Prehn's sign is a clinical test used to help diagnose the cause of scrotal pain. But what exactly is it? Prehn's sign involves lifting the scrotum to see if the pain is relieved. If the pain decreases, it suggests epididymitis, an inflammation of the tube at the back of the testicle. If the pain remains, it might indicate testicular torsion, a more serious condition where the testicle twists, cutting off its blood supply. This simple yet effective test can be crucial in determining the right treatment quickly. Curious about more details? Here are 50 facts about Prehn's sign that will deepen your understanding of this important diagnostic tool.
Key Takeaways:
- Prehn's sign is a simple test that helps doctors figure out if a person's scrotum pain is from testicular torsion or epididymitis. It's like a quick and easy clue for solving a medical mystery!
- Prehn's sign is a cool trick that doctors use to help them make the right diagnosis without needing fancy machines. It's like a secret code that helps them figure out what's wrong with a patient's scrotum.
What is Prehn's Sign?
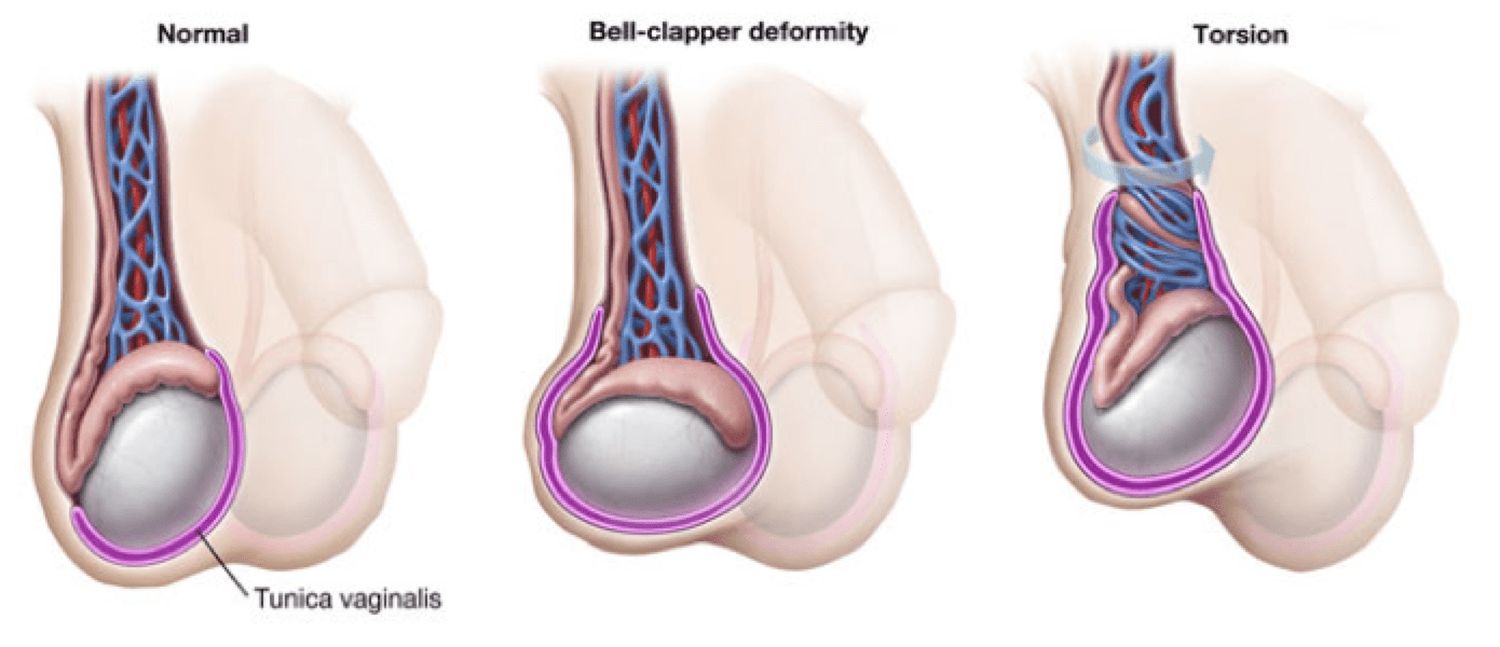
Prehn's sign is a clinical test used to differentiate between testicular torsion and epididymitis. It involves lifting the scrotum to see if pain is relieved. This simple maneuver can provide crucial information for diagnosis.
- Named after Dr. Douglas Prehn, who first described it in the early 20th century.
- Used primarily in urology to assess acute scrotal pain.
- Positive Prehn's sign indicates pain relief upon lifting the scrotum, suggesting epididymitis.
- Negative Prehn's sign means no pain relief, pointing towards testicular torsion.
- Testicular torsion is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
- Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, often treated with antibiotics.
- Simple and non-invasive, making it a quick diagnostic tool.
- Requires no special equipment, just the clinician's hands.
- Can be performed in any clinical setting, from ERs to GP offices.
- Helps avoid unnecessary imaging, reducing healthcare costs.
How to Perform Prehn's Sign
Performing Prehn's sign is straightforward. The clinician gently lifts the affected testicle and observes the patient's response.
- Patient lies on their back during the test.
- Clinician lifts the scrotum from underneath.
- Observes for pain relief or persistence.
- Quick assessment, usually taking less than a minute.
- Requires patient cooperation for accurate results.
- Can be repeated if initial results are inconclusive.
- Part of a broader physical exam, including palpation and inspection.
- May be uncomfortable but not painful.
- Often combined with other tests, like ultrasound.
- Useful in differentiating conditions, guiding further treatment.
Clinical Importance of Prehn's Sign
Understanding the clinical significance of Prehn's sign can aid in prompt and accurate diagnosis.
- Helps prioritize treatment, especially in emergency settings.
- Reduces risk of complications from delayed diagnosis.
- Guides immediate management, such as surgery for torsion.
- Improves patient outcomes by facilitating timely intervention.
- Part of standard urological training, ensuring widespread knowledge.
- Can be life-saving, particularly in young males.
- Reduces unnecessary anxiety for patients and families.
- Supports clinical decision-making, enhancing care quality.
- Aids in differential diagnosis, narrowing down potential causes.
- Valuable in resource-limited settings, where advanced imaging isn't available.
Limitations of Prehn's Sign
Despite its usefulness, Prehn's sign has limitations that clinicians should be aware of.
- Not always definitive, requiring further tests.
- Can be influenced by patient anxiety, affecting results.
- Less reliable in chronic conditions, like long-standing epididymitis.
- May not be applicable in cases of severe pain or swelling.
- False positives can occur, leading to misdiagnosis.
- False negatives are possible, especially in atypical presentations.
- Requires clinical experience, for accurate interpretation.
- Not a standalone test, should be part of a comprehensive evaluation.
- May be less effective in pediatric patients.
- Can be challenging in obese patients, due to anatomical variations.
Historical Context of Prehn's Sign
The history behind Prehn's sign adds depth to its clinical application.
- First described in 1911, by Dr. Douglas Prehn.
- Initially met with skepticism, before gaining acceptance.
- Part of early 20th-century medical advancements, in urology.
- Reflects the evolution of clinical examination techniques.
- Still relevant today, despite technological advancements.
- Included in medical textbooks, as a fundamental diagnostic tool.
- Taught in medical schools, ensuring new generations of doctors are familiar with it.
- Used globally, across various healthcare systems.
- Represents a blend of clinical intuition and scientific observation.
- A testament to the enduring value of simple, hands-on diagnostic methods.
The Final Word on Prehn's Sign
Prehn's Sign, a simple yet effective clinical test, helps doctors differentiate between testicular torsion and epididymitis. Knowing this can save lives and prevent unnecessary surgeries. Testicular torsion, a medical emergency, needs quick intervention to save the affected testicle. On the other hand, epididymitis, often treated with antibiotics, benefits from the relief provided by Prehn's Sign.
Understanding these differences empowers patients and caregivers to seek timely medical help. If you or someone you know experiences sudden testicular pain, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can make all the difference.
So, next time you hear about Prehn's Sign, you'll know it's more than just a medical term. It's a crucial tool in the world of urology, helping doctors make accurate diagnoses and provide the best care possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
