Prolidase Deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain proteins. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms, including skin ulcers, recurrent infections, and developmental delays. Prolidase is an enzyme crucial for recycling proline, an amino acid vital for collagen production and tissue repair. Without proper prolidase function, the body struggles to maintain healthy skin, bones, and immune responses. This deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the defective gene. Understanding the complexities of Prolidase Deficiency can help in managing symptoms and improving quality of life for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Prolidase Deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain proteins, leading to symptoms like skin ulcers and developmental delays. Early diagnosis and proper care are crucial for managing the condition.
- While there is no cure for Prolidase Deficiency, treatments like wound care, antibiotics, and physical therapy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Research is ongoing to find new therapies, offering hope for the future.
What is Prolidase Deficiency?
Prolidase Deficiency (PD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain proteins. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications. Here are some intriguing facts about this rare disorder.
- PD is caused by mutations in the PEPD gene.
- The PEPD gene provides instructions for making the enzyme prolidase.
- Prolidase is crucial for breaking down dipeptides containing proline or hydroxyproline.
- Without functional prolidase, these dipeptides accumulate in the body.
- PD is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
- Both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
- Symptoms of PD can vary widely among individuals.
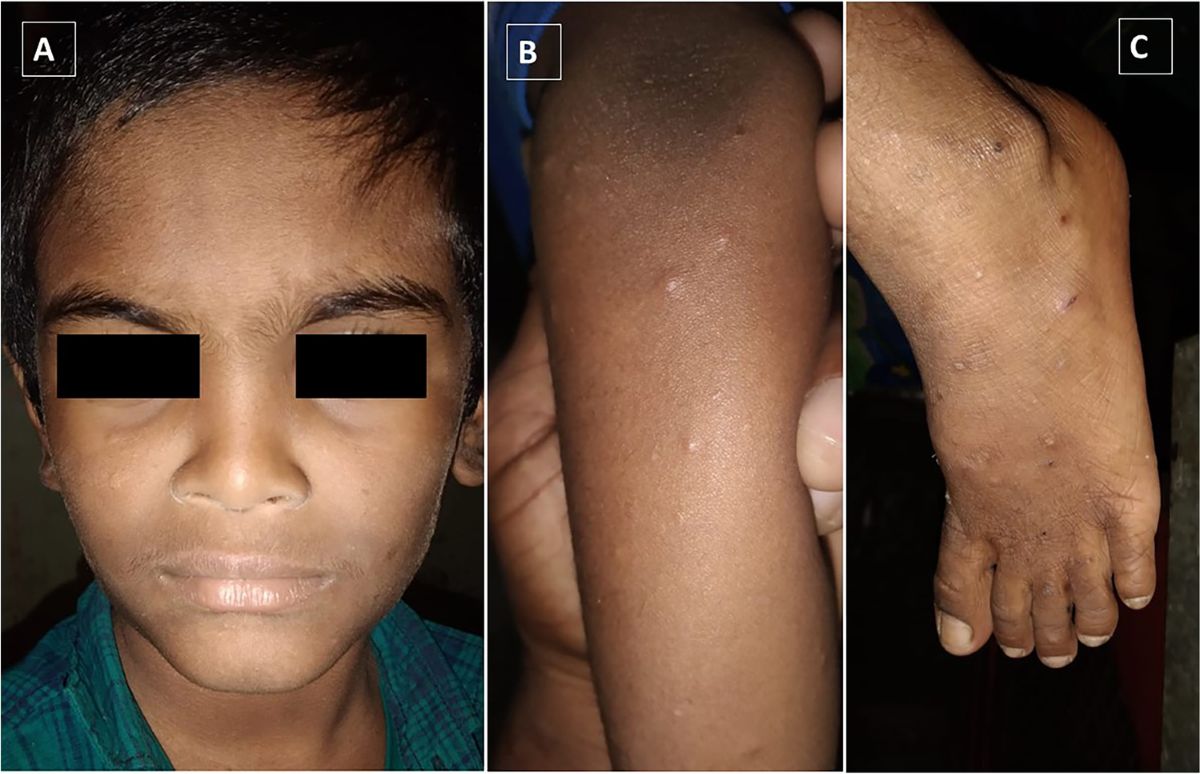
- Common symptoms include skin ulcers, recurrent infections, and developmental delays.
- Some individuals with PD may have distinctive facial features.
- These features can include a prominent forehead, wide-set eyes, and a flat nasal bridge.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how PD is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively. Here are some key points to consider.
- Skin ulcers are often slow to heal and can be painful.
- Recurrent infections may include respiratory and urinary tract infections.
- Developmental delays can affect both motor and cognitive skills.
- Some individuals may experience intellectual disability.
- Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing.
- Elevated levels of imidodipeptides in urine can indicate PD.
- Enzyme activity assays can measure prolidase activity in blood cells.
- Genetic testing can confirm mutations in the PEPD gene.
- Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Newborn screening for PD is not commonly performed.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for PD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some treatment options.
- Wound care is essential for managing skin ulcers.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat recurrent infections.
- Physical therapy can help with developmental delays.
- Speech therapy may be beneficial for individuals with communication difficulties.
- Nutritional support can address growth and feeding issues.
- Regular monitoring by a multidisciplinary team is recommended.
- Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for affected families.
- Research is ongoing to find new treatments and therapies.
- Some experimental treatments include enzyme replacement therapy.
- Support groups can offer emotional and practical support for families.
Living with Prolidase Deficiency
Living with PD can be challenging, but with proper care and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into daily life with PD.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is important for overall well-being.
- Regular medical check-ups can help monitor and manage symptoms.
- Education and awareness about PD can reduce stigma and improve support.
- Adaptive devices may assist with mobility and daily activities.
- Emotional support from family and friends is crucial.
- Connecting with others who have PD can provide a sense of community.
- Advocacy for rare diseases can help improve resources and research funding.
- Schools and workplaces can make accommodations for individuals with PD.
- Mental health support is important for coping with the challenges of PD.
- Staying informed about new research and treatments can empower individuals and families.
Research and Future Directions
Research into PD is ongoing, with scientists exploring new ways to understand and treat this condition. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
- Advances in genetic research are improving our understanding of PD.
- New diagnostic tools are being developed for earlier detection.
- Researchers are investigating the potential of gene therapy for PD.
- Clinical trials are testing new treatments and therapies.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients is key to progress.
- Patient registries are helping to collect valuable data on PD.
- Advocacy organizations are raising awareness and funding for PD research.
- International cooperation is enhancing research efforts.
- Technological advancements are aiding in the study of rare genetic disorders.
- The future holds promise for better treatments and improved quality of life for individuals with PD.
Final Thoughts on Prolidase Deficiency
Prolidase Deficiency, a rare genetic disorder, affects collagen production and can lead to various health issues. Understanding symptoms like skin lesions, recurrent infections, and developmental delays is crucial for early diagnosis. Genetic testing confirms the condition, and while there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Raising awareness about Prolidase Deficiency helps in early detection and better support for affected individuals. Families dealing with this disorder benefit from connecting with support groups and medical professionals specializing in genetic disorders.
Knowledge empowers. By spreading information about Prolidase Deficiency, we contribute to a more informed and supportive community. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance. Stay informed, stay supportive, and let's work together to improve lives affected by this rare condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
