Erythema Multiforme is a skin condition that can appear suddenly, often with red patches or sores. What causes Erythema Multiforme? The main triggers include infections, medications, and sometimes unknown factors. Infections like herpes simplex virus and mycoplasma pneumoniae are common culprits. Medications such as antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and pain relievers can also spark an outbreak. This condition affects people of all ages but is more frequent in young adults. Symptoms range from mild to severe, with some cases leading to serious complications. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help manage and treat this condition effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Erythema Multiforme causes red, target-like spots on the skin and can be triggered by infections or medications. It usually resolves within weeks without treatment, but can recur if the underlying trigger is not managed.
- Erythema Multiforme can lead to painful sores in the mouth or eyes, and may require antiviral medications or corticosteroids for management. Complications like scarring and eye involvement are possible, but early intervention can improve outcomes.
What is Erythema Multiforme?
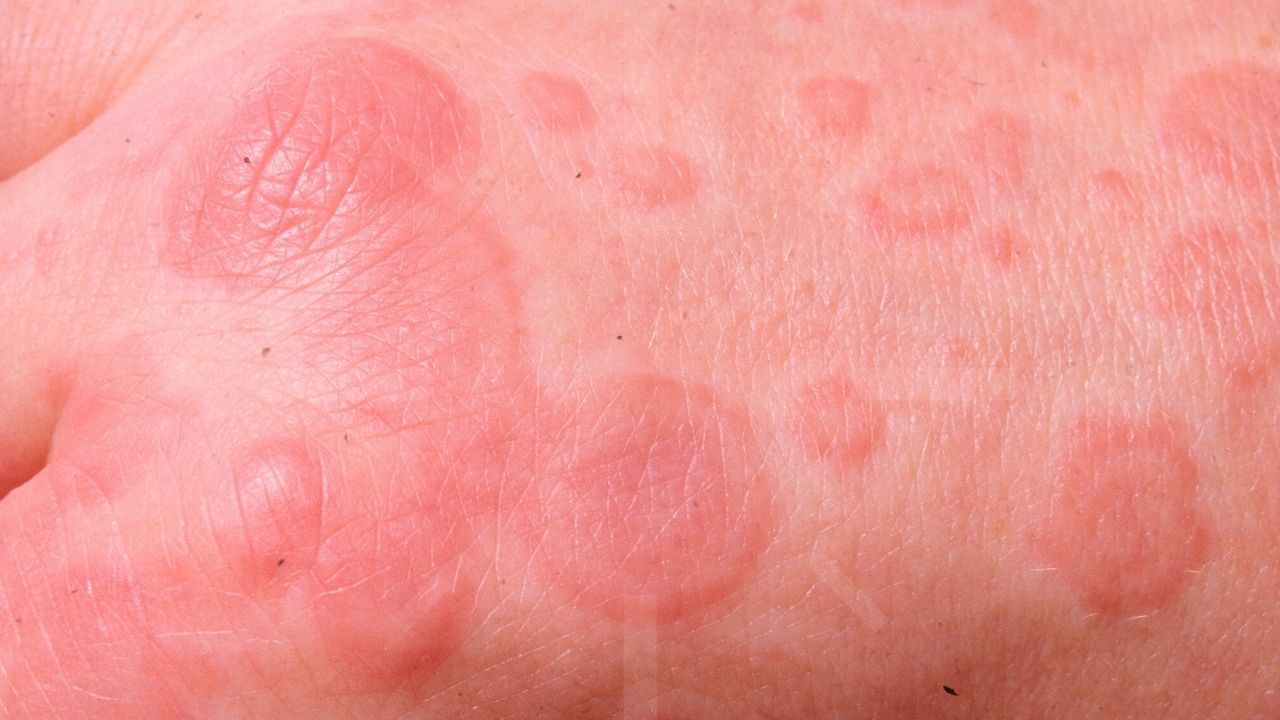
Erythema Multiforme (EM) is a skin condition that causes red, target-like spots on the body. It can be triggered by infections, medications, or other factors. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
- Erythema Multiforme is often associated with infections, particularly the herpes simplex virus.
- EM can also be triggered by medications like antibiotics and anti-seizure drugs.
- The condition is more common in young adults and children.
- Erythema Multiforme is classified into two types: minor and major.
- EM Minor usually affects the skin, while EM Major can involve mucous membranes.
- Lesions typically appear within 24 to 48 hours of exposure to the trigger.
- The rash often starts on the hands and feet before spreading to other areas.
- Target lesions are a hallmark of EM, featuring concentric rings of color.
- Erythema Multiforme can cause itching or a burning sensation.
- The condition is usually self-limiting, resolving within weeks without treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how doctors diagnose Erythema Multiforme can help in managing the condition effectively.
- Common symptoms include fever, malaise, and joint pain.
- Mucosal involvement can lead to painful sores in the mouth or eyes.
- Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the appearance of the lesions.
- Biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests can help identify underlying infections or triggers.
- Differential diagnosis is crucial to rule out other conditions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- A thorough medical history is essential for identifying potential triggers.
- Skin lesions in EM are typically symmetrical.
- Lesions can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- The rash may recur, especially if the underlying trigger is not identified or managed.
Treatment and Management
Managing Erythema Multiforme involves addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms.
- Antiviral medications may be prescribed if herpes simplex virus is the trigger.
- Discontinuing the offending drug is crucial if a medication is the cause.
- Topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Oral antihistamines may be used to relieve itching.
- Severe cases might require systemic corticosteroids.
- Pain management is important, especially for mucosal involvement.
- Hydration is essential, particularly if oral sores make eating and drinking difficult.
- Cool compresses can provide relief from itching and burning.
- Avoiding known triggers is key to preventing recurrence.
- Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are important for monitoring the condition.
Complications and Prognosis
While Erythema Multiforme is usually self-limiting, complications can arise, especially in severe cases.
- Secondary infections can occur if lesions become infected.
- Scarring is rare but possible, particularly with severe mucosal involvement.
- Eye involvement can lead to complications like conjunctivitis or keratitis.
- Dehydration is a risk if oral lesions make it difficult to drink fluids.
- Nutritional deficiencies can occur if eating is painful.
- Psychological impact should not be underestimated, as visible lesions can affect self-esteem.
- Prognosis is generally good for EM Minor, with most cases resolving within weeks.
- EM Major may take longer to resolve and can be more severe.
- Recurrence is common, especially if the underlying trigger is not managed.
- Early intervention can help minimize complications and improve outcomes.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Erythema Multiforme and improve treatment options.
- Genetic factors may play a role in susceptibility to EM.
- New antiviral therapies are being explored for herpes simplex virus-related EM.
- Immunomodulatory treatments are under investigation for severe cases.
- Biomarkers could help predict which patients are at risk of severe EM.
- Patient education is crucial for managing triggers and preventing recurrence.
- Telemedicine offers new opportunities for monitoring and managing EM remotely.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate new treatment options.
- Collaboration between dermatologists and other specialists can improve patient care.
- Awareness campaigns can help educate the public about EM and its triggers.
- Future research aims to develop targeted therapies that address the underlying causes of EM.
Final Thoughts on Erythema Multiforme
Erythema Multiforme (EM) is a complex condition with many facets. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage it better. EM often appears suddenly, with red, target-like spots on the skin. While mild cases might resolve on their own, severe forms need medical attention. Triggers like infections, medications, and even foods can set off EM. Knowing these triggers can help in prevention. Treatments range from topical creams to systemic medications, depending on severity. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best outcomes. Remember, early detection and treatment can make a significant difference. Stay vigilant, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you notice unusual skin changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
