Vascular tumors might sound like a mouthful, but they’re actually quite fascinating. These growths involve blood vessels and can appear anywhere in the body. Some are harmless, while others need medical attention. What exactly are vascular tumors? They are abnormal growths that arise from blood vessels or lymph vessels. These tumors can be benign, like hemangiomas, or malignant, such as angiosarcomas. Understanding them is crucial because they vary greatly in behavior and treatment. Some might just need monitoring, while others require surgery or even chemotherapy. Knowing the type and nature of a vascular tumor helps doctors decide the best course of action. With advances in medical science, treatments have become more effective, offering hope to many. Whether you’re curious or concerned, learning about these tumors can be both enlightening and empowering.
Key Takeaways:
- Vascular tumors can be harmless or cancerous, affecting both children and adults. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes and quality of life.
- Ongoing research and advances offer hope for improved understanding and treatment of vascular tumors, while raising awareness and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing these growths.
What Are Vascular Tumors?
Vascular tumors are growths that arise from blood vessels or lymph vessels. They can be benign or malignant, meaning they can be harmless or cancerous. Understanding these tumors helps in identifying and treating them effectively.
-
Benign vs. Malignant: Vascular tumors can be either benign, like hemangiomas, or malignant, such as angiosarcomas. Benign tumors are usually not life-threatening, while malignant ones can spread and cause serious health issues.
-
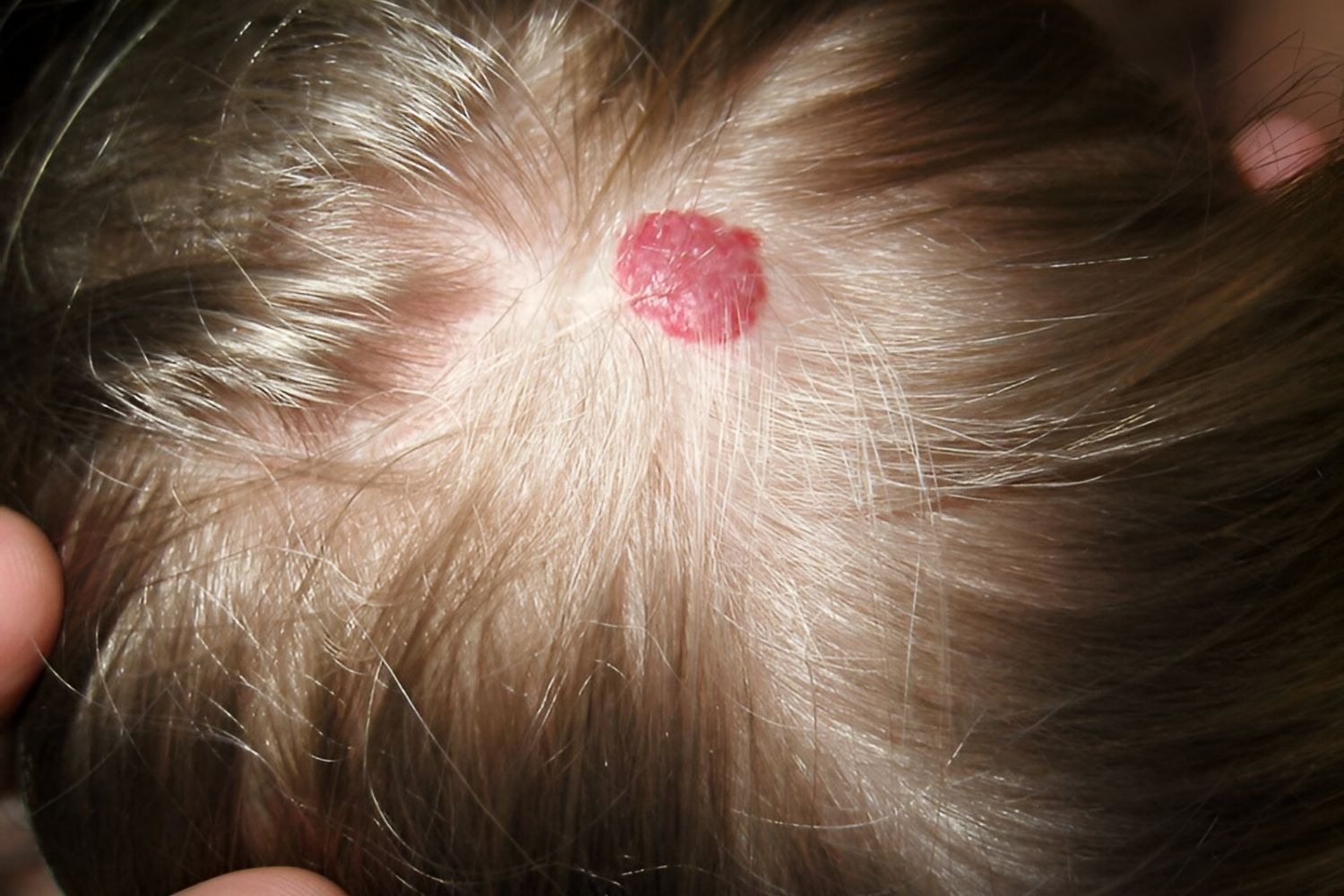
Common in Children: Hemangiomas are the most common type of vascular tumor in children. They often appear as red or purple marks on the skin and usually resolve on their own over time.
-
Rare in Adults: Vascular tumors are less common in adults. When they do occur, they are more likely to be malignant.
-
Origin: These tumors originate from cells that make up blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. They can develop anywhere in the body where these vessels are present.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms depend on the tumor's location and size. They can range from visible skin changes to pain or swelling in affected areas.
Types of Vascular Tumors
Different types of vascular tumors have unique characteristics and behaviors. Knowing these types aids in diagnosis and treatment.
-
Hemangiomas: These are benign tumors often found in infants. They appear as raised red areas on the skin and usually shrink over time.
-
Angiosarcomas: A rare and aggressive form of cancer that arises from the lining of blood vessels. They can occur anywhere but are most common in the skin, breast, liver, and spleen.
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma: Associated with human herpesvirus 8, this tumor is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
-
Lymphangiomas: These are benign tumors that arise from lymphatic vessels. They are often found in children and can appear as soft, spongy masses.
-
Glomus Tumors: Rare and usually benign, these tumors arise from glomus bodies, which are involved in temperature regulation. They often occur under the fingernails.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes vascular tumors and the risk factors involved can help in prevention and early detection.
-
Genetic Factors: Some vascular tumors are linked to genetic mutations or inherited conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau disease.
-
Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation therapy can increase the risk of developing certain types of vascular tumors, like angiosarcomas.
-
Immune System: A weakened immune system, whether due to disease or medication, can increase the risk of developing vascular tumors.
-
Age: Certain types of vascular tumors are more common in specific age groups. For example, hemangiomas are more common in infants, while angiosarcomas are more common in older adults.
-
Gender: Some vascular tumors have a higher prevalence in one gender. For instance, hemangiomas are more common in females.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating vascular tumors involves a combination of medical imaging, biopsies, and various treatment options.
-
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans are commonly used to diagnose vascular tumors and determine their size and location.
-
Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of the tumor tissue for examination under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal is often the primary treatment for benign vascular tumors and some malignant ones, depending on their size and location.
-
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells and is often used for malignant vascular tumors.
-
Chemotherapy: Drugs used in chemotherapy can help shrink or slow the growth of malignant vascular tumors.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The outlook for individuals with vascular tumors varies greatly depending on the type and stage of the tumor.
-
Benign Tumors: Most benign vascular tumors have an excellent prognosis and may not require treatment if they do not cause symptoms.
-
Malignant Tumors: The prognosis for malignant vascular tumors depends on factors like the tumor's size, location, and whether it has spread.
-
Early Detection: Early diagnosis and treatment improve the chances of a favorable outcome, especially for malignant tumors.
-
Recurrence: Some vascular tumors, particularly malignant ones, can recur after treatment, necessitating regular follow-up care.
-
Quality of Life: Treatment and management of vascular tumors focus on maintaining or improving the patient's quality of life.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of vascular tumors, offering hope for better outcomes.
-
Targeted Therapy: New treatments that target specific molecules involved in tumor growth are being developed, offering more precise treatment options.
-
Immunotherapy: This approach uses the body's immune system to fight cancer and is being explored for treating certain types of vascular tumors.
-
Genetic Research: Studies on genetic mutations associated with vascular tumors are helping to identify potential targets for new treatments.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials offers access to cutting-edge treatments and contributes to advancing medical knowledge.
-
Patient Support: Support groups and resources for patients and families affected by vascular tumors are increasingly available, providing emotional and practical assistance.
Prevention and Awareness
Raising awareness and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing vascular tumors.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Routine medical check-ups can help detect vascular tumors early, improving treatment outcomes.
-
Sun Protection: Protecting skin from excessive sun exposure can reduce the risk of developing certain types of skin-related vascular tumors.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, supports overall health and may reduce cancer risk.
-
Vaccination: Vaccines, such as the HPV vaccine, can help prevent infections that may increase cancer risk, including some vascular tumors.
-
Education: Educating the public about the signs and symptoms of vascular tumors can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing tidbits about vascular tumors that highlight their complexity and the ongoing efforts to understand them better.
-
Spontaneous Regression: Some hemangiomas in infants can shrink and disappear without treatment, a phenomenon known as spontaneous regression.
-
Color Changes: Vascular tumors can change color over time, often becoming darker or lighter as they grow or shrink.
-
Rare but Aggressive: Angiosarcomas are rare but highly aggressive, often requiring a combination of treatments for management.
-
Historical Records: Vascular tumors have been documented throughout history, with descriptions found in ancient medical texts.
-
Research Milestones: Advances in imaging and genetic research have significantly improved the diagnosis and treatment of vascular tumors in recent years.
Final Thoughts on Vascular Tumors
Vascular tumors, though complex, are fascinating. These growths, which arise from blood vessels, can be benign or malignant. Hemangiomas are the most common type, often appearing in infants and usually resolving on their own. On the other hand, angiosarcomas are rare but aggressive, requiring prompt medical attention. Understanding the differences between these types is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Advances in medical research continue to shed light on these conditions, offering hope for better therapies. It's important to consult healthcare professionals if you notice any unusual growths or symptoms. Early detection can make a significant difference in outcomes. Staying informed about vascular tumors empowers individuals to make educated decisions about their health. Remember, knowledge is power, and being aware of these facts can help you or someone you know navigate the complexities of vascular tumors with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
