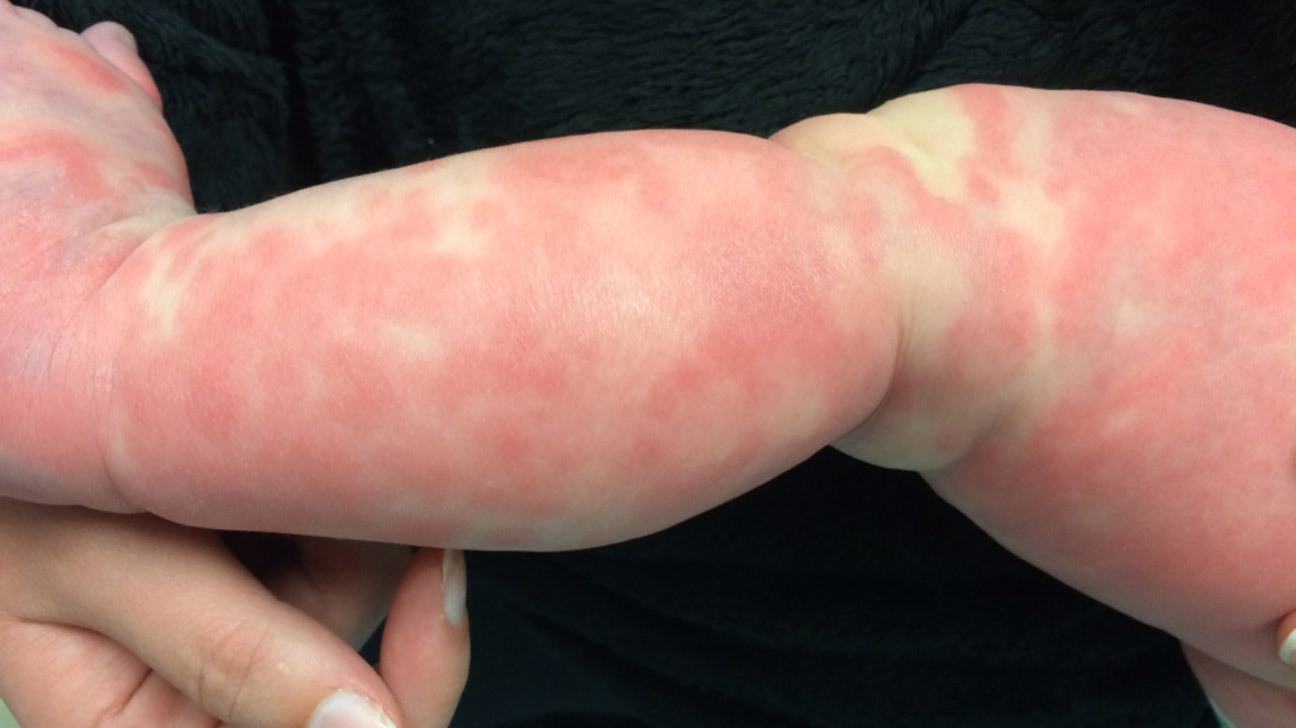
Serum sickness might sound like a rare, old-timey illness, but it’s something that can still affect people today. What is serum sickness? It’s an allergic reaction to certain medications or antiserum, which are used to treat infections or other conditions. Symptoms can include fever, rash, joint pain, and swelling. This reaction typically occurs one to three weeks after exposure to the triggering substance. Understanding serum sickness is crucial because it helps in identifying and managing the symptoms early. By knowing more about this condition, you can better protect yourself and your loved ones from its effects.
Key Takeaways:
- Serum sickness is a rare reaction to medications or antiserum, causing symptoms like fever, rash, and joint pain. Early diagnosis and stopping the triggering substance can lead to full recovery.
- Understanding the causes of serum sickness, such as immune system reactions and genetic factors, can help in preventing and managing this condition effectively. Prompt treatment and supportive care are crucial for recovery.
What is Serum Sickness?
Serum sickness is a reaction to certain medications or antiserum. It can cause various symptoms and complications. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
- Serum sickness occurs when the immune system reacts to proteins in antiserum or medications.
- Symptoms typically appear 7-12 days after exposure to the triggering substance.
- Common symptoms include fever, rash, joint pain, and swelling.
- Serum sickness was first identified in the early 20th century.
- It is considered a type III hypersensitivity reaction.
- Antiserum, used to treat infections or toxins, can sometimes cause serum sickness.
- Antibiotics like penicillin can also trigger this reaction.
- The condition is rare, affecting only a small percentage of people exposed to antiserum or certain medications.
- Symptoms usually resolve within a few weeks without long-term effects.
- Treatment often involves stopping the offending medication and managing symptoms.
Causes of Serum Sickness
Understanding what causes serum sickness can help in preventing and managing it effectively.
- The immune system mistakenly identifies foreign proteins as harmful.
- This leads to the formation of immune complexes.
- These complexes deposit in blood vessel walls, causing inflammation.
- The body's response to these deposits results in the symptoms of serum sickness.
- Antitoxins used for snake bites can sometimes cause serum sickness.
- Vaccines containing animal proteins may also trigger this reaction.
- Monoclonal antibodies, used in some cancer treatments, can be a cause.
- The risk increases with repeated exposure to the same antiserum or medication.
- Genetic factors may play a role in susceptibility.
- Some autoimmune diseases can increase the risk of developing serum sickness.
Symptoms of Serum Sickness
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment and relief.
- Fever is often one of the first symptoms to appear.
- A widespread rash can develop, sometimes resembling hives.
- Joint pain and swelling are common, particularly in the knees and wrists.
- Muscle aches may accompany joint pain.
- Swollen lymph nodes can occur, especially in the neck and armpits.
- Fatigue and malaise are frequent complaints.
- Some people experience gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
- Headaches can be a symptom of serum sickness.
- In severe cases, difficulty breathing may occur.
- Symptoms can vary in intensity from mild to severe.
Diagnosis of Serum Sickness
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
- Diagnosis often begins with a detailed medical history.
- Physical examination can reveal characteristic signs like rash and swollen joints.
- Blood tests may show elevated white blood cell counts.
- Elevated levels of immune complexes can be detected in blood tests.
- Complement levels in the blood may be reduced.
- Skin biopsy can sometimes help confirm the diagnosis.
- Differential diagnosis is important to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
- A history of recent exposure to antiserum or certain medications is a key diagnostic clue.
- Imaging studies like X-rays may be used to assess joint involvement.
- Early diagnosis can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Treatment of Serum Sickness
Effective treatment can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
- The first step is to discontinue the offending medication or antiserum.
- Antihistamines can help relieve itching and rash.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used for joint pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe symptoms.
- Plasmapheresis, a procedure to remove immune complexes from the blood, is sometimes used.
- Supportive care, including rest and hydration, is important.
- Most people recover fully with appropriate treatment.
- Long-term complications are rare but can include kidney damage.
- Preventing future episodes involves avoiding the triggering substance.
- Medical alert bracelets can help inform healthcare providers of a history of serum sickness.
Final Thoughts on Serum Sickness
Serum sickness, a reaction to certain medications or antiserums, can be quite a surprise. Symptoms like fever, rash, and joint pain usually pop up within a week or two after exposure. While it might sound scary, most cases are mild and clear up on their own. Treatment often involves stopping the offending medication and managing symptoms with antihistamines or corticosteroids. Knowing the signs and seeking medical advice early can make a big difference. Staying informed helps you and your loved ones stay safe and healthy. If you ever suspect serum sickness, don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. They can provide the guidance and care needed to navigate this condition. Remember, being proactive about your health is always a smart move. Stay curious, stay informed, and take care!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
