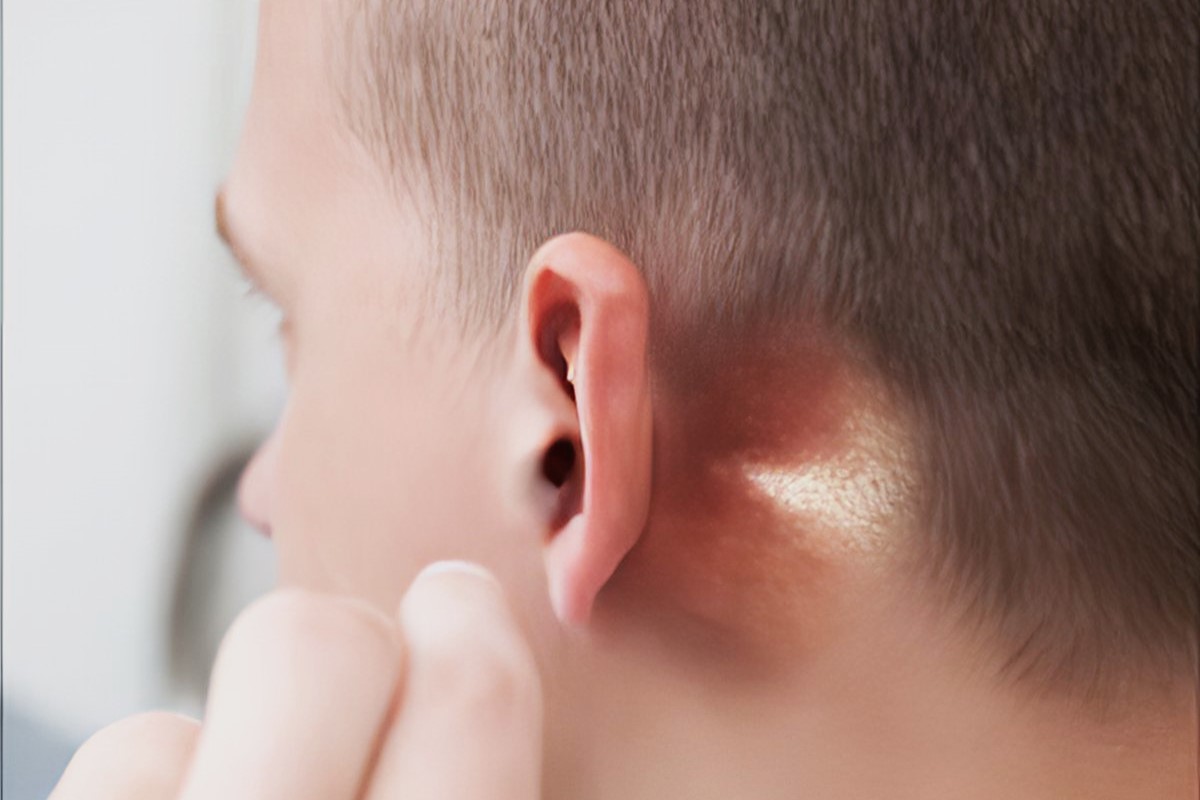
Mastoiditis is a condition that might sound unfamiliar, but it's important to know about. This infection affects the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. What causes mastoiditis? It's usually the result of an untreated ear infection. When bacteria spread from the middle ear to the mastoid bone, it can lead to swelling, pain, and sometimes fever. If left unchecked, it can cause serious complications, including hearing loss or even brain abscesses. How is it treated? Doctors often prescribe antibiotics, and in severe cases, surgery might be necessary to drain the infection. Recognizing symptoms early, like ear pain or redness behind the ear, can make a big difference. While mastoiditis is less common today due to better healthcare, understanding it helps in preventing potential risks. Stay informed and keep those ears healthy!
Key Takeaways:
- Mastoiditis is a serious infection of the mastoid bone behind the ear, often caused by untreated ear infections. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent complications like hearing loss and meningitis.
- Prevention involves timely treatment of ear infections, vaccinations, proper ear hygiene, and regular medical check-ups. Public health campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of ear health and reduce the risk of developing mastoiditis.
Understanding Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. This condition can be quite serious if not treated promptly. Here are some intriguing facts about mastoiditis that shed light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
-
Mastoid Bone's Role: The mastoid bone is part of the temporal bone of the skull. It contains air spaces that help drain the middle ear.
-
Common Cause: Often, mastoiditis results from untreated ear infections, specifically otitis media, which spreads to the mastoid bone.
-
Symptoms to Watch: Symptoms include ear pain, fever, irritability, and swelling behind the ear. These can escalate quickly.
-
Historical Context: Before antibiotics, mastoiditis was a leading cause of death in children. Modern medicine has significantly reduced its severity.
-
Diagnosis Methods: Doctors use CT scans or MRIs to confirm mastoiditis, as these can show the extent of the infection.
-
Antibiotics as Treatment: Intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment. They help combat the infection effectively.
-
Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to drain the infection and prevent complications.
-
Potential Complications: If untreated, mastoiditis can lead to hearing loss, brain abscesses, or meningitis.
-
Age Factor: While anyone can develop mastoiditis, it is more common in children due to their frequent ear infections.
-
Preventive Measures: Timely treatment of ear infections is crucial in preventing mastoiditis.
Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Help
Understanding the symptoms of mastoiditis is crucial for early intervention. Here are some key facts about recognizing and responding to this condition.
-
Ear Discharge: Persistent ear discharge can be a sign of mastoiditis, especially if it follows an ear infection.
-
Swelling and Redness: Swelling behind the ear, along with redness, is a classic symptom that should not be ignored.
-
Hearing Changes: Sudden changes in hearing or a feeling of fullness in the ear can indicate mastoiditis.
-
Fever and Fatigue: High fever and fatigue are common symptoms, as the body fights off the infection.
-
Neck Stiffness: In severe cases, neck stiffness may occur, signaling the spread of infection.
-
Medical Attention: Immediate medical attention is necessary if these symptoms appear, to prevent complications.
-
Pediatric Concerns: In children, symptoms may include irritability, poor feeding, and lethargy.
-
Chronic Ear Infections: Those with a history of chronic ear infections should be vigilant about mastoiditis symptoms.
-
Pain Behind the Ear: Persistent pain behind the ear is a warning sign that should prompt a doctor's visit.
-
Balance Issues: Dizziness or balance problems can occur if the infection affects the inner ear.
Treatment and Recovery
Once diagnosed, treatment for mastoiditis is essential for recovery. Here are some facts about the treatment process and what to expect during recovery.
-
Hospitalization: Severe cases often require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and monitoring.
-
Antibiotic Duration: Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics lasting several weeks.
-
Surgical Options: Mastoidectomy, a surgery to remove infected mastoid air cells, may be necessary.
-
Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments ensure the infection is fully resolved.
-
Hearing Tests: Post-treatment hearing tests may be conducted to assess any impact on hearing.
-
Home Care: Patients may need to continue oral antibiotics at home after hospital discharge.
-
Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest and hydration are important for recovery.
-
Pain Management: Pain relief medications can help manage discomfort during recovery.
-
Monitoring for Recurrence: Patients should be aware of symptoms that could indicate a recurrence.
-
Long-Term Outlook: With prompt treatment, most people recover fully without long-term effects.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventing mastoiditis involves awareness and proactive measures. Here are some facts about how to reduce the risk of developing this condition.
-
Vaccinations: Vaccines against common bacteria that cause ear infections can help prevent mastoiditis.
-
Ear Hygiene: Proper ear hygiene and avoiding inserting objects into the ear can reduce infection risk.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help catch ear infections early.
-
Educating Parents: Parents should be educated about the signs of ear infections and mastoiditis in children.
-
Avoiding Smoke Exposure: Reducing exposure to cigarette smoke can lower the risk of ear infections.
-
Breastfeeding Benefits: Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of ear infections in infants.
-
Prompt Treatment: Treating ear infections promptly and thoroughly is key to prevention.
-
Allergy Management: Managing allergies can help prevent ear infections that lead to mastoiditis.
-
Hydration Importance: Staying hydrated helps maintain healthy mucous membranes, reducing infection risk.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Public health campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of ear health.
Interesting Historical and Medical Facts
Mastoiditis has an interesting history and medical background. Here are some fascinating facts about its past and present.
-
Ancient Treatments: Ancient civilizations used herbal remedies and poultices to treat ear infections.
-
Antibiotic Revolution: The introduction of antibiotics in the 20th century drastically reduced mastoiditis cases.
-
Surgical Advances: Advances in surgical techniques have improved outcomes for severe cases.
-
Cultural Beliefs: Some cultures believed ear infections were caused by evil spirits and used rituals for healing.
-
Medical Research: Ongoing research aims to develop better treatments and preventive measures.
-
Global Incidence: Mastoiditis is more common in developing countries due to limited access to healthcare.
-
Pediatric Focus: Pediatricians play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating mastoiditis in children.
-
Technological Impact: Modern imaging technology has improved the accuracy of mastoiditis diagnosis.
-
Antibiotic Resistance: Concerns about antibiotic resistance highlight the need for careful treatment.
-
Future Prospects: Continued advancements in medicine hold promise for even better management of mastoiditis.
Final Thoughts on Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis, a serious infection affecting the mastoid bone behind the ear, demands attention. Recognizing symptoms like ear pain, fever, and swelling can lead to timely treatment, preventing complications. Antibiotics often serve as the first line of defense, but severe cases might require surgery. Understanding the causes, such as untreated ear infections, helps in prevention. Regular check-ups and ear care can reduce risks.
Parents should be vigilant, as children are more susceptible. Early intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes. Awareness and education about this condition are crucial for both individuals and healthcare providers.
By staying informed, you can protect yourself and loved ones from the potential dangers of mastoiditis. Remember, health is wealth, and taking proactive steps ensures a safer, healthier future. Stay curious, stay informed, and keep those ears healthy!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
