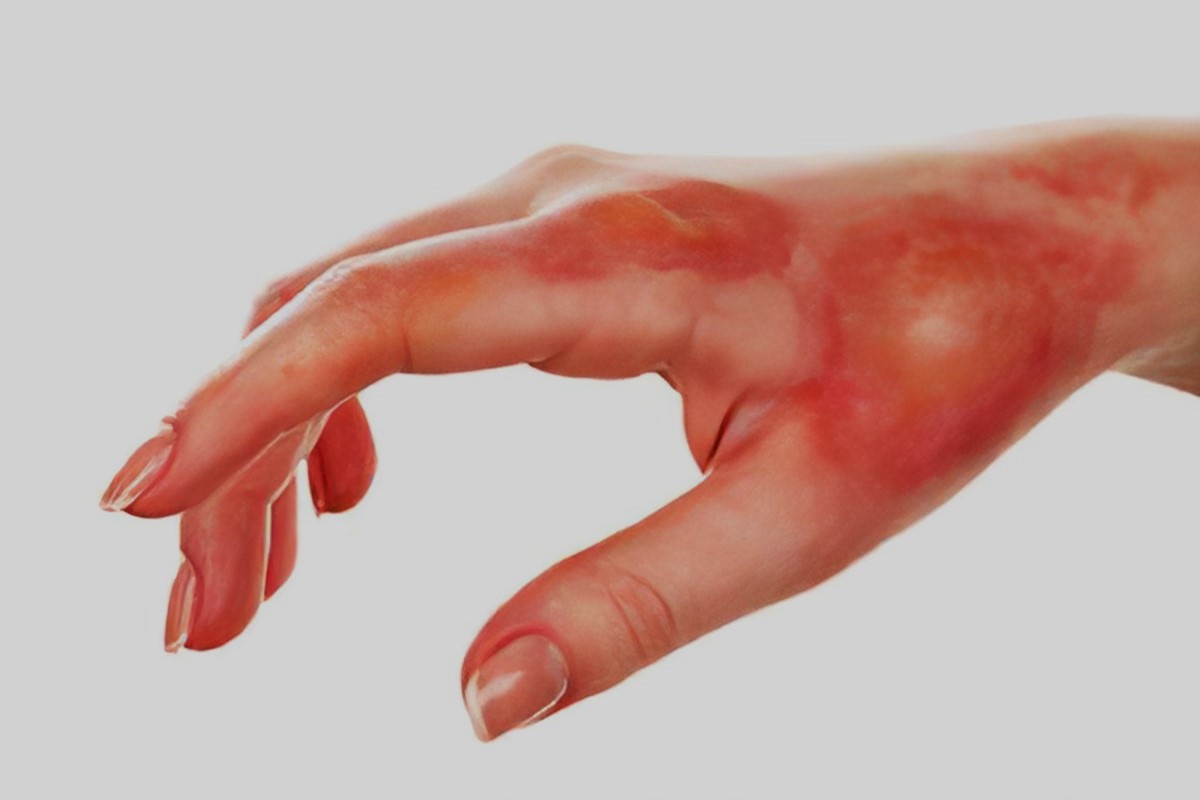
What is necrotizing fasciitis? It's a rare but serious bacterial infection that destroys tissue under the skin. Often called the "flesh-eating disease," it spreads rapidly, causing severe pain, swelling, and discoloration. This infection can start from a minor cut or scrape, making it crucial to seek medical attention quickly. Various bacteria, including Group A Streptococcus, can cause it. Early symptoms might seem like a simple skin infection, but they escalate quickly. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and surgery to remove dead tissue. Without prompt care, it can lead to severe complications or even be life-threatening. Understanding the signs and taking swift action can make a significant difference in outcomes. Stay informed and vigilant to protect yourself and loved ones from this dangerous condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Necrotizing Fasciitis, also known as flesh-eating disease, is a rare but serious bacterial infection that spreads rapidly and can cause severe tissue damage. Early detection and treatment are crucial for survival.
- Prevention involves proper wound care, avoiding contaminated water, good personal hygiene, vaccination, and recognizing early symptoms. Awareness of risk factors and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent severe outcomes.
What is Necrotizing Fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis, often called flesh-eating disease, is a rare but severe bacterial infection. It spreads quickly and can destroy skin, fat, and tissue covering muscles. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and treatment.
-
Necrotizing fasciitis is rare. Only about 700 to 1,200 cases occur in the United States each year, making it an uncommon condition.
-
Multiple bacteria can cause it. While group A Streptococcus is the most common culprit, other bacteria like Clostridium and Vibrio vulnificus can also lead to this infection.
-
It spreads rapidly. The infection can progress quickly, sometimes within hours, making prompt medical attention vital.
-
Symptoms can be misleading. Early signs resemble less severe conditions, such as the flu, with fever, chills, and fatigue.
-
Pain is a key symptom. Intense pain disproportionate to the appearance of the wound is a hallmark of this disease.
How is Necrotizing Fasciitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing necrotizing fasciitis can be challenging due to its rapid progression and non-specific early symptoms. Medical professionals rely on a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests.
-
Physical examination is crucial. Doctors look for signs of severe pain, swelling, and skin changes.
-
Imaging tests help. X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can reveal gas or fluid in tissues, indicating infection.
-
Blood tests are used. Elevated white blood cell counts and C-reactive protein levels can suggest an infection.
-
Tissue samples confirm diagnosis. A biopsy of affected tissue can identify the bacteria causing the infection.
-
Early diagnosis improves outcomes. Prompt identification and treatment are critical for survival.
Treatment Options for Necrotizing Fasciitis
Treating necrotizing fasciitis requires a multi-faceted approach, often involving surgery, antibiotics, and supportive care.
-
Surgery is often necessary. Removing dead tissue is crucial to stop the spread of infection.
-
Antibiotics are essential. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered to combat the bacteria.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can help. This treatment increases oxygen supply to tissues, aiding healing.
-
Supportive care is vital. Patients may need fluids, pain management, and nutritional support.
-
Amputation may be required. In severe cases, removing a limb can be life-saving.
Risk Factors for Necrotizing Fasciitis
Certain conditions and behaviors can increase the risk of developing necrotizing fasciitis. Awareness of these factors can aid in prevention.
-
Compromised immune systems are at risk. Individuals with weakened immunity, such as those with diabetes or cancer, are more susceptible.
-
Chronic diseases increase risk. Conditions like liver cirrhosis and kidney disease can predispose individuals to infection.
-
Recent surgery or trauma can be a trigger. Surgical wounds or injuries provide an entry point for bacteria.
-
Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may mask symptoms. These medications can reduce pain and fever, delaying diagnosis.
-
Intravenous drug use is a risk factor. Sharing needles or using contaminated drugs can introduce bacteria into the body.
Prevention of Necrotizing Fasciitis
Preventing necrotizing fasciitis involves minimizing exposure to bacteria and maintaining good hygiene practices.
-
Proper wound care is essential. Clean and cover cuts, scrapes, and wounds to prevent infection.
-
Avoiding contaminated water is wise. Stay out of warm, brackish water if you have open wounds.
-
Good personal hygiene helps. Regular handwashing reduces the risk of bacterial transmission.
-
Vaccination can protect. Vaccines for certain bacteria, like Streptococcus, can lower infection risk.
-
Awareness of symptoms is key. Recognizing early signs and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent severe outcomes.
Complications of Necrotizing Fasciitis
If not treated promptly, necrotizing fasciitis can lead to severe complications, affecting various body systems.
-
Sepsis is a serious risk. The infection can spread to the bloodstream, causing a life-threatening response.
-
Organ failure can occur. As the body fights the infection, organs like the heart and kidneys may fail.
-
Scarring and disfigurement are common. Extensive tissue removal can lead to significant cosmetic and functional issues.
-
Psychological impact is significant. Survivors may experience anxiety, depression, or PTSD due to their ordeal.
-
Long-term rehabilitation may be needed. Physical therapy and reconstructive surgery can help restore function and appearance.
Historical Cases of Necrotizing Fasciitis
Throughout history, necrotizing fasciitis has affected individuals, sometimes with high-profile cases bringing attention to the disease.
-
The disease has ancient roots. Descriptions of similar infections date back to Hippocrates in the 5th century BC.
-
Civil War soldiers suffered. Poor hygiene and battlefield injuries led to many cases among troops.
-
Modern outbreaks have occurred. In 2012, a Georgia woman made headlines after contracting the disease from a zip-lining accident.
-
Celebrity cases raise awareness. Actor Jim Henson, creator of the Muppets, died from complications related to the infection.
-
Medical advancements have improved outcomes. Despite its history, modern medicine has significantly increased survival rates.
Myths and Misconceptions about Necrotizing Fasciitis
Misunderstandings about necrotizing fasciitis can lead to fear and misinformation. Clearing up these myths is important for public awareness.
-
It's not always flesh-eating. The term "flesh-eating" is a misnomer; bacteria release toxins that damage tissue.
-
It's not highly contagious. The infection doesn't spread easily from person to person.
-
Healthy individuals can be affected. While risk factors exist, anyone can contract the disease.
-
Antibiotics alone aren't enough. Surgery is often necessary to remove infected tissue.
-
It's not a new disease. Despite recent attention, necrotizing fasciitis has been around for centuries.
Necrotizing Fasciitis in Popular Culture
The dramatic nature of necrotizing fasciitis has captured the attention of media and entertainment, often dramatizing the condition.
-
Movies have featured it. Films like "The Bay" depict fictional outbreaks of flesh-eating bacteria.
-
TV shows explore it. Medical dramas like "Grey's Anatomy" have episodes centered around the disease.
-
Books have been written. Authors use the disease as a plot device in thrillers and horror novels.
-
News stories highlight cases. Media coverage of real-life cases raises public awareness.
-
Social media spreads information. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook share stories and updates about the disease.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of necrotizing fasciitis, offering hope for better outcomes.
-
New antibiotics are being developed. Scientists work to create drugs targeting resistant bacteria.
-
Vaccine research is underway. Efforts focus on preventing infections by common bacteria causing the disease.
-
Genetic studies offer insights. Understanding genetic factors may help identify those at higher risk.
-
Improved diagnostic tools are in development. Faster, more accurate tests could lead to earlier detection.
-
Public health initiatives aim to educate. Campaigns focus on raising awareness and promoting prevention strategies.
Final Thoughts on Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis, often called the "flesh-eating disease," is a rare but serious condition that demands quick medical attention. Understanding its symptoms, like sudden pain, swelling, and fever, can make a big difference in outcomes. Early diagnosis and treatment, often involving antibiotics and surgery, are crucial for recovery. While it's uncommon, knowing how it spreads—through cuts, wounds, or surgical sites—can help in prevention. Maintaining good hygiene and caring for wounds properly reduces risk. Though alarming, it's important to remember that with prompt care, many recover fully. Awareness and education are key in combating this disease. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can protect themselves and others from this potentially life-threatening infection. Knowledge empowers us to act swiftly and seek help when needed, ensuring better health and safety for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
