depending on the nerve being tested.
- Tinel's sign has been the subject of clinical research to evaluate its diagnostic accuracy and reliability.
- The test is sometimes combined with other physical examination maneuvers, like Phalen's test, to increase diagnostic accuracy.
- Tinel's sign can help identify nerve regeneration in patients recovering from nerve injuries or surgeries.
- The test's name is sometimes misspelled as "Tinnel's sign" or "Tinnell's sign" in medical literature.
- Tinel's sign has been adapted for use in telemedicine, where healthcare providers guide patients to perform the test on themselves during virtual consultations.
- The test's principles have inspired the development of other diagnostic techniques for nerve disorders.
- Tinel's sign remains a valuable and widely used tool in modern medicine, over a century after its initial description.
The Final Word on Tinel's Sign
Tinel's Sign is a fascinating and crucial diagnostic tool in the world of neurology. Named after French neurologist Jules Tinel, this test helps identify nerve damage and regeneration. By tapping over a nerve, doctors can pinpoint areas of nerve compression or injury. This simple yet effective method has stood the test of time, proving invaluable in diagnosing conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome.
Understanding Tinel's Sign can empower patients to seek timely medical advice, potentially preventing further nerve damage. It's a reminder of how small, seemingly simple tests can have a significant impact on our health. So, next time you experience tingling or numbness, remember Tinel's Sign and consult a healthcare professional. Knowledge is power, and being informed about such diagnostic tools can make all the difference in your health journey.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
